
Copernical Team
As Shatner heads toward the stars, visions of space collide

ICEYE commercial satellites join the EU Copernicus programme
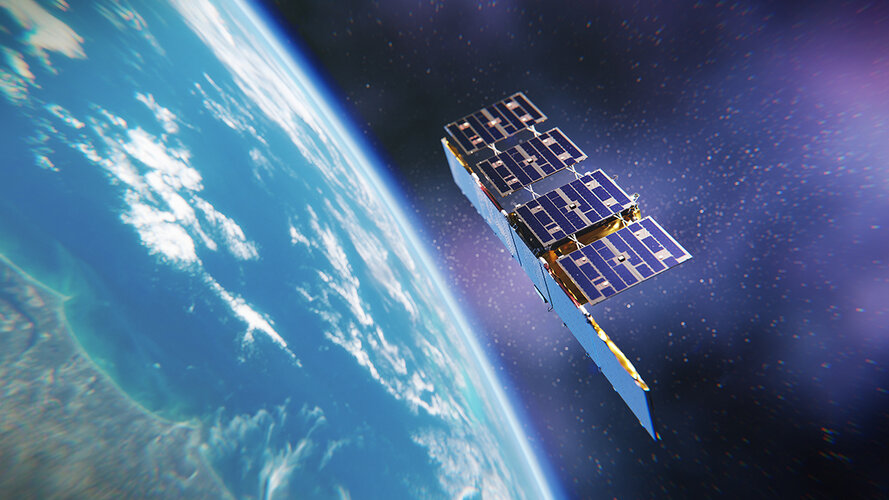

ESA signed a contract that brings the ICEYE constellation of small satellites into the fleet of missions contributing to Europe’s Copernicus environmental monitoring programme. As a commercial provider of satellite radar imagery, ICEYE is a perfect example of European New Space being implemented within Copernicus.
Contract secures build for HydroGNSS Scout mission
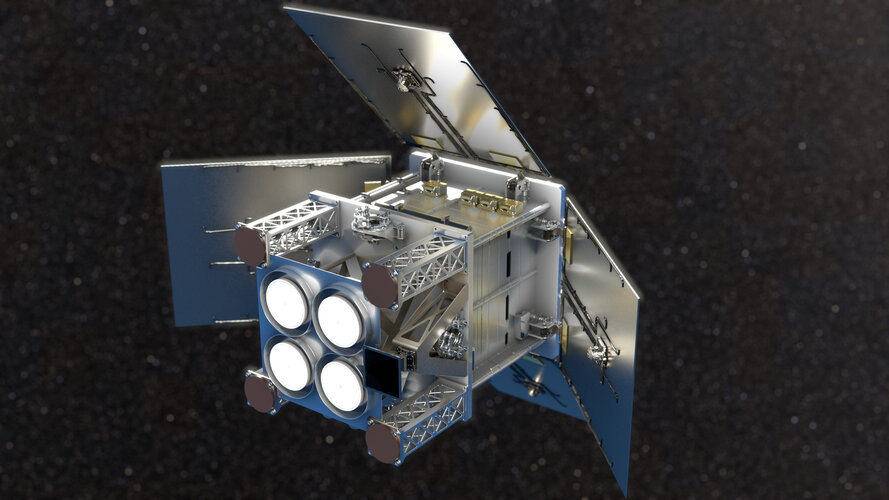
Today, as Φ-week gets underway, ESA has signed a contract with Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd to build the HydroGNSS Scout mission. Embracing the concept of New Space, HydroGNSS is a micro satellite that will use a technique called Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) reflectometry to measure climate variables such as soil moisture, freeze–thaw state over permafrost and inundation.
International Space Station in 2021
 Image:
International Space Station in 2021
Image:
International Space Station in 2021 Life on Mars: simulating Red Planet base in Israeli desert
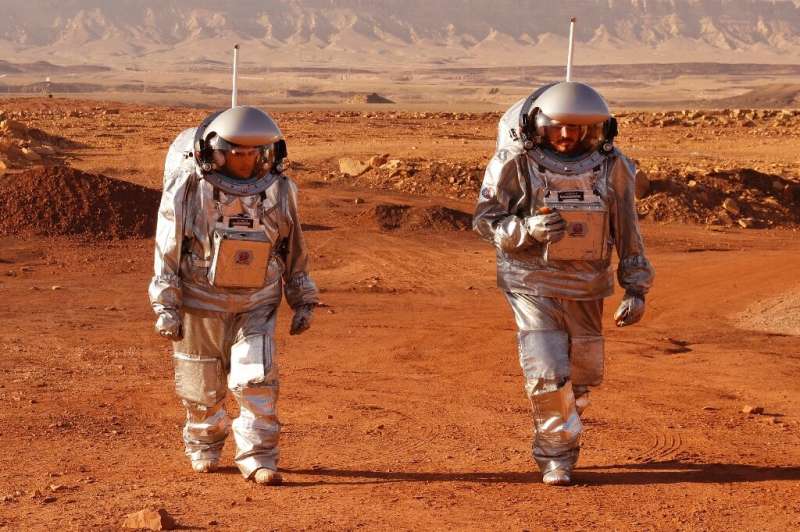

