
Copernical Team
Tuesday, 02 November 2021 07:28
SwRI-Led cubesat to assess the origins of hot plasma in the Sun's corona
San Antonio TX (SPX) Nov 02, 2021
 NASA has selected the CubeSat Imaging X-Ray Solar Spectrometer (CubIXSS), led by Southwest Research Institute, to measure the elemental composition of hot, multimillion-degree plasmas in the Sun's corona - its outermost atmosphere. The nanosatellite is expected to be launched in 2024 as a secondary payload on another satellite launch. CubIXSS will determine the origins of hot plasma - highly ion
NASA has selected the CubeSat Imaging X-Ray Solar Spectrometer (CubIXSS), led by Southwest Research Institute, to measure the elemental composition of hot, multimillion-degree plasmas in the Sun's corona - its outermost atmosphere. The nanosatellite is expected to be launched in 2024 as a secondary payload on another satellite launch. CubIXSS will determine the origins of hot plasma - highly ion
 NASA has selected the CubeSat Imaging X-Ray Solar Spectrometer (CubIXSS), led by Southwest Research Institute, to measure the elemental composition of hot, multimillion-degree plasmas in the Sun's corona - its outermost atmosphere. The nanosatellite is expected to be launched in 2024 as a secondary payload on another satellite launch. CubIXSS will determine the origins of hot plasma - highly ion
NASA has selected the CubeSat Imaging X-Ray Solar Spectrometer (CubIXSS), led by Southwest Research Institute, to measure the elemental composition of hot, multimillion-degree plasmas in the Sun's corona - its outermost atmosphere. The nanosatellite is expected to be launched in 2024 as a secondary payload on another satellite launch. CubIXSS will determine the origins of hot plasma - highly ion
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 02 November 2021 07:28
Building planets from protoplanetary disks
Boston MA (SPX) Nov 02, 2021
 Planets and their stars form from the same reservoir of nebular material and their chemical compositions should therefore be correlated but the observed compositions of planets do not match completely those of their central stars.
In our Solar system, for example, all the rocky planets and planetesimals contain near-solar proportions of refractory elements (elements like aluminum that cond
Planets and their stars form from the same reservoir of nebular material and their chemical compositions should therefore be correlated but the observed compositions of planets do not match completely those of their central stars.
In our Solar system, for example, all the rocky planets and planetesimals contain near-solar proportions of refractory elements (elements like aluminum that cond
 Planets and their stars form from the same reservoir of nebular material and their chemical compositions should therefore be correlated but the observed compositions of planets do not match completely those of their central stars.
In our Solar system, for example, all the rocky planets and planetesimals contain near-solar proportions of refractory elements (elements like aluminum that cond
Planets and their stars form from the same reservoir of nebular material and their chemical compositions should therefore be correlated but the observed compositions of planets do not match completely those of their central stars.
In our Solar system, for example, all the rocky planets and planetesimals contain near-solar proportions of refractory elements (elements like aluminum that cond
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 02 November 2021 07:28
NASA, SpaceX delay ISS mission again for medical issue
Washington (AFP) Nov 1, 2021
 NASA and SpaceX on Monday delayed for the second time a mission to send four astronauts to the International Space Station due to a "minor medical issue" with a crew member.
"The issue is not a medical emergency and not related to COVID-19," NASA said in a statement, without giving further details.
The members of "Crew-3" - US astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron and Tom Marshburn, as we
NASA and SpaceX on Monday delayed for the second time a mission to send four astronauts to the International Space Station due to a "minor medical issue" with a crew member.
"The issue is not a medical emergency and not related to COVID-19," NASA said in a statement, without giving further details.
The members of "Crew-3" - US astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron and Tom Marshburn, as we
 NASA and SpaceX on Monday delayed for the second time a mission to send four astronauts to the International Space Station due to a "minor medical issue" with a crew member.
"The issue is not a medical emergency and not related to COVID-19," NASA said in a statement, without giving further details.
The members of "Crew-3" - US astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron and Tom Marshburn, as we
NASA and SpaceX on Monday delayed for the second time a mission to send four astronauts to the International Space Station due to a "minor medical issue" with a crew member.
"The issue is not a medical emergency and not related to COVID-19," NASA said in a statement, without giving further details.
