Copernical Team
Judge tosses Blue Origin's lawsuit over SpaceX lunar contract
 A federal judge on Thursday threw out Blue Origin's latest legal attempt to block SpaceX's $2.9 billion lunar lander contract from NASA.
"The defendant's motion to dismiss ... is granted," Federal Claims Court judge Richard Hertling wrote in an order, citing a sealed opinion that he also signed.
Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos' rocket company, had sued Elon Musk's SpaceX and the U.S. gov
A federal judge on Thursday threw out Blue Origin's latest legal attempt to block SpaceX's $2.9 billion lunar lander contract from NASA.
"The defendant's motion to dismiss ... is granted," Federal Claims Court judge Richard Hertling wrote in an order, citing a sealed opinion that he also signed.
Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos' rocket company, had sued Elon Musk's SpaceX and the U.S. gov iRocket And Turion Space ink agreement for 10 launches to low earth orbit
 On November 4, 2021, iRocket announced that the company signed an agreement with Turion Space Corp in Irvine, CA. Said iRocket CEO Asad Malik, "We are excited about this new partnership with Turion Space to provide rapid access to space and cost competitive launch costs for their 20 Droid satellites and the low-cost final orbit delivery option their Droid satellites will bring to some of our own
On November 4, 2021, iRocket announced that the company signed an agreement with Turion Space Corp in Irvine, CA. Said iRocket CEO Asad Malik, "We are excited about this new partnership with Turion Space to provide rapid access to space and cost competitive launch costs for their 20 Droid satellites and the low-cost final orbit delivery option their Droid satellites will bring to some of our own Your ticket to space, with ‘Space Station Earth’

European dates for the ‘Space Station Earth’ immersive concert tour, have been announced this week.
Earth from Space: Shetland Islands
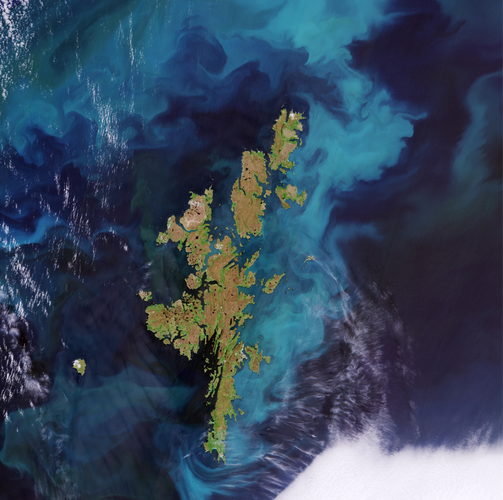

The Shetland Islands, an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, are featured in this Copernicus Sentinel-2 image.
Melt – ESA’s newly released documentary

Melt – ESA’s newly released documentary
Glaciers across the globe have lost over nine trillion tonnes of ice in half a century. How will glaciers look over the coming decades?
A CADRE of mini-rovers navigates the lunar terrain of SLOPE
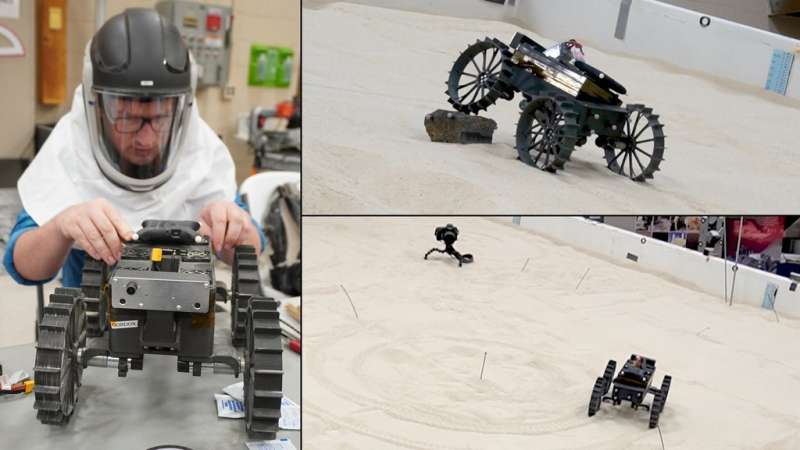

