
Copernical Team
Study of Sample Brought Back by Chang'e-5 Unveils Formation of Nanophase Iron on the Moon
 By studying lunar soil brought back by China's Chang'e-5 probe, researchers found reliable evidence of disproportionation origin of nanophase iron on the moon, according to a study published on Nature Astronomy on Thursday.
The peer-reviewed study was conducted by the Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Kunming University of Science and Technology.
Researc
By studying lunar soil brought back by China's Chang'e-5 probe, researchers found reliable evidence of disproportionation origin of nanophase iron on the moon, according to a study published on Nature Astronomy on Thursday.
The peer-reviewed study was conducted by the Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Kunming University of Science and Technology.
Researc ISRO demonstrates new technology with Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator
 An IAD, designed and developed by VSSC, has been successfully test flown in a Rohini sounding rocket from TERLS, Thumba at 12.20 pm Saturday Sep 3. The IAD was initially folded and kept inside the payload bay of the rocket. At around 84 km altitude, the IAD was inflated and it descended through atmosphere with the payload part of sounding rocket.
The pneumatic system for inflation was deve
An IAD, designed and developed by VSSC, has been successfully test flown in a Rohini sounding rocket from TERLS, Thumba at 12.20 pm Saturday Sep 3. The IAD was initially folded and kept inside the payload bay of the rocket. At around 84 km altitude, the IAD was inflated and it descended through atmosphere with the payload part of sounding rocket.
The pneumatic system for inflation was deve mu Space reveals a 10-Year Plan to build a Space Supply Chain in Thailand and Southeast Asia
 mu Space and Advance Technology Co., Ltd., a satellite manufacturer and satellite communication service provider, reveals plans to advance the business in the next 10 years. The company announced their intentions to continue to invest in building a network for the aerospace industry with aims to being a leading aerospace manufacturer in Southeast Asia.
mu Space intends to build a supply ch
mu Space and Advance Technology Co., Ltd., a satellite manufacturer and satellite communication service provider, reveals plans to advance the business in the next 10 years. The company announced their intentions to continue to invest in building a network for the aerospace industry with aims to being a leading aerospace manufacturer in Southeast Asia.
mu Space intends to build a supply ch Rocketlab sent this engine to space and then retrieved it: A new test shows it's still working fine
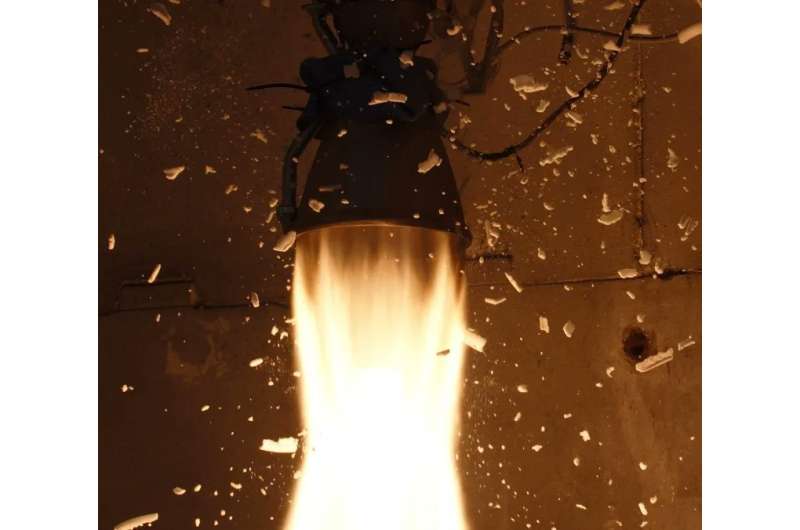

Reusable rocket engines have become all the rage lately, even as NASA's continually delayed Artemis I mission attempts to launch with non-reusable technology. Realistically, the only way to significantly lower launch costs is to reuse the engines rather than build them from scratch every time. Another small start-up company, RocketLab, has successfully retested a rocket that has flown in space.
SpaceX famously has flown several of its Raptor engines into space multiple times already, making headlines along the way. But it's not the only company with ambitions for reusing its rockets. RocketLab, which makes a much smaller rocket called the Electron, has also been eyeing this milestone for a while now.
The company made headlines back in May when it made a spectacular show of catching its rocket stage out of the air with a helicopter.
