
Copernical Team
OneWeb and Kazakhstan National Railways to work together
 OneWeb, a company specializing in low Earth orbit satellite communications, has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Kazakhstan National Railways Company "Kazakhstan Temir Zholy" to investigate providing high-speed, low-latency broadband satellite connectivity to railway stations and rolling stock throughout Kazakhstan.
This collaboration aims to enhance the connectivity and
OneWeb, a company specializing in low Earth orbit satellite communications, has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Kazakhstan National Railways Company "Kazakhstan Temir Zholy" to investigate providing high-speed, low-latency broadband satellite connectivity to railway stations and rolling stock throughout Kazakhstan.
This collaboration aims to enhance the connectivity and Sidus Space closes public offering
 Sidus Space, Inc. (Nasdaq: SIDU), reported Friday the closing of its underwritten public offering of 17,250,000 shares of its Class A common stock (or pre-funded warrants (the "Pre-Funded Warrants") in lieu thereof, which included the full exercise of the underwriters' over-allotment option.
Each share of Class A common stock was sold to the public at a price of $0.30 per share. The gross
Sidus Space, Inc. (Nasdaq: SIDU), reported Friday the closing of its underwritten public offering of 17,250,000 shares of its Class A common stock (or pre-funded warrants (the "Pre-Funded Warrants") in lieu thereof, which included the full exercise of the underwriters' over-allotment option.
Each share of Class A common stock was sold to the public at a price of $0.30 per share. The gross Poland's SatRev signs on for future Virgin Orbit flights
 Virgin Orbit (NASDAQ: VORB) and Poland-based satellite manufacturer SatRev announced a follow-on launch services agreement (LSA) for additional launches of SatRev's satellites in 2023 and beyond.
This new agreement provides SatRev with the flexibility to launch 500 kg over multiple launches to a variety of different orbital planes from the Mojave Air and Space Port in California, USA and/o
Virgin Orbit (NASDAQ: VORB) and Poland-based satellite manufacturer SatRev announced a follow-on launch services agreement (LSA) for additional launches of SatRev's satellites in 2023 and beyond.
This new agreement provides SatRev with the flexibility to launch 500 kg over multiple launches to a variety of different orbital planes from the Mojave Air and Space Port in California, USA and/o A nearby potentially habitable Earth-mass exoplanet
 A team of astronomers led by MPIA scientist Diana Kossakowski have discovered an Earth-mass exoplanet orbiting in the habitable zone of the red dwarf star Wolf 1069. Although the rotation of this planet, named Wolf 1069 b, is probably tidally locked to its path around the parent star, the team is optimistic it may provide durable habitable conditions across a wide area of its dayside. The absenc
A team of astronomers led by MPIA scientist Diana Kossakowski have discovered an Earth-mass exoplanet orbiting in the habitable zone of the red dwarf star Wolf 1069. Although the rotation of this planet, named Wolf 1069 b, is probably tidally locked to its path around the parent star, the team is optimistic it may provide durable habitable conditions across a wide area of its dayside. The absenc Cloudy Sols Are Here Again
 Mars clouds are very much like Earth's cirrus clouds but thinner. While Earth clouds can contain liquid water, the low temperatures and pressures on Mars only allow for water-ice (and CO2 ice) clouds to form. However, these water-ice clouds are optically thin because of the low amounts of water present in the Martian atmosphere; if all the water were on the surface, it would make a layer thinner
Mars clouds are very much like Earth's cirrus clouds but thinner. While Earth clouds can contain liquid water, the low temperatures and pressures on Mars only allow for water-ice (and CO2 ice) clouds to form. However, these water-ice clouds are optically thin because of the low amounts of water present in the Martian atmosphere; if all the water were on the surface, it would make a layer thinner Curiosity Roundup Sols 3725-3731
 The drive in our last plan took us to an area that appeared somewhat smoother and brighter from orbit (as well as from drive direction imaging) on the so-called "Marker band" that we have been investigating. The Marker band was identified as of interest prior to Curiosity landing within Gale crater owing to its distinct texture and appearance from orbit within the layers of rock that make up Mou
The drive in our last plan took us to an area that appeared somewhat smoother and brighter from orbit (as well as from drive direction imaging) on the so-called "Marker band" that we have been investigating. The Marker band was identified as of interest prior to Curiosity landing within Gale crater owing to its distinct texture and appearance from orbit within the layers of rock that make up Mou Mars Helicopter at Three Forks
 NASA's Perseverance Mars Rover took an image on December 18th, 2022, during its 650th day of mission that captured the Mars Helicopter Ingenuity near the base of Jezero Crater's river delta, approximately 1,115 feet (340 meters) away from the rover. The image was captured using the left camera of Mastcam-Z with an RGB color filter and the middle of its seven zoom settings, at a focal length of 6
NASA's Perseverance Mars Rover took an image on December 18th, 2022, during its 650th day of mission that captured the Mars Helicopter Ingenuity near the base of Jezero Crater's river delta, approximately 1,115 feet (340 meters) away from the rover. The image was captured using the left camera of Mastcam-Z with an RGB color filter and the middle of its seven zoom settings, at a focal length of 6 Long-delayed ExoMars mission still dreams of 2028 launch
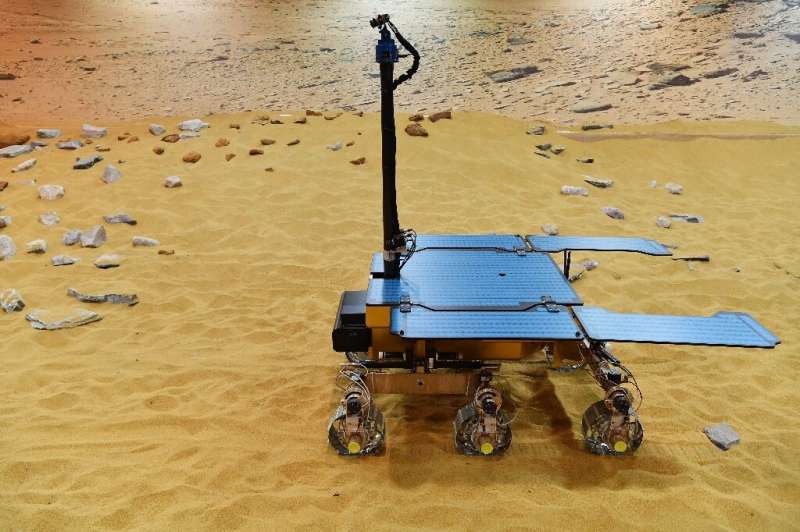

War, budget cuts, a pandemic and a crash: For all its trials, Europe's ExoMars mission might be more deserving of the name Perseverance than NASA's Martian rover.
