
Copernical Team
The Parkes dish is still making breakthroughs 60 years after it first gazed at the skies
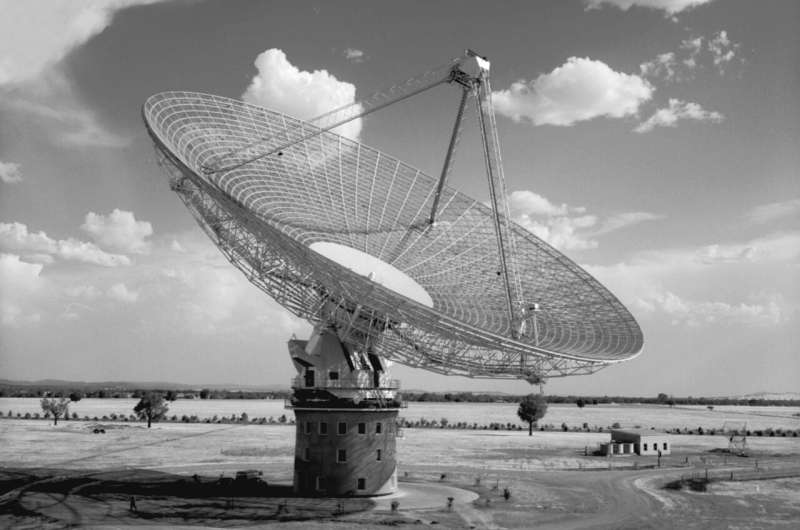

The CSIRO's 64-meter Parkes Radio Telescope was commissioned on October 31 1961. At the time it was the most advanced radio telescope in the world, incorporating many innovative features that have since become standard in all large-dish antennas.
Through its early discoveries it quickly became the leading instrument of its kind. Today, 60 years later, it is still arguably the finest single-dish radiotelescope in the world. It is still performing world-class science and making discoveries that shape our understanding of the Universe.
The telescope's origins date back to wartime radar research by the Radiophysics Laboratory, part of the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), the forerunner of the CSIRO. On the Sydney clifftops at Dover Heights, the laboratory developed radar for use in the Pacific theater. When the second world war ended, the technology was redirected into peaceful applications, including studying radio waves from the Sun and beyond.
In 1946, British physicist Edward "Taffy" Bowen was appointed chief of the Radiophysics Laboratory. He had been one of the brilliant engineers, dubbed "boffins," who developed radar as part of Britain's secret prewar military research.
Jupiter mission unveils the depth and structure of planet's shrinking red spot and colorful bands
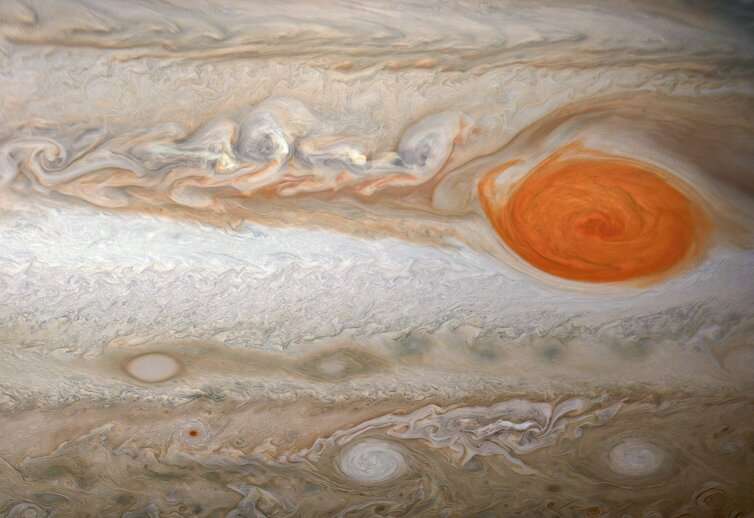