While Artemis scrubs, SpaceX treats Space Coast to launches
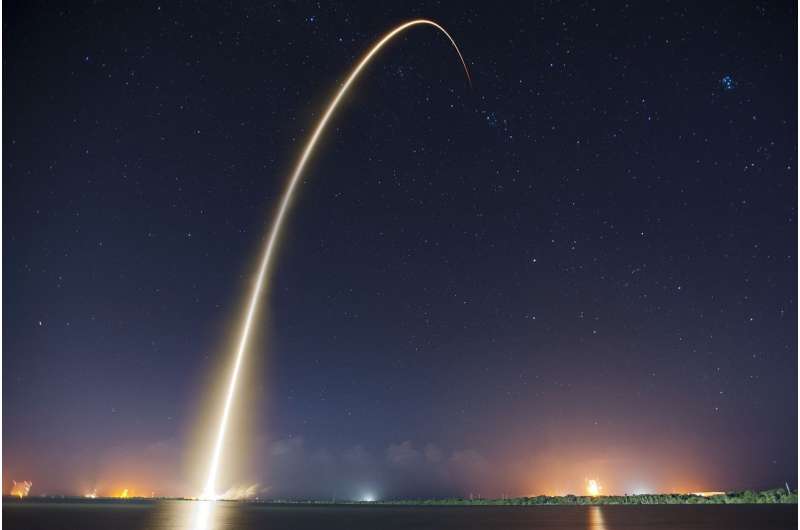

While hundreds of thousands of people made their way to the Space Coast two weekends in a row for a shot to see the most powerful rocket to ever lift off from Earth, a couple of scrubs for NASA's Artemis I mission left them disappointed.
But for those who were making a weekend out of their efforts, there was at least one rocket that lit up the sky for those who hung around.
SpaceX has continued its frenetic pace of Falcon 9 launches including a couple of Starlink missions that took flight: one right before midnight last weekend on Aug. 27, about 32 hours before NASA called off its first Artemis I attempt; and then again Sunday night about 32 hours after NASA was aiming for its second try to send up its Space Launch System rocket with the Orion capsule to the moon.
So while NASA may eventually have to roll back the Artemis I hardware capable of 8.8 million pounds of thrust on liftoff to the Vehicle Assembly Building, SpaceX keeps sending up its 1.7 million pounds of thrust servings.
Explore the solar system with NASA's new-and-improved 3D 'eyes'
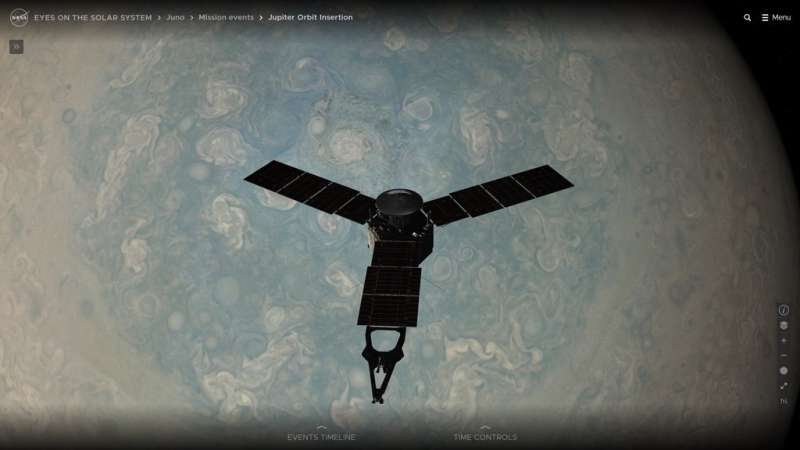

NASA has revamped its "Eyes on the Solar System" 3D visualization tool, making interplanetary travel easier and more interactive than ever. More than two years in the making, the update delivers better controls, improved navigation, and a host of new opportunities to learn about our incredible corner of the cosmos—no spacesuit required. All you need is a device with an internet connection.
Trace the course Artemis I will take to lunar orbit, or touch down with Perseverance during its harrowing entry, descent, and landing on the Red Planet. Learn the basics about dwarf planets or the finer points of gas giants, and ride alongside no fewer than 126 space missions past and present. You can even follow the paths of spacecraft and celestial bodies as far back as 1949 and as far into the future as 2049.
