Displaying items by tag: Rover
Yutu rover
Yutu is a Chinese lunar rover which forms part of the Chang'e 3 mission to the Moon.
Launched on 1 December 2013, and landed on 14 December 2013. If successful it will be the first rover to operate on the Moon since Lunokhod 2 ceased operations in May 1973.
The official mission objective is to achieve China's first soft-landing and roving exploration on the Moon, as well as to develop and analyze key technological developments.
(Yutu, or Jade Rabbit, was a name selected in an online poll; it is a Chinese myth about a white pet rabbit of the Moon goddess Chang'e.)
Spirit rover (MER-A)
Spirit, MER-A (Mars Exploration Rover – A), is a robotic rover on Mars, active from 2004 to 2010.
It was one of two rovers of NASA's ongoing Mars Exploration Rover Mission. It landed successfully on Mars at 04:35 Ground UTC on January 4, 2004, three weeks before its twin, Opportunity (MER-B), landed on the other side of the planet. Its name was chosen through a NASA-sponsored student essay competition. The rover became stuck in late 2009, and its last communication with Earth was sent on March 22, 2010.
The rover completed its planned 90-sol mission. Aided by cleaning events that resulted in higher power from its solar panels, Spirit went on to function effectively over twenty times longer than NASA planners expected. Spirit also logged 7.73 km (4.8 mi) of driving instead of the planned 600 m (0.4 mi), allowing more extensive geological analysis of Martian rocks and planetary surface features. Initial scientific results from the first phase of the mission (the 90-sol prime mission) were published in a special issue of the journal Science.
Opportunity rover (MER-B)
Opportunity, MER-B (Mars Exploration Rover – B), is a robotic rover active on the planet Mars since 2004.
Launched on July 7, 2003, Opportunity landed on Mars' Meridiani Planum on January 25, 2004, three weeks after its twin Spirit (MER-A), also part of NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Mission, touched down on the other side of the planet. While Spirit became immobile in 2009 and ceased communications in 2010, Opportunity remains active as of 2013, having already exceeded its planned 90 sol (Martian days) duration of activity by 9 years, 215 days (in Earth time). Opportunity has continued to move, gather scientific observations, and report back to Earth for over 38 times its designed lifespan.
Mission highlights include the initial 90 sol mission, finding extramartian meteorites such as Meridiani Planum, and over two years studying Victoria crater. It survived dust-storms and reached Endeavour crater in 2011, which has been described as a "second landing site".
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Exploration Rover project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C..
Curiosity rover
The Curiosity rover is a car-sized Mars rover currently exploring Gale Crater, near the equator of Mars. The rover is designed to examine whether Mars could have once supported life. It arrived on the Martian surface on 6 August 2012, after leaving Earth on 26 November 2011.
The rover is a nuclear-powered, mobile scientific laboratory, with dozens of instruments. It is part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission by the United States. The MSL mission has four scientific goals:
- investigation of Mars' climate,
- geology,
- investigation of whether Mars could ever have supported life,
- investigation of the role of water.
It is also useful preparation for future missions, perhaps a manned mission to Mars. Curiosity carries the most advanced payload of scientific equipment ever used on the surface of Mars.
The MSL spacecraft carrying Curiosity was launched on November 26, 2011, and the rover was successfully landed on Aeolis Palus in Gale Crater on August 6, 2012 UTC (August 5, 2012 PDT, NASA mission control time).
Mars Pathfinder
Mars Pathfinder (MESUR Pathfinder) was an American spacecraft that landed a base station with roving probe onMars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight (10.6 kilograms/23 pounds) wheeled robotic rover named Sojourner.
Launched on December 4, 1996 by NASA aboard a Delta II booster a month after the Mars Global Surveyor was launched, it landed on July 4, 1997 on Mars' Ares Vallis, in a region called Chryse Planitia in the Oxia Palus quadrangle. The lander then opened, exposing the rover which conducted many experiments on the Martian surface. The mission carried a series of scientific instruments to analyze the Martian atmosphere, climate, geology and the composition of its rocks and soil. It was the second project from NASA's Discovery Program, which promotes the use of low-cost spacecraft and frequent launches under the motto "cheaper, faster and better" promoted by the then administrator, Daniel Goldin. The mission was directed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), a division of the California Institute of Technology, responsible for NASA's Mars Exploration Program.
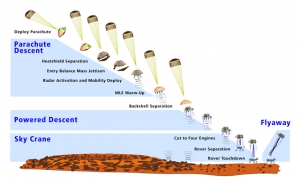
The MSL mission (Mars Science Laboratory)
The Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) mission with the aim to land and operate a rover named Curiosity on the surface of Mars.
The MSL was launched November 26, 2011 at 10:02 am EST and will land on Mars at Gale Craterbetween August 6 and August 20, 2012. It will attempt to perform the first-ever precision landing on Mars. The rover Curiosity will help assess Mars' habitability, that is, whether Mars is, or ever was an environment able to support microbial life. It will also analyze samples scooped up from the soil and drilled powders from rocks.