Copernical Team
Ingenuity Mars Helicopter set to fly lower for detailed surface imaging
 Following Flight 12's scouting images of "South Seitah," which were the most valuable Ingenuity has taken to date, we are taking Winston's advice for Ingenuity's 13th flight. We will again be venturing across into Seitah to scout an area of outcrops glimpsed in Flight 12 imagery - but we're taking these new pictures while looking back, pointing in the opposite direction.
Taking place no ea
Following Flight 12's scouting images of "South Seitah," which were the most valuable Ingenuity has taken to date, we are taking Winston's advice for Ingenuity's 13th flight. We will again be venturing across into Seitah to scout an area of outcrops glimpsed in Flight 12 imagery - but we're taking these new pictures while looking back, pointing in the opposite direction.
Taking place no ea 'Dune' brings galactic-scale blockbuster to Venice
 Giant worms and inter-planetary battles rocked the Venice Film Festival on Friday as "Dune", one of the most hotly anticipated blockbusters in years, was finally set for its world premiere.
It brought a cavalcade of A-listers to the city's glitzy Lido island, along with fans packing the waterfront for the arrival of Timothee Chalamet, Zendaya, Oscar Isaac, Josh Brolin and Javier Bardem.
Giant worms and inter-planetary battles rocked the Venice Film Festival on Friday as "Dune", one of the most hotly anticipated blockbusters in years, was finally set for its world premiere.
It brought a cavalcade of A-listers to the city's glitzy Lido island, along with fans packing the waterfront for the arrival of Timothee Chalamet, Zendaya, Oscar Isaac, Josh Brolin and Javier Bardem. Mini CRISPR system promises easier cell engineering, gene therapy
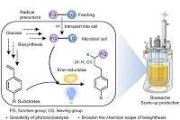
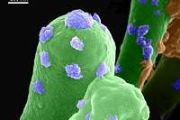
 Scientists have developed a more compact CRISPR system that can be more easily delivered to cells.
The technology, described Friday in the journal Molecular Cell, promises to make cell-engineering more effective and efficient.
The world's most popular and powerful gene-editing tool, CRISPR-Cas9, has enabled numerous scientific discoveries. It works by excising specific DNA sequen
Scientists have developed a more compact CRISPR system that can be more easily delivered to cells.
The technology, described Friday in the journal Molecular Cell, promises to make cell-engineering more effective and efficient.
The world's most popular and powerful gene-editing tool, CRISPR-Cas9, has enabled numerous scientific discoveries. It works by excising specific DNA sequen Independent group formed to advance interoperability in satellite and ground system networks
 Leading companies and organizations in the space industry, including two major branches of the U.S. Department of Defense, have come together to form the Digital IF Interoperability (DIFI) Consortium, a non-profit industry group created to advance interoperability among space and ground system networks.
Formed under the auspices of The IEEE Industry Standards and Technology Organization (I
Leading companies and organizations in the space industry, including two major branches of the U.S. Department of Defense, have come together to form the Digital IF Interoperability (DIFI) Consortium, a non-profit industry group created to advance interoperability among space and ground system networks.
Formed under the auspices of The IEEE Industry Standards and Technology Organization (I Chandra resumes science operations
 NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory has successfully resumed observations after recovery from a problem involving one of its science instruments, the Low Energy Transmission Grating (LETG). The LETG is used to measure the intensity of X-rays at different energies.
In preparation for an observing run Aug. 31 using the LETG, the movement of this instrument into its operating position - where it
NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory has successfully resumed observations after recovery from a problem involving one of its science instruments, the Low Energy Transmission Grating (LETG). The LETG is used to measure the intensity of X-rays at different energies.
In preparation for an observing run Aug. 31 using the LETG, the movement of this instrument into its operating position - where it Astronomers create the first 3D-printed stellar nurseries
 Astronomers can't touch the stars they study, but astrophysicist Nia Imara is using 3-dimensional models that fit in the palm of her hand to unravel the structural complexities of stellar nurseries, the vast clouds of gas and dust where star formation occurs.
Imara and her collaborators created the models using data from simulations of star-forming clouds and a sophisticated 3D printing pr
Astronomers can't touch the stars they study, but astrophysicist Nia Imara is using 3-dimensional models that fit in the palm of her hand to unravel the structural complexities of stellar nurseries, the vast clouds of gas and dust where star formation occurs.
Imara and her collaborators created the models using data from simulations of star-forming clouds and a sophisticated 3D printing pr Cosmonaut calls 1st approach to Nauka Module during spacewalk from ISS 'Historic Moment'
 During his spacewalk from the International Space Station (ISS), cosmonaut Pyotr Dubrov first approached the new module Nauka, calling it a historic moment, according to the crew's talks with the Earth, broadcast by Roscosmos.
On Friday, Dubrov and his colleague Oleg Novitsky make a spacewalk to connect Nauka module to the US power supply.
"A historic moment - the first grab of the h
During his spacewalk from the International Space Station (ISS), cosmonaut Pyotr Dubrov first approached the new module Nauka, calling it a historic moment, according to the crew's talks with the Earth, broadcast by Roscosmos.
On Friday, Dubrov and his colleague Oleg Novitsky make a spacewalk to connect Nauka module to the US power supply.
"A historic moment - the first grab of the h Hurricane Ida recovery assessments continue at NASA Michoud
 Recovery and damage assessments continue at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans following Hurricane Ida. The powerful category 4 hurricane made landfall in Louisiana Aug. 29 on the 16th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina.
The Michoud Safety and Security team completed an initial assessment of the 829-acre facility and its 81 buildings and structures on Aug. 31. Teams determined M
Recovery and damage assessments continue at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans following Hurricane Ida. The powerful category 4 hurricane made landfall in Louisiana Aug. 29 on the 16th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina.
The Michoud Safety and Security team completed an initial assessment of the 829-acre facility and its 81 buildings and structures on Aug. 31. Teams determined M Planetary radar observes 1,000th near-earth asteroid since 1968
 Seven days after this historic milestone, a massive antenna at NASA's Deep Space Network Goldstone complex imaged another, far larger object.
On Aug. 14, 2021, a small near-Earth asteroid (NEA) designated 2021 PJ1 passed our planet at a distance of over 1 million miles (about 1.7 million kilometers). Between 65 and 100 feet (20 and 30 meters) wide, the recently discovered asteroid wasn't a
Seven days after this historic milestone, a massive antenna at NASA's Deep Space Network Goldstone complex imaged another, far larger object.
On Aug. 14, 2021, a small near-Earth asteroid (NEA) designated 2021 PJ1 passed our planet at a distance of over 1 million miles (about 1.7 million kilometers). Between 65 and 100 feet (20 and 30 meters) wide, the recently discovered asteroid wasn't a After six months on Mars, NASA's tiny copter is still flying high
 It was only supposed to fly five times. And yet NASA's helicopter on Mars, Ingenuity, has completed 12 flights and it isn't ready to retire.
Given its stunning and unexpected success, the US space agency has extended Ingenuity's mission indefinitely.
The tiny helicopter has become the regular travel companion of the rover Perseverance, whose core mission is to seek signs of ancient life
It was only supposed to fly five times. And yet NASA's helicopter on Mars, Ingenuity, has completed 12 flights and it isn't ready to retire.
Given its stunning and unexpected success, the US space agency has extended Ingenuity's mission indefinitely.
The tiny helicopter has become the regular travel companion of the rover Perseverance, whose core mission is to seek signs of ancient life