
Copernical Team
Earth from Space: Monterrey, Mexico
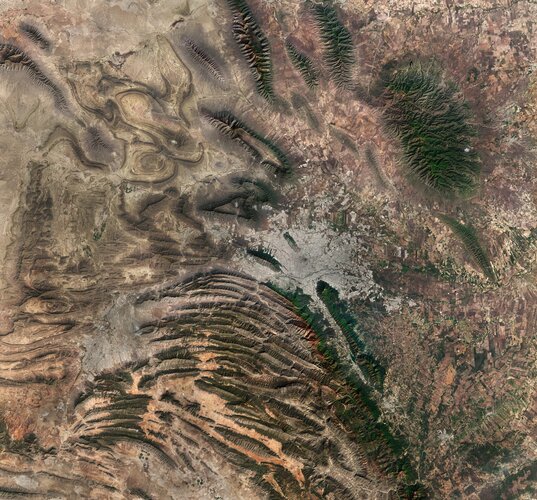 Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features the diverse landscape surrounding Monterrey, the capital of the northeast state of Nuevo León, Mexico.
Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features the diverse landscape surrounding Monterrey, the capital of the northeast state of Nuevo León, Mexico. Researchers detect silicate clouds, methane, water, carbon monoxide on distant planet
 Researchers using data from NASA's James Webb telescope have observed silicate clouds, water, methane, and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of a distant planet.
The discovery is the most number of different molecules ever seen collected on one planet outside of our solar system, scientists say.
Researchers lead by the University of Arizona's Brittany Miles studied spectra data fr
Researchers using data from NASA's James Webb telescope have observed silicate clouds, water, methane, and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of a distant planet.
The discovery is the most number of different molecules ever seen collected on one planet outside of our solar system, scientists say.
Researchers lead by the University of Arizona's Brittany Miles studied spectra data fr Russia's only female cosmonaut praises ISS mission
 Russia's only active female cosmonaut Anna Kikina on Thursday described a "wonderful" atmosphere during her mission to the International Space Station where she travelled aboard a SpaceX spaceship.
The orbital station is one of the few remaining areas of cooperation between Moscow and Washington amid a breakdown of ties since Moscow sent troops to Ukraine.
Kikina is only the fifth profe
Russia's only active female cosmonaut Anna Kikina on Thursday described a "wonderful" atmosphere during her mission to the International Space Station where she travelled aboard a SpaceX spaceship.
The orbital station is one of the few remaining areas of cooperation between Moscow and Washington amid a breakdown of ties since Moscow sent troops to Ukraine.
Kikina is only the fifth profe Sweden's sky lights up with northern lights research

Scientists in Sweden put on a light show in the night sky on Thursday, releasing material from a sounding rocket to research the spectacular northern lights phenomena.
The northern lights, also known as aurora borealis or polar lights, appear as swathes of blue, green and purple lights flickering and dancing across the sky.
They can occasionally be seen across the Arctic on clear nights.
Researchers at the Swedish Institute of Space Physics sent up the rocket from the Esrange Space Center in the country's far north, releasing materials similar to those in fireworks into the sky at an altitude of between 100-200 kilometers (62-124 miles).
Waves of greenish-white lights could be seen across the dark sky just after 1830 GMT above the northern Swedish town of Kiruna and within a 200-kilometer radius.
Somewhat less spectacular than the real northern lights, the experiment ended up blocking out a real aurora borealis occurring naturally.
The experiment was part of aurora research aimed at helping scientists improve near-space weather forecasts to protect satellites and critical infrastructures.
"People nowadays cannot imagine life without GPS, without TV, without satellite TV, without mobile phones and so on.
The science of Moon hopping

The videos of the first Moon landing with astronauts bouncing around the lunar surface are looking like a lot of fun - but jumping around on the Moon could also be good for astronaut's muscles, bones and the cardiorespiratory system.
ESA School Days – ESRIN, 13-17 March 2023
 Video:
00:02:20
Video:
00:02:20
In the week of 13-17 March 2023, more than 1400 students attended the ESA School Days event at ESRIN, the ESA Centre for Earth Observation located in Frascati, near Rome, Italy. The students and their teachers, coming from Lazio and other Italian regions, discovered more about ESA and the projects it is involved in, thanks also to creative hands-on labs, a visit to the Earth observation multimedia centre and the launch of rocket models. During the full-day visit, the focus was on themes such as Earth observation, satellites in orbit, ESA launch programmes, asteroid tracking, and how
Media information session from ESA’s 315th Council
 Video:
01:03:07
Video:
01:03:07
Watch the replay of the media information session to hear about further transformation measures and ambitious, new ideas for space exploration following ESA's 315th Council, taking place in the freshly renovated ESA HQ Nikis building in Paris.
ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher and ESA Council Chair Anna Rathsman will cover the following topics: the implementation steps of the results of CM22, including the transformation of ESA to be fit for the future, the Space Summit planned for November 2023, as well as the public release of certain official ESA documents. Moreover, the final report and recommendations of the
Hubble monitors changing weather and seasons on Jupiter and Uranus
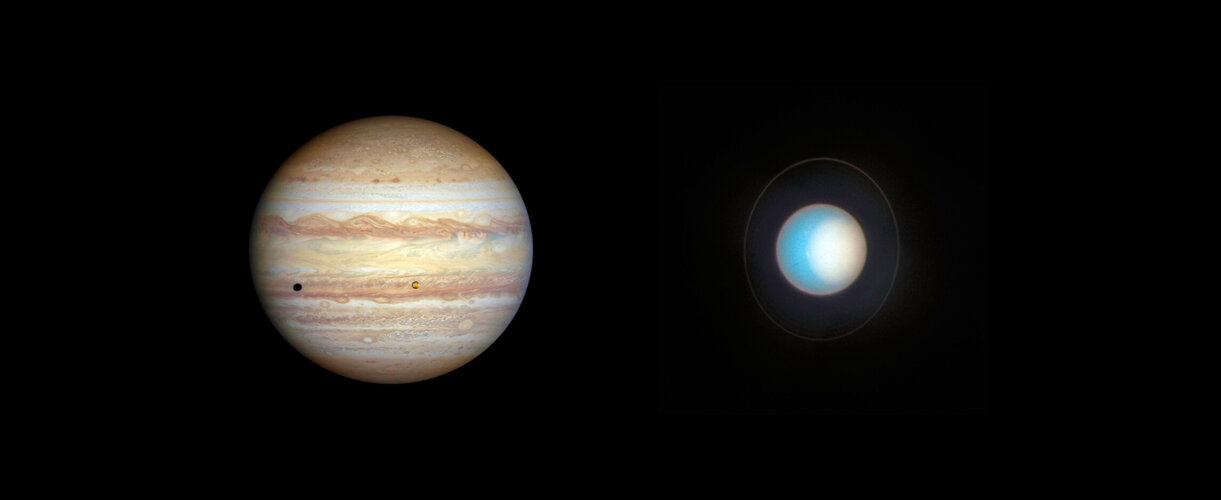

Ever since its launch in 1990, the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has been an interplanetary weather observer, keeping an eye on the ever-changing atmospheres of the largely gaseous outer planets. And it’s an unblinking eye that allows Hubble’s sharpness and sensitivity to monitor a kaleidoscope of complex activities over time. Today new images are shared of Jupiter and Uranus.
Europe’s Spaceport: digitalisation contract opportunities

ESA and CNES invite space and non-space companies from all European Member, Associate and Cooperating States to support the digital modernisation of several activities at Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.
Independent advisory group presents report on European space revolution to ESA


