
Copernical Team
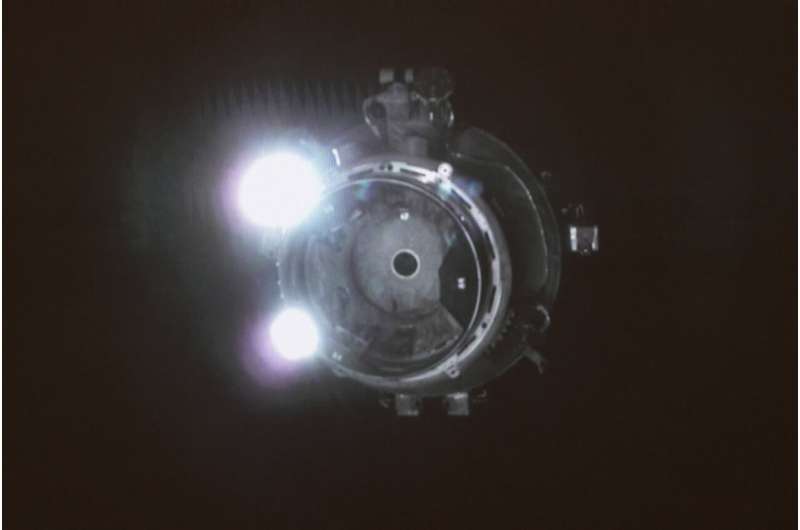
New crew docks at China's first permanent space station

NASA's asteroid hunter Lucy soars into sky with diamonds
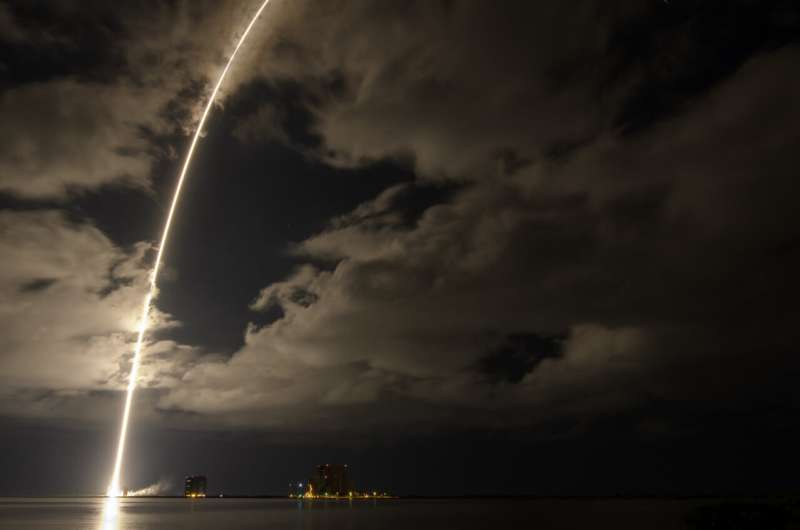

NASA, ULA Launch Lucy Mission to ‘Fossils’ of Planet Formation
 NASA’s Lucy mission, the agency’s first to Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids, launched at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
NASA’s Lucy mission, the agency’s first to Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids, launched at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. China launches 3 astronauts on 6-month space station mission
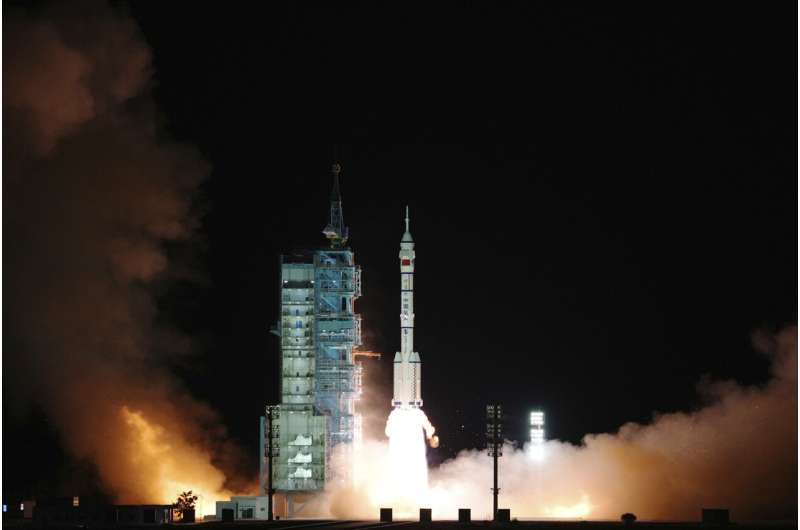

