
Copernical Team
China's manned moon landing possible before 2030: scientist
 It is "entirely possible" for China to perform a crewed lunar landing before 2030, said a senior Chinese scientist in deep-space exploration.
"I personally think that as long as the technological research for manned moon landing continues, and as long as the country is determined (to achieve the goal), it is entirely possible for China to land people on the moon before 2030, " Ye Peijian
It is "entirely possible" for China to perform a crewed lunar landing before 2030, said a senior Chinese scientist in deep-space exploration.
"I personally think that as long as the technological research for manned moon landing continues, and as long as the country is determined (to achieve the goal), it is entirely possible for China to land people on the moon before 2030, " Ye Peijian NASA announces 10 latest astronaut trainees
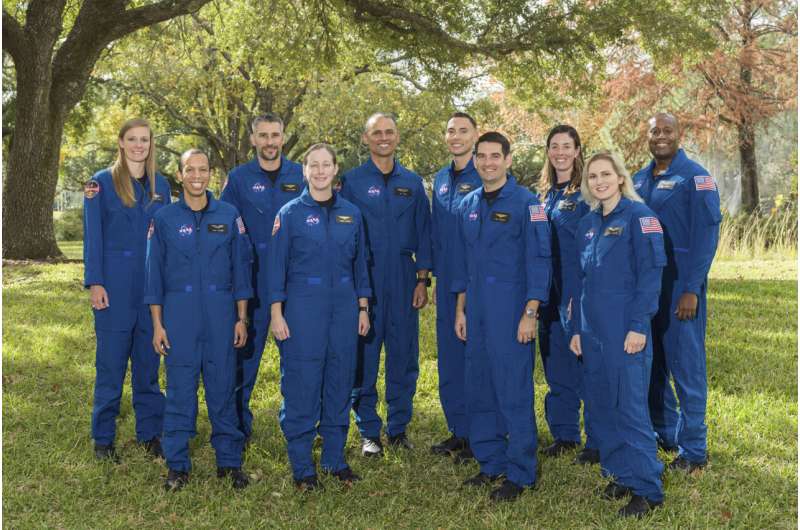
 NASA announced Monday its 10 latest trainee astronauts, who include a firefighter turned Harvard professor, a former member of the national cycle team, and a pilot who led the first-ever all-woman F-22 formation in combat.
The 2021 class was whittled down from a field of more than 12,000 applicants and will now report for duty in January at the Johnson Space Center in Texas, where they will
NASA announced Monday its 10 latest trainee astronauts, who include a firefighter turned Harvard professor, a former member of the national cycle team, and a pilot who led the first-ever all-woman F-22 formation in combat.
The 2021 class was whittled down from a field of more than 12,000 applicants and will now report for duty in January at the Johnson Space Center in Texas, where they will RUAG Space: First fully U.S.-made fairing to fly into space
 On Sun., Dec. 5, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket will launch the Space Test Program (STP)-3 mission for the U.S. Space Force (USSF) Space Systems Command (SSC) from Cape Canaveral, Fla. "This flight is a key milestone for us," said Dan Merenda, managing director RUAG Space USA.
"For the very first time, a fully U.S.-made fairing from us will fly into space." It is also the first ti
On Sun., Dec. 5, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket will launch the Space Test Program (STP)-3 mission for the U.S. Space Force (USSF) Space Systems Command (SSC) from Cape Canaveral, Fla. "This flight is a key milestone for us," said Dan Merenda, managing director RUAG Space USA.
"For the very first time, a fully U.S.-made fairing from us will fly into space." It is also the first ti Japanese duo prepare for first tourist flight to space station since 2009
 Two Japanese businessmen plan to become the first paying tourists to visit the International Space Station since 2009 by rocketing into orbit from Kazakhstan on Wednesday.
Billionaire Yusaku Maezawa, who made his fortune in the fashion industry, booked seats for himself and his production assistant, Yozo Hirano, aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft through Virginia-based spacecraft broker
Two Japanese businessmen plan to become the first paying tourists to visit the International Space Station since 2009 by rocketing into orbit from Kazakhstan on Wednesday.