NASA's Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration (CADRE) project is developing small robots programmed to work autonomously as a team to explore the lunar surface.
A team of shoebox-size rover scouts was recently put to the test at a NASA Glenn Research Center lab. The facility, called the Simulated Lunar Operations lab (or SLOPE) is designed to mimic lunar and planetary surface operations. The mini-rovers traversed simulated lunar soil—called regolith—to better understand the types of challenges that lunar rovers of this size will face on the Moon's surface. The results of the tests will be used to characterize small rover performance and improve the rovers' mobility design.
NASA to deflect asteroid in test of 'planetary defense'
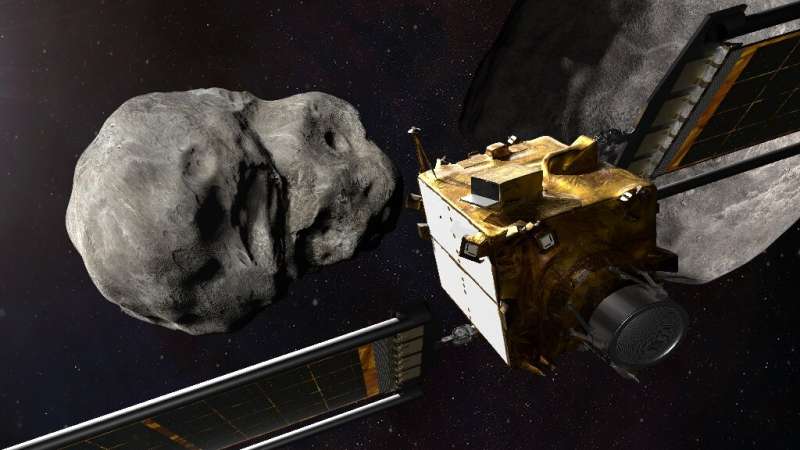

In the 1998 Hollywood blockbuster "Armageddon," Bruce Willis and Ben Affleck race to save the Earth from being pulverized by an asteroid.
While the Earth faces no such immediate danger, NASA plans to crash a spacecraft traveling at a speed of 15,000 miles per hour (24,000 kph) into an asteroid next year in a test of "planetary defense."
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) is to determine whether this is an effective way to deflect the course of an asteroid should one threaten the Earth in the future.
NASA provided details of the DART mission, which carries a price tag of $330 million, in a briefing for reporters on Thursday.
"Although there isn't a currently known asteroid that's on an impact course with the Earth, we do know that there is a large population of near-Earth asteroids out there," said Lindley Johnson, NASA's Planetary Defense Officer.
NASA could bring astronauts home from space station before replacements arrive

Four astronauts could leave the International Space Station on Sunday without their replacement team having arrived to take over, NASA announced Thursday, but the timing remains uncertain due to weather conditions.
The four members of the Crew-2 mission, including a French and a Japanese astronaut, are due to return to Earth this month after spending about six months on board the ISS.
Normally they would have to wait for four other astronauts—three Americans and a German from the Crew-3 mission—to arrive aboard the space station to take their place.
But the takeoff of the next mission's rocket, which had already been postponed several times and had been rescheduled for this weekend, was once again canceled because of unfavorable weather conditions, NASA said in a statement.
As a result, the space agency is now considering returning Crew-2 to Earth before Crew-3 launches.
"The earliest possible opportunity for undocking" the capsule to bring Crew-2 back to Earth would be at 1:05 pm Sunday Florida time (1705 GMT), NASA said.
From space, astronaut sounds the alarm about climate crisis

SpaceX crew launch bumped to next week; astronaut on mend