China on Saturday sent three astronauts to its space station for a record-setting six-month stay as the country moves toward completing the new orbiting outpost
The Shenzhou-13 spacecraft carrying the three astronauts was launched by a Long March-2F rocket at 12:25 a.m. Saturday.
The two men and one woman are the second crew to move into the spacestation, which was launched last April. The first crew stayed three months.
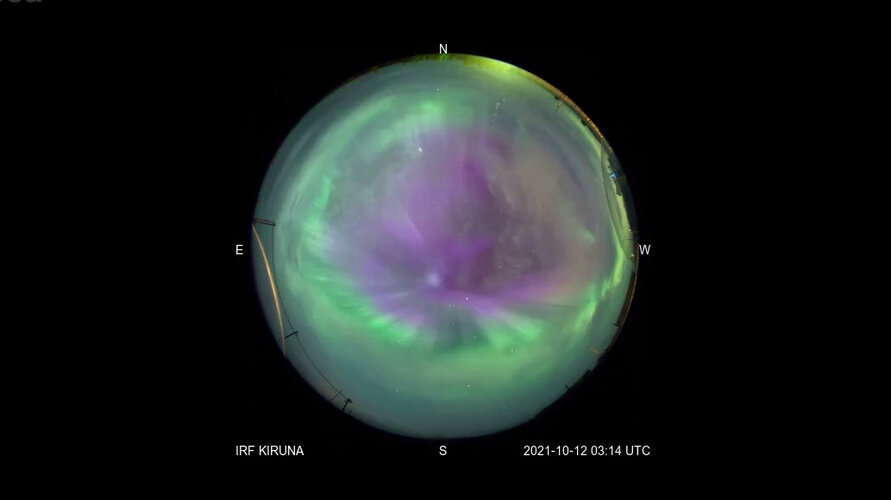
Solar storm stirs stunning aurora
 Video:
00:00:29
Video:
00:00:29
After the Sun ejected a violent mass of fast-moving plasma into space on 9 October, ESA waited for the storm to strike. A few days later, the coronal mass ejection (CME) arrived at Earth, crashing into our planet’s magnetosphere, and lighting up the sky.
CMEs explode from the Sun, rush through the Solar System and while doing so speed up the solar wind – a stream of charged particles continuously released from the Sun’s upper atmosphere.
While most of the solar wind is blocked by Earth’s protective magnetosphere, some charged particles become trapped in Earth’s magnetic field and flow
Imminent asteroid missions could reveal our origins, and help save Earth from deadly strike

Asteroids are remnants of the early Solar System, with the potential to reveal secrets of our planet's origins. But they could also bring an end to life on Earth. Now two missions, Lucy and DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) will provide further insights into both of these features—with DART even attempting to redirect the orbit of a moon around an asteroid.
Space rocks are generally considered to be asteroids if they are larger than approximately 1km in size, and made principally of "non-volatile" materials—chemicals that can be easily vaporized. Carbon monoxide, for example, is volatile as it vaporizes at a temperature of -191°C. But iron, with a vaporization point of 2,862°C is non-volatile.
This is somewhat different to comets. Asteroids are found more commonly in the inner Solar System, whereas comets with their volatile-rich composition tend to lurk in the outer part, far from the heat of the Sun.
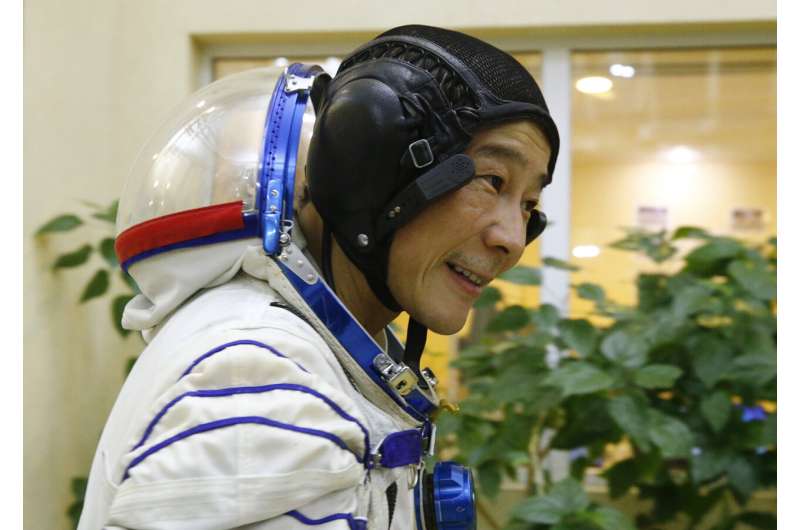
Japanese billionaire gets ready for December space mission