But the European Space Agency still hopes the mission can launch in 2028 on its long-delayed quest to search for extraterrestrial life on the Red Planet.
This time last year, the ESA's Rosalind Franklin rover was all ready for a September launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, planning to catch a ride on a Russian rocket and descend to the Martian surface on a Russian lander.
Then Moscow invaded Ukraine in March, and sanctions imposed by the ESA's 22 member states led to Russia pulling out and the mission being suspended.
Experiments to complete scientific understanding of how reduced gravity affects boiling and condensation
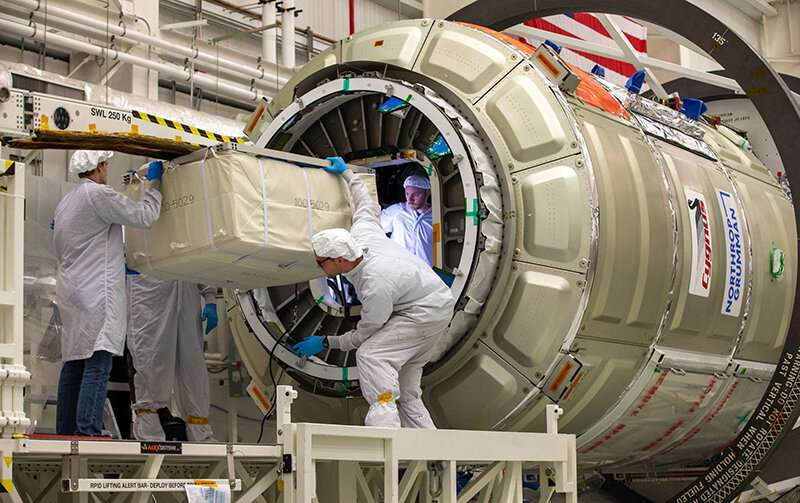

With temperatures on the moon ranging from minus 410 to a scorching 250 degrees Fahrenheit, it's an understatement to say that humans will need habitats with heat and air conditioning to survive there long term.
But heating and cooling systems won't be effective enough to support habitats for lunar exploration or even longer trips to Mars without an understanding of what reduced gravity does to boiling and condensation.
France pledges not to conduct anti-satellite missile tests but leaves other options open
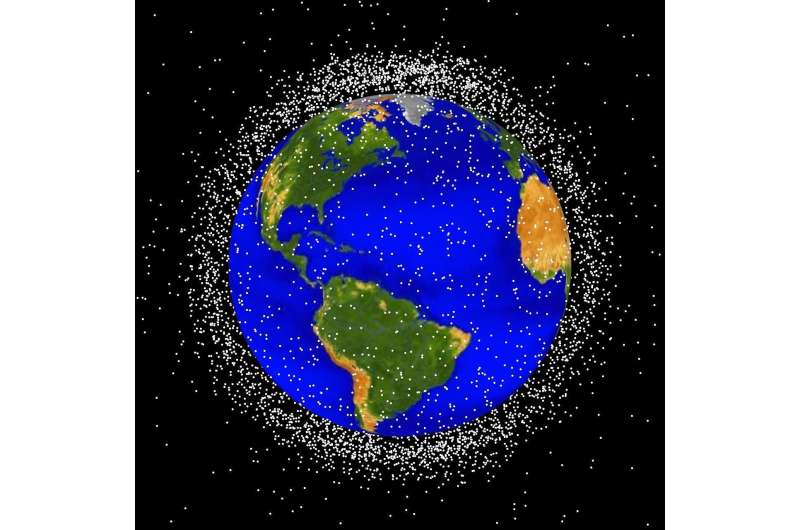
Driven by concerns over space debris, in late November the French Ministry for the Armed Forces formally committed not to conduct anti-satellite missile tests. And yet, France's space strategy of 2019 resolved to "toughen" the country's space capabilities.
Given the short lapse of just three years, how can we make sense of France's seemingly contradictory space military policy?
A historic but surprising decision?
In October 2022, the United Nations voted to work towards putting an end to "destructive direct-ascent antisatellite missile testing"—that is, missiles fired at satellites from Earth's surface or from the air. France cosponsored the resolution and voted for it, despite possessing the technical expertise required to develop such a capacity.
The ministry's statement, published on 9 November 2022, is strongly worded. It dubs anti-satellite testing as "destabilizing and irresponsible," and insists France never conducted such tests. It also voices concerns about the potential impact of space debris on the integrity of in-use satellites, as well as for the space domain. France's decision follows that of the United States on 9 April 2022, which the Elysée Palace had then applauded.

