Displaying items by tag: science
The Aerospace Corporation
The Aerospace Corporation is a private, non-profit corporation headquartered in El Segundo, California that has operated a Federally Funded Research and Development Center (FFRDC) for the United States Air Force since 1960.
The purposes of the corporation are exclusively scientific: to engage in, assist and contribute to the support of scientific activities and projects for, and to perform and engage in research, development and advisory services to or for, the United States Government. As the FFRDC for national-security space, Aerospace works closely with organizations such as the United States Air Force Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC) and the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) to provide "objective technical analyses and assessments for space programs that serve the national interest."
University of Birmingham, Astrophysics & Space Research Group
The Astrophysics & Space Research Group at the University of Birmingham:
The group's research interests span a wide swathe of astronomy and fundamental physics, including the study of galaxies and larger cosmological structures, of black holes and neutron stars, using both electromagnetic and gravitational radiation, of stars and the planets which appear to orbit many of them, and of our own sun and its surrounding heliosphere. We also study gravity itself, and other ultra-weak forces, using sensitive experiments in the laboratory and in space.
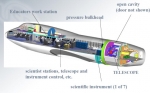
SOFIA observatory
The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) is a joint project of NASA and the German Aerospace Center ( DLR) to construct and maintain an airborne observatory. NASA awarded the contract for the development of the aircraft, operation of the observatory and management of the American part of the project to the Universities Space Research Association (USRA) in 1996.
The DSI (Deutsches SOFIA Institut) manages the German parts of the project which are primarily science and telescope related. SOFIA's telescope saw first light on May 26, 2010. SOFIA is the successor to the Kuiper Airborne Observatory.
Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA)
The Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) is one of the largest and most diverse astrophysical institutions in the world, where scientists carry out a broad program of research in astronomy, astrophysics, earth and space sciences, and science education. The center's mission is to advance knowledge and understanding of the universe through research and education in astronomy and astrophysics.
The center was founded in 1973 as a joint venture between the Smithsonian Institution and Harvard University. It consists of the Harvard College Observatory and the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. The center's main facility is located at Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA. Beyond this location there are also additional satellite facilities elsewhere around the globe.
AURA
The Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA) is a consortium of universities and other institutions that operates astronomical observatories and telescopes. AURA recognizes its mission statement as "To promote excellence in astronomical research by providing access to state-of-the-art facilities".
Founded October 10, 1957 with the encouragement of the National Science Foundation (NSF), AURA was incorporated by a group of seven U.S. universities: California, Chicago, Harvard, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio State, and Wisconsin.
AURA began as a small organization dedicated to ground-based optical astronomy, managing a range of 1- to 4-meter telescopes and providing community advocacy for optical/infrared astronomy. Over the years, AURA expanded its focus to include Solar Astronomy and the Gemini 8-meter telescopes, going on to partner with other consortia such as WIYN (Wisconsin Indiana Yale & NOAO) and SOAR (Southern Astrophysical Research). In the 1980s, AURA took on the management of the Space Telescope Science Institute, opening up the ultraviolet, optical, and infrared wavelength bands in space with the Hubble Space Telescope. AURA is furthering its aims in infrared space astronomy through the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
The organization is responsible for the operation of several important observatories, known as "AURA centers":
- the Gemini Observatory;
- the National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO);
- the National Solar Observatory (NSO);
- the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI);
- and the AURA Observatory (AURA-O).
Space Telescope Science Institute
The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) is the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST; in orbit since 1990) and for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST; scheduled to be launched in 2018).
STScI is located on the Johns Hopkins University Homewood campus in Baltimore, Maryland and was established in 1981 as a community-based science center that is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA). In addition to performing continuing science operations of HST and preparing for scientific exploration with JWST, STScI manages and operates the Multi-mission Archive at Space Telescope (MAST), the Data Management Center for the Kepler mission and a number of other activities benefiting from its expertise in and infrastructure for supporting the operations of space-based astronomical observatories. Most of the funding for STScI activities comes from contracts with NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center but there are smaller activities funded by NASA's Ames Research Center, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and the European Space Agency (ESA).
The staff at STScI consists of scientists (mostly astronomers and astrophysicists), software engineers, data management and telescope operations personnel, education and public outreach experts, and administrative and business support personnel.
National Solar Observatory (NSO)
the National Solar Observatory is an American observatory operated by the association AURA.
The mission of the National Solar Observatory is to advance knowledge of the Sun, both as an astronomical object and as the dominant external influence on Earth, by providing forefront observational opportunities to the research community. The mission includes the operation of cutting edge facilities, the continued development of advanced instrumentation both in-house and through partnerships, conducting solar research, and educational and public outreach.
SAC-D
SAC-D (Spanish: Satelite de Aplicaciones Cientificas-D, meaning Satellite for Scientific Applications-D), also known as Aquarius after its primary instrument, is an Argentine Earth science satellite built by INVAP and launched on June 10, 2011. It carries seven instruments to study the environment, and a technology demonstration experiment.
Its primary instrument, Aquarius, was built by and is operated by the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
SAC-D is operated by CONAE, the Argentine space agency. The satellite is expected to operate for five years; however the Aquarius instrument is only expected to operate for three.
CONAE - Comision Nacional de Actividades Espaciales
As a specialized agency of the Argentine State, CONAE is the only government body to understand, design, execute, control, manage and administer space projects and entrepreneurships throughout the country. It represents the Nation's civil research and development capabilities in space activities.
To accomplish its mission, CONAE has to plan, execute and evaluate a National Space Program for peaceful use of space science and technology.
For more info: http://www.conae.gov.ar/
NASA - Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC)
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center. GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors, and is located approximately 6.5 miles (10.5 km) northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, USA. GSFC, one of ten major NASA field centers, is named in recognition of Dr. Robert H. Goddard (1882–1945), the pioneer of modern rocket propulsion in the United States.
GSFC is the largest combined organization of scientists and engineers in the United States dedicated to increasing knowledge of the Earth, the Solar System, and the Universe via observations from space. GSFC is a major U.S. laboratory for developing and operating unmanned scientific spacecraft. GSFC conducts scientific investigation, development and operation of space systems, and development of related technologies. Goddard scientists can develop and support a mission, and Goddard engineers and technicians can design and build the spacecraft for that mission. Goddard scientist John C. Mather shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on COBE.
GSFC also operates two spaceflight tracking and data acquisition networks (the Space Network and the Near Earth Network), develops and maintains advanced space and Earth science data information systems, and develops satellite systems for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
GSFC manages operations for many NASA and international missions including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), the Explorer program, the Discovery Program, the Earth Observing System (EOS), INTEGRAL, the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO), the Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) and Swift. Past missions managed by GSFC include the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, SMM, COBE, IUE, and ROSAT. Typically, unmanned earth observation missions and observatories in Earth orbit are managed by GSFC, while unmanned planetary missions are managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California.