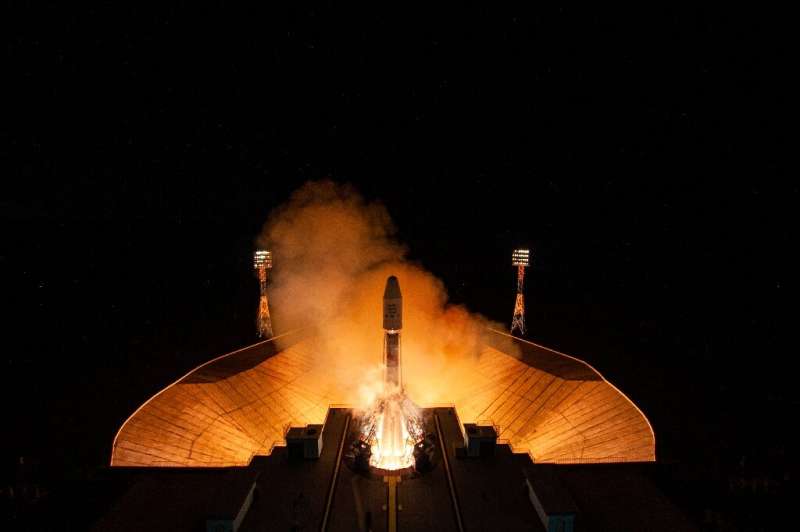
Russian rocket tests briefly destabilise space station

The International Space Station was briefly destabilised Friday during tests of a Russian-made Soyuz rocket, but the crew and the orbital station were not in danger, Moscow said.
Russia's Roscosmos space agency said the incident happened during tests of the engines of the Soyuz MS-18 spacecraft set to return a Russian actress and filmmaker aboard the ISS to Earth on Sunday.
"As a result, the International Space Station temporarily changed its position," Roscosmos said in a statement.
"The station and the crew are not in danger."
Russian actress Yulia Peresild and film director Klim Shipenko travelled to the ISS earlier this month to make the first movie in orbit ahead of the United States.
Peresild and Shipenko are set to go back to Earth with cosmonaut Oleg Novitsky, who has been on the space station for the past six months.
The Russian segment of the ISS has experienced a number of problems in recent months.
In July, the space station tilted out of orbit after the thrusters of the Nauka module reignited several hours after docking.
US firm sees 'exciting' moment as space tourism booms

As competition in the space tourism industry heats up, a US-based firm said Friday it was excited to re-enter the sector with the upcoming launch of a Japanese billionaire.
Space Adventures, headed by Tom Shelley, is set in December to send Japanese tycoon Yusaku Maezawa to the International Space Station (ISS) from the Russia-leased Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
It's the company's first launch in over a decade after suspending trips to the ISS as NASA bought up seats on Russia-operated flights and no other vehicles were available.
"It's a very exciting time for us," Shelley, 48, the president of Space Adventures, told AFP during an interview in Moscow on Friday.
He added that Space Adventures with Russia was planning future launches "to innovate and find new offerings" for clients.
Ariane 6 development: progress on all fronts
 Video:
00:05:15
Video:
00:05:15
These are exciting days at Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana and throughout several sites in ESA Member States as the development of Ariane 6 enters its final phase. Ariane 6 parts are being shipped from Europe for combined tests on the new Ariane 6 launch base. These tests rehearse all activities and systems involving the rocket and launch base on an Ariane 6 launch campaign. On the final test, the Ariane 6 core stage will perform a static hot firing while standing on its recently inaugurated launch pad. It will be from this new launch base that ESA’s

