Copernical Team
Key role of the reactor surface in Miller's experiment on the molecular origin of life
 A team of researchers from the CSIC and the University of Tuscia (Italy) has demonstrated the role that glass played in the historical experiment carried out by Stanley Miller in 1952 to simulate the conditions that would have given rise to life on the early Earth. The results, published in Scientific Reports, open a new way to study the emergence of life.
Miller built a glass apparatus in
A team of researchers from the CSIC and the University of Tuscia (Italy) has demonstrated the role that glass played in the historical experiment carried out by Stanley Miller in 1952 to simulate the conditions that would have given rise to life on the early Earth. The results, published in Scientific Reports, open a new way to study the emergence of life.
Miller built a glass apparatus in AFRL Space Vehicles Directorate holds first Space Cyber Summit
 The Air Force Research Laboratory's Space Vehicles Directorate held an inaugural Space Cyber Summit October 13-14. More than 140 space professionals participated in the in-person and virtual event held at Kirtland AFB.
The gathering included space experts from across AFRL, the U.S. Space Force, several federally funded research and development centers, NASA, and many other organizations.
The Air Force Research Laboratory's Space Vehicles Directorate held an inaugural Space Cyber Summit October 13-14. More than 140 space professionals participated in the in-person and virtual event held at Kirtland AFB.
The gathering included space experts from across AFRL, the U.S. Space Force, several federally funded research and development centers, NASA, and many other organizations. Leicester researchers analyse consequences of China space weapon test
 University of Leicester experts in the military uses of outer space have urged further international dialogue and 'cool heads' following flight tests of a new Chinese hypersonic missile system. Reports of China testing a new orbital launch vehicle, known as Fractional Orbital Bombardment System (FOBS), have fuelled concerns about the nuclear weapon state's advancing military capabilities and pos
University of Leicester experts in the military uses of outer space have urged further international dialogue and 'cool heads' following flight tests of a new Chinese hypersonic missile system. Reports of China testing a new orbital launch vehicle, known as Fractional Orbital Bombardment System (FOBS), have fuelled concerns about the nuclear weapon state's advancing military capabilities and pos NASA to Hold Double Asteroid Redirection Test Launch Preview Briefing
 NASA will hold a virtual media briefing at 1 p.m. EDT Thursday, Nov. 4, to preview the launch of the agency’s first planetary defense test mission, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART).
NASA will hold a virtual media briefing at 1 p.m. EDT Thursday, Nov. 4, to preview the launch of the agency’s first planetary defense test mission, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART). Supporting life beyond Earth could be possible thanks to graphene innovation
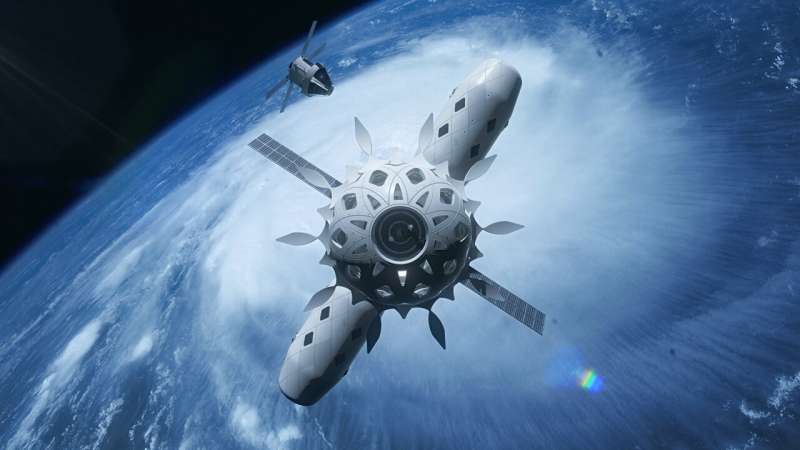

