Displaying items by tag: ISS module
Destiny (ISS module)
The Destiny laboratory is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It is the primary operating facility for U.S. research payloads aboard the ISS.
It was berthed to the Unity module and activated over a period of five days in February, 2001. Destiny is NASA's first permanent operating orbital research station since Skylab was vacated in February 1974.
The Boeing Company began construction of the state-of-the art research laboratory in 1995 at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Destiny was shipped to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in 1998, and was turned over to NASA for pre-launch preparations in August 2000. It was launched on February 7, 2001 aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on STS-98.
Astronauts work inside the pressurized facility to conduct research in numerous scientific fields. Scientists throughout the world will use the results to enhance their studies in medicine, engineering, biotechnology, physics, materials science, and Earth science.
Nauka / Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM)
Nauka (Russian: Нау́ка; lit. Science), also known as the Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM), (Russian: Многофункциональный лабораторный модуль, or МЛМ), will be a component of the International Space Station (ISS), funded by the Russian Federal Space Agency.
The MLM launch is currently (in Sept. 2012) scheduled for 2014.
Node2&3 (ISS modules)
[To be edited: Objectives, missions, functions]
Node 2 & Node3 are two major components of the ISS international Space Station
node 1: Unity module
node 2: Harmony module
node 3: Tranquility module
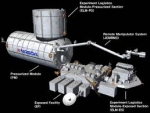
Kibo (ISS module)
The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), also known with the nickname Kibo (きぼう Kibō, Hope), is a Japanese science module for the International Space Station (ISS) developed by JAXA.
It is the largest single ISS module. The first two pieces of the module were launched on space shuttle missions STS-123 and STS-124. The third and final components were launched on STS-127.