NASA's Juno mission, the solar-powered robotic explorer of Jupiter, has completed its five-year prime mission to reveal the inner workings of the solar system's biggest planet. Since 2016, the spacecraft has flown within a few thousand kilometers of Jupiter's colorful cloud tops every 53 days, using a carefully selected array of instruments to peer deeper into the planet than ever before.
The most recent findings from these measurements have now been published in a series of papers, revealing the three-dimensional structure of Jupiter's weather systems—including of its famous Great Red Spot, a centuries-old storm big enough to swallow the Earth whole.
Before Juno, decades of observations had revealed the famous striped appearance of Jupiter's atmosphere, with white bands known as zones, and red-brown bands known as belts.
Proposed Centaur mission could catch comets in the act of formation
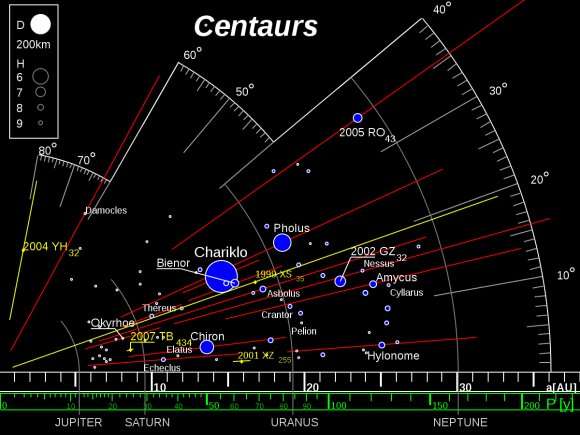
From Mercury to the depths of the distant Kuiper Belt, there aren't many unexplored corners of the solar system out there. One class of object, however, remains to be visited: the transitional Centaurs out beyond the orbit of Jupiter. Now, a new study from the University of Chicago recently accepted in The Planetary Science Journal looks at the feasibility of sending a mission by mid-century to intercept, follow and watch a Centaur asteroid as it evolves into a mature inner solar system comet.
It's a major mystery for planetary astronomy: how do comets get trapped in short-period path (that is, a comet with an orbital period of less than 200 years) in the inner solar system? Jupiter plays a major role in this regard, deflecting incoming debris both into and out of the solar system.
A proactive approach to removing space junk

Space has become a trash heap.
According to NASA, there are more than 27,000 pieces of spacedebris bigger than the size of a softball currently orbiting Earth, and they are traveling at speeds of up to 17,500 mph, fast enough for a small chunk to damage a satellite or spacecraft like an intergalactic cannonball.
Consequently, cleaning up this space junk will be an important task if agencies are to shoot more rockets and satellites into orbit.
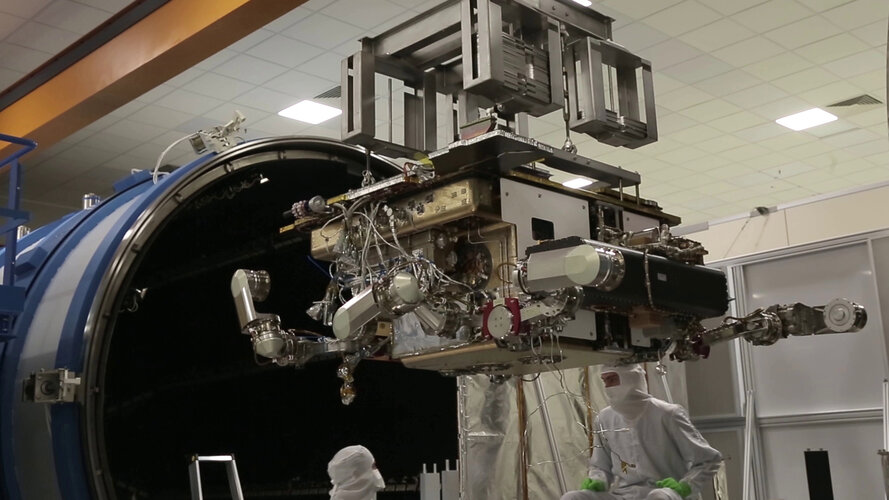
ExoMars rover comes out of the ‘oven’
 Video:
00:00:43
Video:
00:00:43
The Rosalind Franklin rover that will search for life on Mars has completed an important bakeout to help clean the rover from organic molecules from Earth.
The rover sat inside a vacuum chamber for 120 hours at 35ºC at the Thales Alenia Space facility in Rome, Italy. The temperature is enough to sublimate hidden contaminants generated by the off-gassing of some of the rover’s internal parts, such as small bits of glue. The goal is to reduce as much as possible any contamination signature of Earth origin, to allow a clean detection of organic compounds on Mars.
An additional
Q&A with ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer
 Video:
01:01:43
Video:
01:01:43
Watch the replay of Matthias Maurer’s last Q&A session before liftoff!
The ESA astronaut joined from his pre-launch quarantine in the USA to discuss launch preparations and highlights of his mission, called Cosmic Kiss. Matthias will be the 600th human to fly to space.
His first launch attempt is on Sunday 31 October at 07:21 CET (06:21 GMT, 02:21 EDT) alongside NASA astronauts Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn and Raja Chari on the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft “Endurance”.
Week in images: 25 - 29 October 2021

