Copernical Team
Shenzhou XIII crew ready for first spacewalk
 The Shenzhou XIII mission crew will soon carry out their first extravehicular activity, or spacewalk, according to the China Manned Space Agency.
The agency said in a news release on Friday the three-member crew - Major General Zhai Zhigang, Senior Colonel Wang Yaping and Senior Colonel Ye Guangfu - are in good condition and ready for the operation.
The astronauts had been inside the
The Shenzhou XIII mission crew will soon carry out their first extravehicular activity, or spacewalk, according to the China Manned Space Agency.
The agency said in a news release on Friday the three-member crew - Major General Zhai Zhigang, Senior Colonel Wang Yaping and Senior Colonel Ye Guangfu - are in good condition and ready for the operation.
The astronauts had been inside the Harris to announce first National Space Council meeting in nearly a year
 Vice President Kamala Harris is scheduled to host the Biden administration's first meeting of the National Space Council on Dec. 1.
Her announcement will come Friday during her visit to the Goddard Space Flight Center, which will focus on efforts to use space missions to monitor and address the climate crisis.
She will be accompanied by NASA administrator Bill Nelson and officials fr
Vice President Kamala Harris is scheduled to host the Biden administration's first meeting of the National Space Council on Dec. 1.
Her announcement will come Friday during her visit to the Goddard Space Flight Center, which will focus on efforts to use space missions to monitor and address the climate crisis.
She will be accompanied by NASA administrator Bill Nelson and officials fr Sols 3287-3288: Assessing a New Potential Drill Target
 After our short bump on Tuesday, Curiosity has reached a new potential drill location. When we first arrived at the clay-sulfate transition, the science team decided on a strategy to drill every ~25 m in elevation gain.
This allows us to systematically document any changes in the composition of the terrain while being reasonable with our limited rover resources. The terrain is beginning t
After our short bump on Tuesday, Curiosity has reached a new potential drill location. When we first arrived at the clay-sulfate transition, the science team decided on a strategy to drill every ~25 m in elevation gain.
This allows us to systematically document any changes in the composition of the terrain while being reasonable with our limited rover resources. The terrain is beginning t Flight #15 - Start of the Return Journey
 With conjunction over and our first flight at 2,700 RPM behind us, Ingenuity is ready to begin the journey back to the Wright Brothers Field at the Octavia E. Butler landing site, before venturing beyond. The above figure depicts the mission ahead of Ingenuity, which is to join Perseverance in the trek north along the east edge of Seitah, before traveling west to reach the Jezero ancient river d
With conjunction over and our first flight at 2,700 RPM behind us, Ingenuity is ready to begin the journey back to the Wright Brothers Field at the Octavia E. Butler landing site, before venturing beyond. The above figure depicts the mission ahead of Ingenuity, which is to join Perseverance in the trek north along the east edge of Seitah, before traveling west to reach the Jezero ancient river d NASA plans crashing spacecraft into asteroid to study Earth-impact defense
 NASA plans to launch a spacecraft as early as Nov. 23 and crash it into an asteroid next year so scientists can try to understand how to redirect dangerous space objects away from potential catastrophic Earth collisions.
The mission is NASA's first flight demonstration for planetary defense, space agency officials said.
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, is scheduled for
NASA plans to launch a spacecraft as early as Nov. 23 and crash it into an asteroid next year so scientists can try to understand how to redirect dangerous space objects away from potential catastrophic Earth collisions.
The mission is NASA's first flight demonstration for planetary defense, space agency officials said.
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, is scheduled for Tidying up planetary nurseries
 A group of astronomers, led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, propose and have tested a mechanism that explains most of the properties observed in dispersing planet-forming disks around newborn stars for the first time. The key ingredients to this new physical concept are X-ray emissions from the central star and a calm inner disk, well shielded from the incident radiati
A group of astronomers, led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, propose and have tested a mechanism that explains most of the properties observed in dispersing planet-forming disks around newborn stars for the first time. The key ingredients to this new physical concept are X-ray emissions from the central star and a calm inner disk, well shielded from the incident radiati NASA takes additional steps to investigate Hubble in safe mode
 NASA is continuing work to resolve an issue that has suspended science operations on the Hubble Space Telescope. The science instruments entered a safe mode configuration on Oct. 25 after detecting a loss of specific data synchronization messages.
The Hubble team is focusing its efforts to isolate the problem on hardware that commands the instruments and is part of the Science Instrument C
NASA is continuing work to resolve an issue that has suspended science operations on the Hubble Space Telescope. The science instruments entered a safe mode configuration on Oct. 25 after detecting a loss of specific data synchronization messages.
The Hubble team is focusing its efforts to isolate the problem on hardware that commands the instruments and is part of the Science Instrument C New dates for Crew-2 return and Crew-3 launch