The members of "Crew-3" - US astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron and Tom Marshburn, as we
Published in
News
Tagged under
Monday, 01 November 2021 13:19
NASA selects CubeSat to assess the origins of hot plasma in the Sun's corona
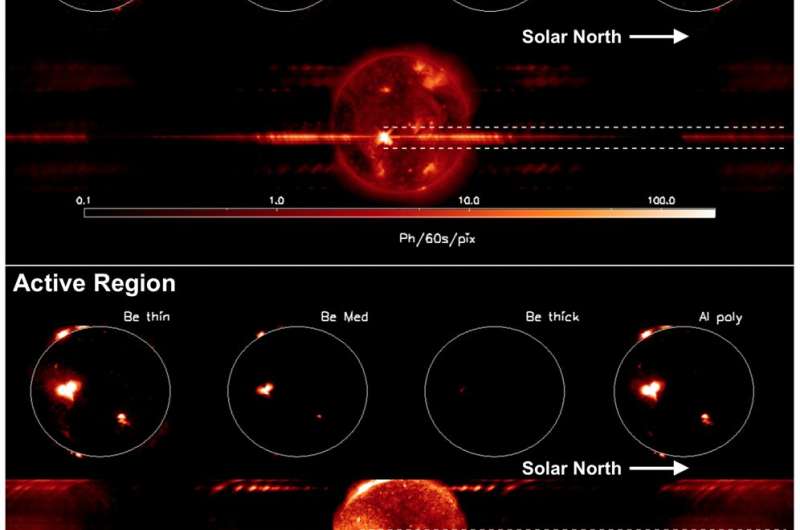
Published in
News
Tagged under
Friday, 29 October 2021 12:40
Géraldine Naja, Director of Commercialisation, Industry and Procurement

Géraldine Naja took up duty as Director of Commercialisation, Industry and Procurement (D/CIP), based at ESA Headquarters in Paris, on 1 November 2021.
Published in
News
Tagged under
Monday, 01 November 2021 07:48
Satellites used to track methane leaks in climate fight
Paris (AFP) Oct 27, 2021
 A yellow streak representing high concentrations of methane, a dangerous greenhouse gas, is visible over southern Iraq on a map produced by Kayrros, a French firm that uses satellites to track leaks from fossil fuel facilities.
The source of the immense leak discovered in 2019 was never officially confirmed - and it is only one of many.
The satellite map shows blotches of colour splatte
A yellow streak representing high concentrations of methane, a dangerous greenhouse gas, is visible over southern Iraq on a map produced by Kayrros, a French firm that uses satellites to track leaks from fossil fuel facilities.
The source of the immense leak discovered in 2019 was never officially confirmed - and it is only one of many.
The satellite map shows blotches of colour splatte
 A yellow streak representing high concentrations of methane, a dangerous greenhouse gas, is visible over southern Iraq on a map produced by Kayrros, a French firm that uses satellites to track leaks from fossil fuel facilities.
The source of the immense leak discovered in 2019 was never officially confirmed - and it is only one of many.
The satellite map shows blotches of colour splatte
A yellow streak representing high concentrations of methane, a dangerous greenhouse gas, is visible over southern Iraq on a map produced by Kayrros, a French firm that uses satellites to track leaks from fossil fuel facilities.
The source of the immense leak discovered in 2019 was never officially confirmed - and it is only one of many.
The satellite map shows blotches of colour splatte
Published in
News
Tagged under
Monday, 01 November 2021 07:48
OpenET: A satellite-based water data resource
Greenbelt MD (SPX) Oct 26, 2021
 OpenET uses publicly available data to provide satellite-based information on evapotranspiration (the "ET" in OpenET). The primary satellite dataset for OpenET is from the Landsat program, a partnership between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The most recent satellite in the program, Landsat 9, successfully launched on Sept. 27, 2021.
Evapotranspiration is the process through w
OpenET uses publicly available data to provide satellite-based information on evapotranspiration (the "ET" in OpenET). The primary satellite dataset for OpenET is from the Landsat program, a partnership between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The most recent satellite in the program, Landsat 9, successfully launched on Sept. 27, 2021.
Evapotranspiration is the process through w
 OpenET uses publicly available data to provide satellite-based information on evapotranspiration (the "ET" in OpenET). The primary satellite dataset for OpenET is from the Landsat program, a partnership between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The most recent satellite in the program, Landsat 9, successfully launched on Sept. 27, 2021.