Billionaire Yusaku Maezawa, who made his fortune in the fashion industry, booked seats for himself and his production assistant, Yozo Hirano, aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft through Virginia-based spacecraft broker NASA's 10 new astronauts: pilots, doctor, physicist, cyclist

European space firm to build small, reusable launcher
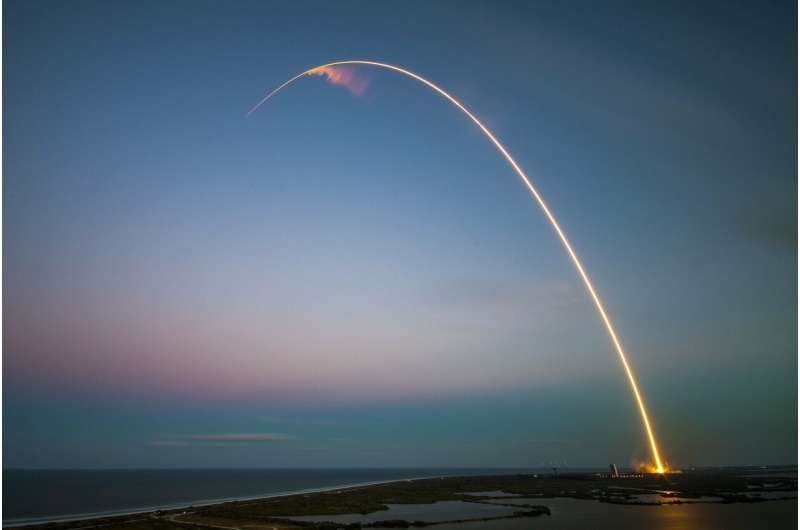

European space firm ArianeGroup will develop a small, reusable carrier rocket to compete with SpaceX, the pioneer of the technology, France's economy minister said Monday.
The launch vehicle should be operational by 2026, Bruno Le Maire said in a visit to ArianeGroup's large rocket testing facility in Vernon, northwest France.
Le Maire admitted that Europe was "behind the curve on reusable launchers".
"We didn't believe in it. We fell behind our American partners who developed Space X and Falcon 9, and we must narrow the gap," he said.
Elon Musk's SpaceX has become a major leader in the sector, with its rockets taking satellites and astronauts into orbit.
Explore further
© 2021 AFP
Webb moved for fuelling
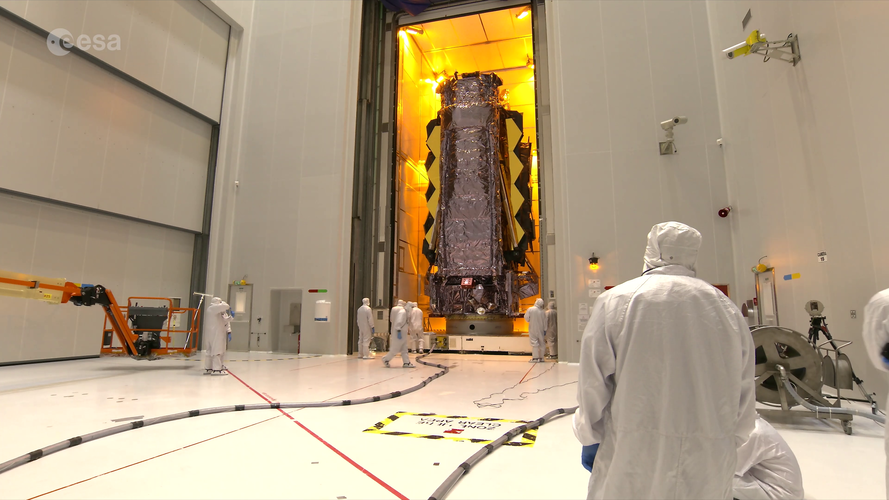 Video:
00:00:51
Video:
00:00:51
The James Webb Space Telescope, configured for flight, was moved from the cleanroom to the payload preparation facility for fuelling at Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana on 11–12 November 2021.