Week in images: 25 - 29 October 2021
Discover our week through the lens
Low-gravity simulator design offers new avenues for space research and mission training
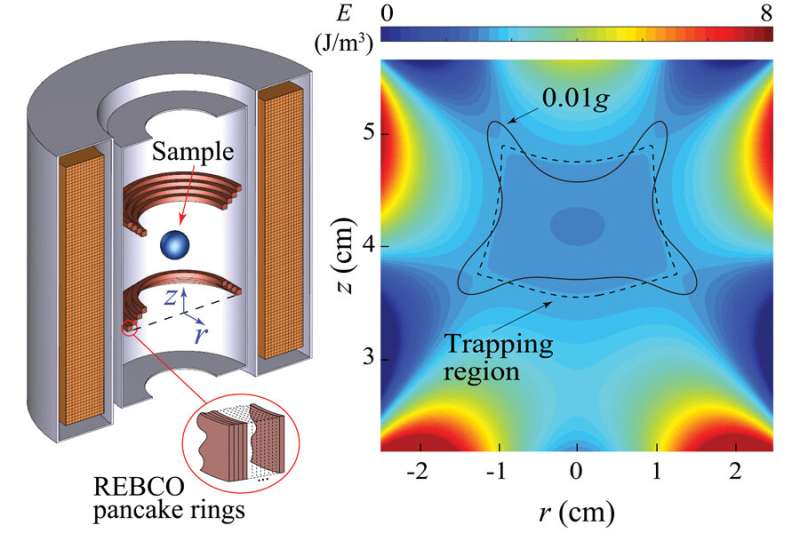
As humanity continues its exploration of the universe, the low-gravity environment of space presents unusual challenges for scientists and engineers.
Researchers at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering and the Florida State University-headquartered National High Magnetic Field Laboratory have developed a new tool to help meet that challenge—a novel design for a low-gravity simulator that promises to break new ground for future space research and habitation.
Watch live: liftoff of ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer
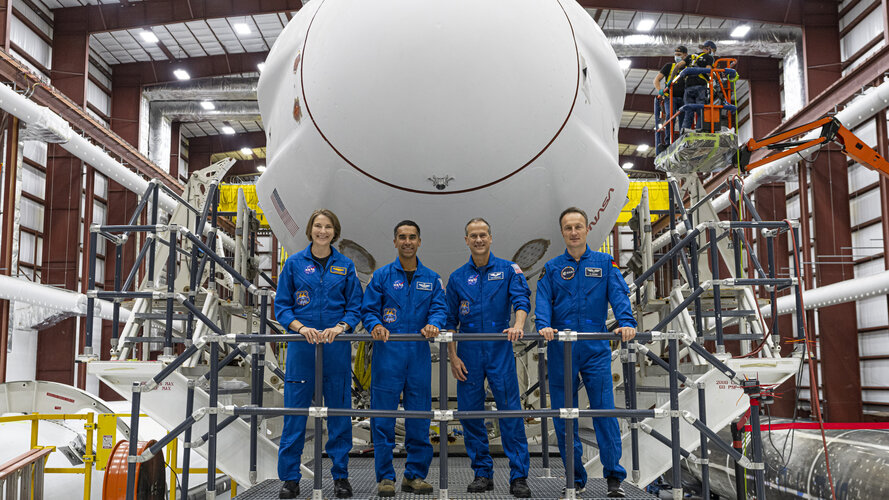

At 07:21 CET (06:21 GMT) Sunday 31 October ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer will be launched to the International Space Station to begin his Cosmic Kiss mission. Tune in to ESA Web TV channel two from 03:00 CET (01:00 GMT) for live coverage of the launch.
DARPA, NGA transition novel optics technology to fieldable prototypes
 Materials with novel optical properties developed under DARPA's Extreme Optics and Imaging (EXTREME) program are providing new capabilities for government and military imaging systems. EXTREME, a basic research program in DARPA's Defense Sciences Office, successfully developed new optical components, devices, systems, architectures, and design tools using engineered optical materials, or metamat
Materials with novel optical properties developed under DARPA's Extreme Optics and Imaging (EXTREME) program are providing new capabilities for government and military imaging systems. EXTREME, a basic research program in DARPA's Defense Sciences Office, successfully developed new optical components, devices, systems, architectures, and design tools using engineered optical materials, or metamat 