Inside a huge crater in Israel's sun-baked Negev desert, a team wearing space suits ventures forth on a mission to simulate conditions on Mars.
The Austrian Space Forum has set up a pretend Martian base with the Israeli space agency at Makhtesh Ramon, a 500-metre (1,600-foot) deep, 40 kilometre (25 mile) wide crater.
The six so-called "analogue astronauts" will live in isolation in the virtual station until the end of the month.
"It's a dream come true," Israeli Alon Tenzer, 36, told AFP. "It's something we've been working on for years.
Spotlight on climate and the New Space economy

Kicking off with a bold flourish, Φ-week 2021 promises to bring space even closer to the forefront of addressing society’s biggest challenges, namely issues associated with the climate crisis, while boosting the economy through transformative New Space, artificial intelligence, and quantum and cognitive computing.
La Palma volcano: How satellites help us monitor eruptions

Since the Cumbre Vieja volcano began erupting on 19 September 2021, lava has burned through homes, roads and farmlands causing mass destruction on the west part of the Canary Island of La Palma. Satellite imagery has helped authorities monitor and manage the ongoing crisis. From capturing images of the rivers of lava, to measuring gas emissions and assessing damage, the fleet of Copernicus Sentinel satellites have been providing crucial data for local teams.
Scaling up ESA’s asteroid facilities

The new heart of ESA’s Planetary Defence Office was inaugurated today, heralding a new chapter in the Agency’s work to protect Earth from dangerous near-Earth objects, aka asteroids.
Blue Origin delays William Shatner's space flight
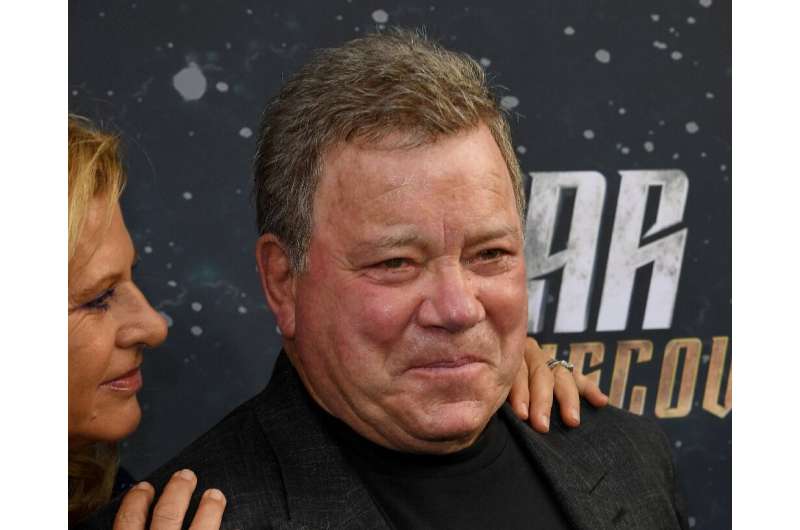

Blue Origin announced Sunday it was delaying an upcoming flight set to carry actor William Shatner to space due to anticipated winds.
Shatner, who played Captain James T. Kirk in the cult classic TV series "Star Trek," is due to become the first member of the iconic show's cast to journey to the final frontier as a guest aboard a Blue Origin suborbital rocket.
Beam me up, Jeff! William Shatner lends Blue Origin star power
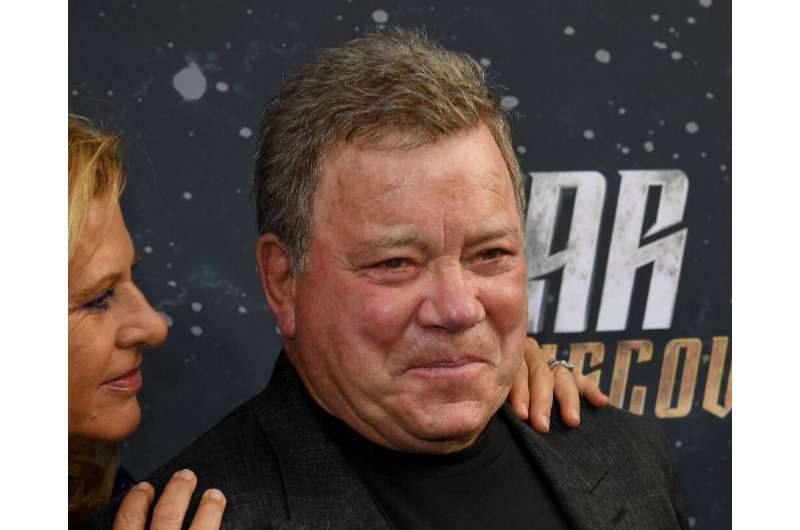

When Star Trek first aired in 1966, America was still three years away from putting people on the Moon and the idea that people could one day live and work in space seemed like a fantasy.
On October 12, William Shatner—Captain James T. Kirk to Trekkies—is set to become the first member of the iconic show's cast to journey to the final frontier, as a guest aboard a Blue Origin suborbital rocket.