Advanced manufacturing experts from Manchester have revealed what human life in space could look like—with a graphene-enhanced space habitat developed to meet anticipated demand for human settlements beyond Earth.
A community of specialists at The University of Manchester have teamed up with global architect firm Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM) to research the design and manufacturing of space habitats for the space industry.
A small telescope past Saturn could solve some mysteries of the universe better than giant telescopes near Earth

Dozens of space-based telescopes operate near Earth and provide incredible images of the universe. But imagine a telescope far away in the outer solar system, 10 or even 100 times farther from the sun than Earth. The ability to look back at our solar system or peer into the darkness of the distant cosmos would make this a uniquely powerful scientific tool.
I'm an astrophysicist who studies the formation of structure in the universe. Since the 1960s, scientists like me have been considering the important scientific questions we might be able to answer with a telescope placed in the outer solar system.
Researchers analyze consequences of China space weapon test

University of Leicester experts in the military uses of outer space have urged further international dialog and 'cool heads' following flight tests of a new Chinese hypersonic missile system.
Reports of China testing a new orbital launch vehicle, known as Fractional Orbital Bombardment System (FOBS), have fuelled concerns about the nuclear weapon state's advancing military capabilities and possible consequences for the United States and its allies.
High-profile flight tests conducted in July and August saw a rocket launched into orbital flight, which later re-entered the atmosphere and released a maneuverable glide vehicle traveling at hypersonic speeds, in excess of five times the speed of sound.
Long-range missile systems like this can carry nuclear or non-nuclear warheads. With no official explanation from the Chinese government, some US commentators were quick to assume the worst—a new Chinese ability to bombard the United States from outer space with nuclear weapons.
But now, in a new policy brief for the Asia-Pacific Leadership Network by Dr. Bleddyn Bowen and Dr. Cameron Hunter, the international relations experts have called for cooler heads in response to the tests.
Hunting for marine plastic
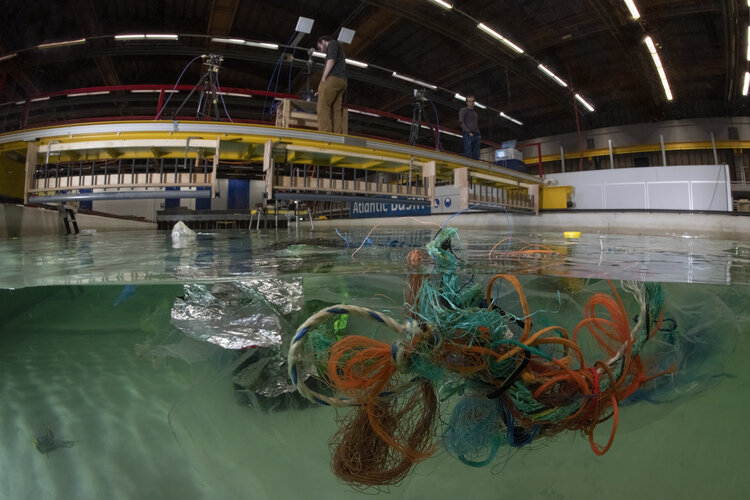 Image:
Hunting for marine plastic
Image:
Hunting for marine plastic Space for a Green Future
 Video:
00:02:12
Video:
00:02:12
The climate crisis is the most urgent challenge faced by humankind – affecting every region, continent, and ocean on Earth. Space has an untapped potential to make a difference in tackling the threats and challenges faced by humanity. Satellites watch over Earth continuously, helping us to monitor, understand, model, predict and act on climate change and its related challenges.
As part of one of the three ‘Accelerators’ that will drive Europe’s increased use of space, the Space for a Green Future Accelerator will help Europe act to mitigate climate change. It will provide actionable information, helping form the
Change in the Arctic
 Video:
00:03:17
Video:
00:03:17
Satellites play a vital role in monitoring the rapid changes taking place in the Arctic. Tracking ice lost from the world’s glaciers, ice sheets and frozen land shows that Earth is losing ice at an accelerating rate. Currently more than a trillion tonnes of ice is lost each year. The sooner Earth’s temperature is stabilised, the more manageable the impacts of ice loss will be.