Webb will be loaded with propellants before being mounted on top of the rocket and then encapsulated by the Ariane 5 fairing.
Webb will be the largest, most powerful telescope ever launched into space. As part of an international collaboration agreement, ESA is providing the telescope’s launch service using the Ariane 5 launch vehicle. Working with partners, ESA was responsible for the development and qualification
Webb fuelled for launch
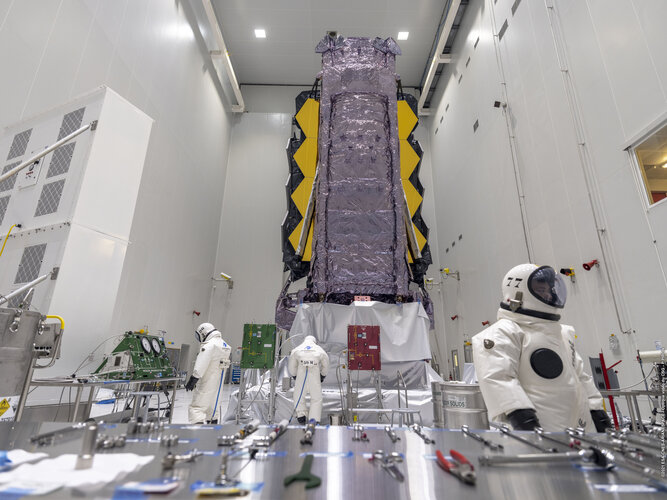 Image:
Webb fuelled for launch
Image:
Webb fuelled for launch ESA spurs 5G digital connectivity
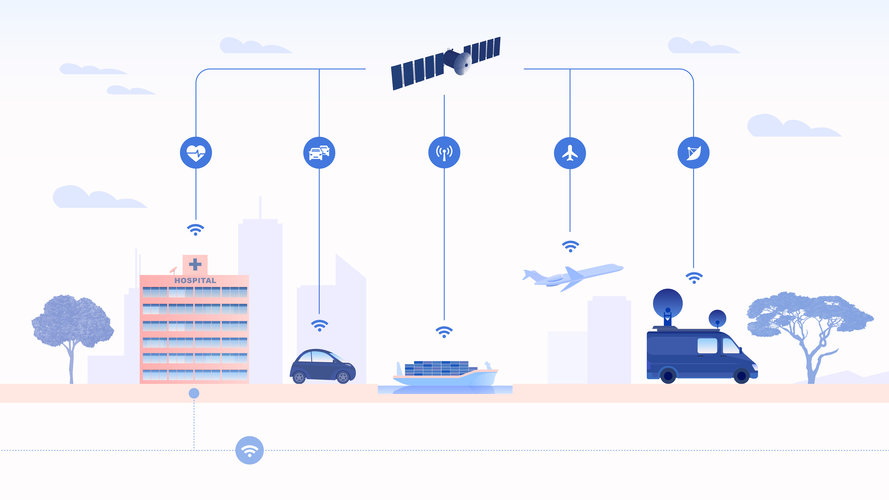
Efforts to enable seamless connectivity and reduce the digital divide by using telecommunications satellites to enhance terrestrial 5G services have leapt forward.
Russia to send Japanese tycoon to ISS in return to space tourism
 Russia on Wednesday will send Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa to the International Space Station in a move marking Moscow's return to the now booming space tourism business after a decade-long break.
One of Japan's richest men, Maezawa, 46, will blast off from the Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan accompanied by his assistant Yozo Hirano.
On Sunday morning, their Soyuz spacecraft wi
Russia on Wednesday will send Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa to the International Space Station in a move marking Moscow's return to the now booming space tourism business after a decade-long break.
One of Japan's richest men, Maezawa, 46, will blast off from the Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan accompanied by his assistant Yozo Hirano.
On Sunday morning, their Soyuz spacecraft wi 