Scientists apply boron to tungsten components in fusion facilities
 What is the connection between boron, an element in a common household cleaner, and tokamaks, ring-shaped fusion facilities that heat fuel to million-degree temperatures? Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have conducted research showing that a PPPL-developed powder dropper can successfully drop boron powder into high-temperature plasma
What is the connection between boron, an element in a common household cleaner, and tokamaks, ring-shaped fusion facilities that heat fuel to million-degree temperatures? Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have conducted research showing that a PPPL-developed powder dropper can successfully drop boron powder into high-temperature plasma Coronal mass ejection hits Solar Orbiter before Venus flyby
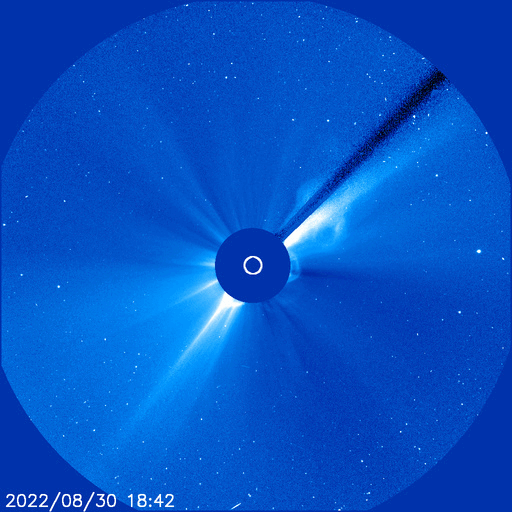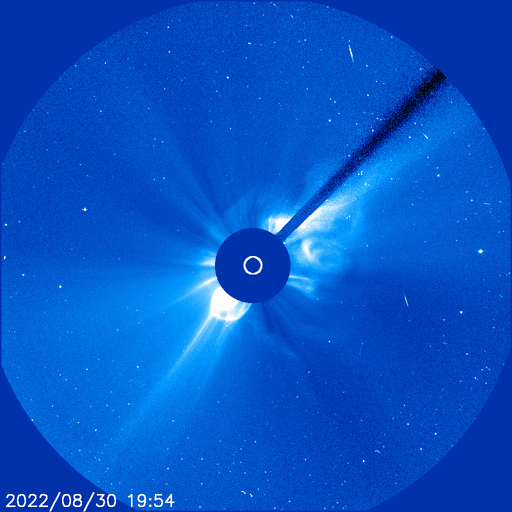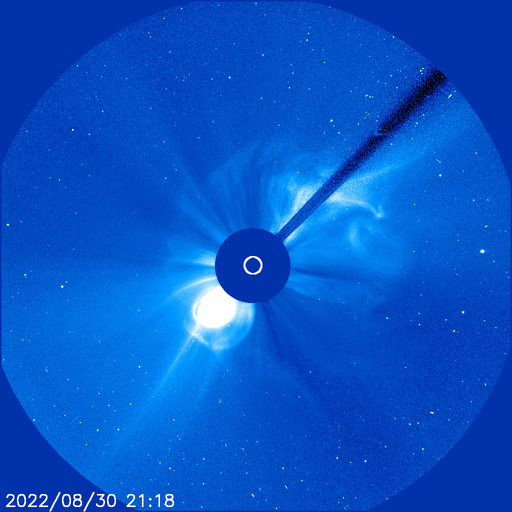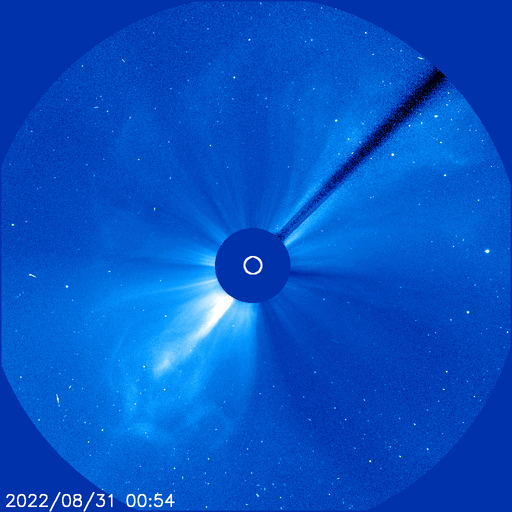
Rocket to carry Mengtian space lab module arrives at launch site
 A Long March-5B Y4 rocket, tasked with sending China's space station lab module Mengtian into orbit, has been transported to the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site in the southern province of Hainan, the China Manned Space Agency said Saturday.
The rocket will undergo final assembly and testing together with the Mengtian lab module, which arrived earlier.
Preparations for the launch mis
A Long March-5B Y4 rocket, tasked with sending China's space station lab module Mengtian into orbit, has been transported to the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site in the southern province of Hainan, the China Manned Space Agency said Saturday.
The rocket will undergo final assembly and testing together with the Mengtian lab module, which arrived earlier.
Preparations for the launch mis NASA awards LISA mission laser instrument contract
 NASA has selected Ball Aerospace and Technology Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, to provide the Laser Prestabilizaton System (LPS) for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) laser assembly.
The total value of the cost-plus-fixed-fee contract is $11,906,675, and the period of performance is from Sept. 1, 2022, through April 1, 2025. The work will be performed at the contractor's facility
NASA has selected Ball Aerospace and Technology Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, to provide the Laser Prestabilizaton System (LPS) for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) laser assembly.
The total value of the cost-plus-fixed-fee contract is $11,906,675, and the period of performance is from Sept. 1, 2022, through April 1, 2025. The work will be performed at the contractor's facility 