Update: Undocking of Crew-2 with Thomas Pesquet now planned for Sunday, 7 November, 18:05 GMT/19:05 CET for a splashdown on Monday, around 12:14 GMT/13:14 CET. Next launch opportunity for Crew-3 with Matthias Maurer is planned for Thursday, 11 November, 02:03 GMT/03:03 CET.
No toilet for returning SpaceX crew, stuck using diapers
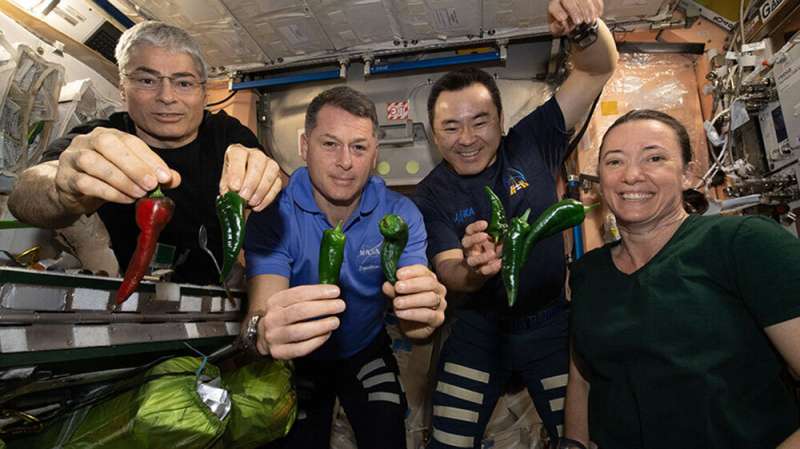

The astronauts who will depart the International Space Station on Sunday will be stuck using diapers on the way home because of their capsule's broken toilet.
NASA astronaut Megan McArthur described the situation Friday as "suboptimal" but manageable. She and her three crewmates will spend 20 hours in their SpaceX capsule, from the time the hatches are closed until Monday morning's planned splashdown.
"Spaceflight is full of lots of little challenges," she said during a news conference from orbit.
Astronauts to return from space station next week: NASA
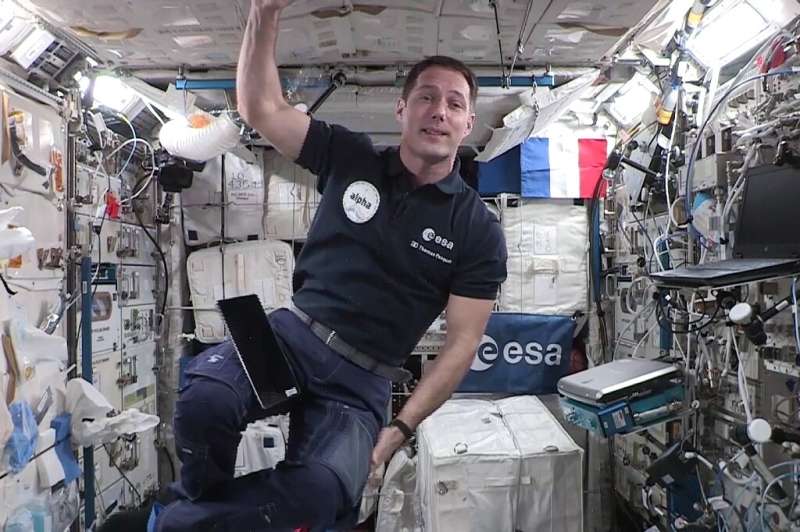

Four astronauts are scheduled to return to Earth from the International Space Station early Monday after spending more than six months in space, NASA announced.
The four members of the Crew-2 mission, including a French and a Japanese astronaut, will therefore return to Earth before the arrival of a replacement crew, whose take-off was delayed several times due to unfavorable weather conditions.
NASA said in a statement late Friday that Crew-2 members are due to return to Earth "no earlier than 7:14 am EST (1214 GMT) Monday, Nov. 8, with a splashdown off the coast of Florida."
"As we're preparing to leave, it's kind of a bittersweet feeling, we might never come back to see the ISS, and it's really a magical place," French astronaut Thomas Pesquet said earlier Friday during a press conference from the space station.