Copernical Team
Gravitational 'kick' may explain the strange shape at the center of Andromeda
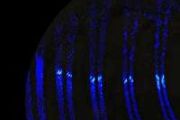
 When two galaxies collide, the supermassive black holes at their cores release a devastating gravitational "kick," similar to the recoil from a shotgun. New research led by CU Boulder suggests that this kick may be so powerful it can knock millions of stars into wonky orbits.
The research, published Oct. 29 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, helps solve a decades-old mystery surrounding
When two galaxies collide, the supermassive black holes at their cores release a devastating gravitational "kick," similar to the recoil from a shotgun. New research led by CU Boulder suggests that this kick may be so powerful it can knock millions of stars into wonky orbits.
The research, published Oct. 29 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, helps solve a decades-old mystery surrounding The Road to Launch and Beyond for NASA's James Webb Space Telescope
 Now that NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has safely arrived at its launch site in French Guiana, on the northeastern coast of South America, technical teams have begun making progress on the final checklist of preparations before liftoff later this year.
These preparations are expected to last 55 days from the observatory's arrival by ship to the day of launch.
After Webb arrived a
Now that NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has safely arrived at its launch site in French Guiana, on the northeastern coast of South America, technical teams have begun making progress on the final checklist of preparations before liftoff later this year.
These preparations are expected to last 55 days from the observatory's arrival by ship to the day of launch.
After Webb arrived a Rocky Exoplanets Are Even Stranger Than We Thought
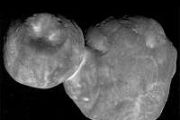
 Astronomers have discovered thousands of planets orbiting stars in our galaxy - known as exoplanets. However, it's difficult to know what exactly these planets are made of, or whether any resemble Earth. To try to find out, astronomer Siyi Xu of NSF's NOIRLab partnered with geologist Keith Putirka of California State University, Fresno, to study the atmospheres of what are known as polluted whit
Astronomers have discovered thousands of planets orbiting stars in our galaxy - known as exoplanets. However, it's difficult to know what exactly these planets are made of, or whether any resemble Earth. To try to find out, astronomer Siyi Xu of NSF's NOIRLab partnered with geologist Keith Putirka of California State University, Fresno, to study the atmospheres of what are known as polluted whit Supporting life beyond earth could be possible - thanks to graphene innovation
 Advanced manufacturing experts from Manchester have revealed what human life in space could look like - with a graphene-enhanced space habitat developed to meet anticipated demand for human settlements beyond Earth.
A community of specialists at The University of Manchester have teamed up with global architect firm Skidmore, Owings and Merrill (SOM) to research the design and manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing experts from Manchester have revealed what human life in space could look like - with a graphene-enhanced space habitat developed to meet anticipated demand for human settlements beyond Earth.
A community of specialists at The University of Manchester have teamed up with global architect firm Skidmore, Owings and Merrill (SOM) to research the design and manufacturing NASA prepares to fuel James Webb telescope for Dec. 18 launch
 NASA is in the final stages of preparation to launch the nearly $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope, an engineering marvel that may reveal secrets of time and the universe, from South America on Dec. 18.
Technicians are preparing to load the space observatory with fuel that will power it for up to 13 years as it orbits the sun about one million miles from Earth, NASA officials said T
NASA is in the final stages of preparation to launch the nearly $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope, an engineering marvel that may reveal secrets of time and the universe, from South America on Dec. 18.
Technicians are preparing to load the space observatory with fuel that will power it for up to 13 years as it orbits the sun about one million miles from Earth, NASA officials said T Vast patches of glassy rock in Chilean desert likely created by ancient exploding comet
 Around 12,000 years ago, something scorched a vast swath of the Atacama Desert in Chile with heat so intense that it turned the sandy soil into widespread slabs of silicate glass. Now, a research team studying the distribution and composition of those glasses has come to a conclusion about what caused the inferno.
In a study published in the journal Geology, researchers show that samples o
Around 12,000 years ago, something scorched a vast swath of the Atacama Desert in Chile with heat so intense that it turned the sandy soil into widespread slabs of silicate glass. Now, a research team studying the distribution and composition of those glasses has come to a conclusion about what caused the inferno.
In a study published in the journal Geology, researchers show that samples o An artificial material that can sense, adapt to its environment
 Move over, Hollywood - science fiction is getting ready to leap off the big screen and enter the real world. While recent science fiction movies have demonstrated the power of artificially intelligent computer programs, such as the fictional character J.A.R.V.I.S. in the Avenger film series, to make independent decisions to carry out a set of actions, these imagined movie scenarios could now be
Move over, Hollywood - science fiction is getting ready to leap off the big screen and enter the real world. While recent science fiction movies have demonstrated the power of artificially intelligent computer programs, such as the fictional character J.A.R.V.I.S. in the Avenger film series, to make independent decisions to carry out a set of actions, these imagined movie scenarios could now be Late bombardment of the Moon revealed
 The lunar surface is covered by numerous craters that date back to the impacts of asteroids. Age determinations on lunar rocks formed during these impacts show a surprising clustering at ages of about 3.9 billion years before present, or about 500 million years after the Moon was formed. These observations have led to the theory of a Late Heavy Bombardment of the Moon (or LHB).
But what wa
The lunar surface is covered by numerous craters that date back to the impacts of asteroids. Age determinations on lunar rocks formed during these impacts show a surprising clustering at ages of about 3.9 billion years before present, or about 500 million years after the Moon was formed. These observations have led to the theory of a Late Heavy Bombardment of the Moon (or LHB).
But what wa Earth's orbit affects millennial climate variability
 Abundant geological evidence demonstrates that Earth's climate has experienced millennial-scale variability superimposed on glacial-interglacial fluctuations through the Pleistocene. The magnitude of millennial climate variability has been linked to glacial cycles over the past 800 thousand years?(kyr).
For the period before the Mid-Pleistocene Transition, when global glaciations were less
Abundant geological evidence demonstrates that Earth's climate has experienced millennial-scale variability superimposed on glacial-interglacial fluctuations through the Pleistocene. The magnitude of millennial climate variability has been linked to glacial cycles over the past 800 thousand years?(kyr).
For the period before the Mid-Pleistocene Transition, when global glaciations were less UK and France reach new agreement on climate change mission
 The UK Space Agency has provided new funding for a joint British and French MicroCarb mission dedicated to monitoring atmospheric carbon dioxide - the main greenhouse gas responsible for climate change.
Dr Paul Bate, Chief Executive of the UK Space Agency, and Laurence Monnoyer-Smith, Director of Sustainable Development of the French space agency, CNES, signed an implementation arrangement
The UK Space Agency has provided new funding for a joint British and French MicroCarb mission dedicated to monitoring atmospheric carbon dioxide - the main greenhouse gas responsible for climate change.
Dr Paul Bate, Chief Executive of the UK Space Agency, and Laurence Monnoyer-Smith, Director of Sustainable Development of the French space agency, CNES, signed an implementation arrangement