Evapotranspiration is the process through w
OpenET uses publicly available data to provide satellite-based information on evapotranspiration (the "ET" in OpenET). The primary satellite dataset for OpenET is from the Landsat program, a partnership between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The most recent satellite in the program, Landsat 9, successfully launched on Sept. 27, 2021.
Evapotranspiration is the process through w
Published in
News
Tagged under
Monday, 01 November 2021 07:48
Chinese hypersonic test like a "Sputnik moment': top US general
Washington (AFP) Oct 27, 2021
 The Pentagon's top general said Wednesday that China's recent test of an earth-circling hypersonic missile was akin to the Soviet Union's stunning launch of the world's first satellite, Sputnik, in 1957, which sparked the superpowers' space race.
Mark Milley, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, confirmed for the first time the Chinese test of a nuclear-capable missile that would be very d
The Pentagon's top general said Wednesday that China's recent test of an earth-circling hypersonic missile was akin to the Soviet Union's stunning launch of the world's first satellite, Sputnik, in 1957, which sparked the superpowers' space race.
Mark Milley, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, confirmed for the first time the Chinese test of a nuclear-capable missile that would be very d
 The Pentagon's top general said Wednesday that China's recent test of an earth-circling hypersonic missile was akin to the Soviet Union's stunning launch of the world's first satellite, Sputnik, in 1957, which sparked the superpowers' space race.
Mark Milley, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, confirmed for the first time the Chinese test of a nuclear-capable missile that would be very d
The Pentagon's top general said Wednesday that China's recent test of an earth-circling hypersonic missile was akin to the Soviet Union's stunning launch of the world's first satellite, Sputnik, in 1957, which sparked the superpowers' space race.
Mark Milley, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, confirmed for the first time the Chinese test of a nuclear-capable missile that would be very d
Published in
News
Tagged under
Monday, 01 November 2021 07:48
Astronomers discover massive galaxy 'shipyard' in the distant universe
Tucson AZ (SPX) Oct 29, 2021
 Even galaxies don't like to be alone. While astronomers have known for a while that galaxies tend to congregate in groups and clusters, the process of going from formation to friend groups has remained an open question in cosmology.
In a paper published in the Astronomy and Astrophysics Journal, an international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a group of objects that appear to
Even galaxies don't like to be alone. While astronomers have known for a while that galaxies tend to congregate in groups and clusters, the process of going from formation to friend groups has remained an open question in cosmology.
In a paper published in the Astronomy and Astrophysics Journal, an international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a group of objects that appear to
 Even galaxies don't like to be alone. While astronomers have known for a while that galaxies tend to congregate in groups and clusters, the process of going from formation to friend groups has remained an open question in cosmology.
In a paper published in the Astronomy and Astrophysics Journal, an international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a group of objects that appear to
Even galaxies don't like to be alone. While astronomers have known for a while that galaxies tend to congregate in groups and clusters, the process of going from formation to friend groups has remained an open question in cosmology.
In a paper published in the Astronomy and Astrophysics Journal, an international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a group of objects that appear to
Published in
News
Tagged under
Monday, 01 November 2021 07:48
Smart material switches between heating and cooling in minutes
Durham NC (SPX) Oct 28, 2021
 As anyone who has ever parked a car in the sun on a hot summer day knows, glass windows are great at letting sunlight in but terrible at allowing heat out. Now, engineers at Duke University have developed smart window-like technology that, with the flip of a switch, can alternate between harvesting heat from sunlight and allowing an object to cool. The approach could be a boon for HVAC savings,
As anyone who has ever parked a car in the sun on a hot summer day knows, glass windows are great at letting sunlight in but terrible at allowing heat out. Now, engineers at Duke University have developed smart window-like technology that, with the flip of a switch, can alternate between harvesting heat from sunlight and allowing an object to cool. The approach could be a boon for HVAC savings,
 As anyone who has ever parked a car in the sun on a hot summer day knows, glass windows are great at letting sunlight in but terrible at allowing heat out. Now, engineers at Duke University have developed smart window-like technology that, with the flip of a switch, can alternate between harvesting heat from sunlight and allowing an object to cool. The approach could be a boon for HVAC savings,
As anyone who has ever parked a car in the sun on a hot summer day knows, glass windows are great at letting sunlight in but terrible at allowing heat out. Now, engineers at Duke University have developed smart window-like technology that, with the flip of a switch, can alternate between harvesting heat from sunlight and allowing an object to cool. The approach could be a boon for HVAC savings,
Published in
News
Tagged under

