
Copernical Team
Juice's RIME antenna breaks free
 Over three weeks since the initiation of the deployment process for Juice's Radar for Icy Moons Exploration (RIME) antenna, the 16-meter-long boom has finally been liberated from its mounting bracket.
During the first attempt at stretching out the compacted antenna, only the initial segments of each half were released. The flight controllers theorized that a minuscule stuck pin prevented t
Over three weeks since the initiation of the deployment process for Juice's Radar for Icy Moons Exploration (RIME) antenna, the 16-meter-long boom has finally been liberated from its mounting bracket.
During the first attempt at stretching out the compacted antenna, only the initial segments of each half were released. The flight controllers theorized that a minuscule stuck pin prevented t Cosmonauts wrap up 5-hour ISS spacewalk
 Russian cosmonauts Dmitri Petelin and Sergey Prokopyev concluded their five-hour spacewalk at the International Space Station Friday.
The cosmonauts first spent the day readying their Orlan spacesuits in the Station's Poisk airlock, where they attached batteries, checked for leaks and tested the suits' communications systems.
The pair had completed two previous spacewalks since A
Russian cosmonauts Dmitri Petelin and Sergey Prokopyev concluded their five-hour spacewalk at the International Space Station Friday.
The cosmonauts first spent the day readying their Orlan spacesuits in the Station's Poisk airlock, where they attached batteries, checked for leaks and tested the suits' communications systems.
The pair had completed two previous spacewalks since A Pioneer 11, launched 50 years ago, helped solve mysteries of the universe
 As NASA and private industry prepare for a U.S. return to the moon after more than five decades, observers fondly remember early ventures that traveled deep into interstellar space and sparked excitement about exploring cosmic wonders.
One of the trailblazers was Pioneer 11, a robotic forerunner of such exploration and the first spacecraft to reach Saturn, the ringed and most iconic pla
As NASA and private industry prepare for a U.S. return to the moon after more than five decades, observers fondly remember early ventures that traveled deep into interstellar space and sparked excitement about exploring cosmic wonders.
One of the trailblazers was Pioneer 11, a robotic forerunner of such exploration and the first spacecraft to reach Saturn, the ringed and most iconic pla Stuck antenna freed on Jupiter-bound spacecraft
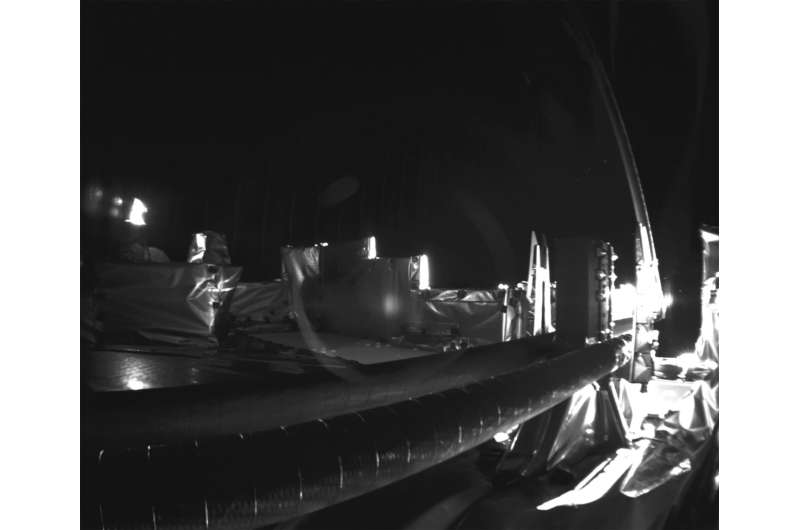

A crucial radar antenna on a European spacecraft bound for Jupiter is no longer jammed.
China has its own secret space plane, and it just landed
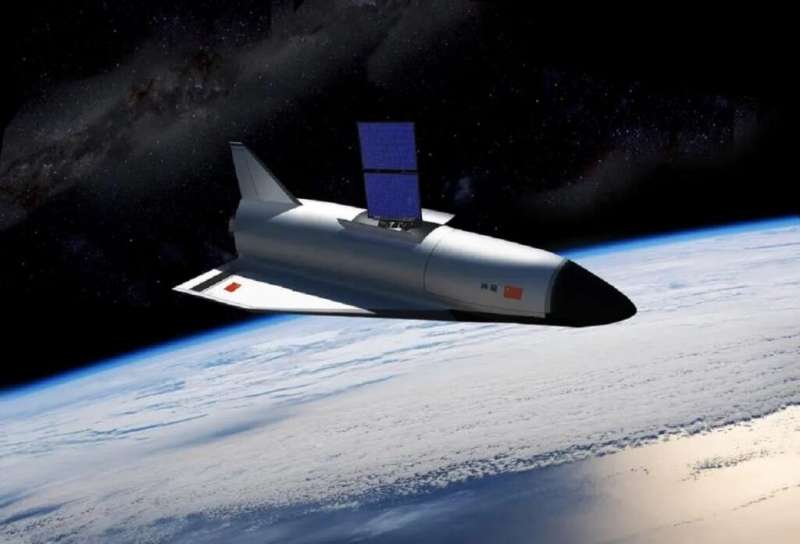

A lot has changed since the last Space Age. Unlike the days of Sputnik, Vostok, Mercury, and Apollo, the current era is not defined by two superpowers constantly vying for dominance and one-upmanship. More than ever, international cooperation is the name of the game, with space agencies coming together to advance common exploration and science goals.
Similarly, there is the way the private space sector has become a major participant, providing everything from launch services and commercial payloads to satellite constellations and crews.
But in some ways, old habits die hard. Since the turn of the century, China has emerged as a major power in space, to the point of becoming a direct competitor with NASA's human space programs. For the past few years, China has been developing a reusable autonomous spaceplane to compete with the X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV).
Known as Shenlong ("divine dragon"), this spaceplane recently concluded its second test flight after spending 276 days in orbit.
Europe's first lunar ‘lamb-bassador’

Last month, ESA’s woolly astronaut became Europe's first lunar ‘lamb-bassador’: Shaun the Sheep returned home from his Artemis I mission to a hero's welcome and then was herded off on a celebratory post-flight tour.
Juice’s RIME antenna breaks free

More than three weeks after efforts began to deploy Juice’s ice-penetrating Radar for Icy Moons Exploration (RIME) antenna, the 16-metre-long boom has finally escaped its mounting bracket.
Week in images: 08-12 May 2023
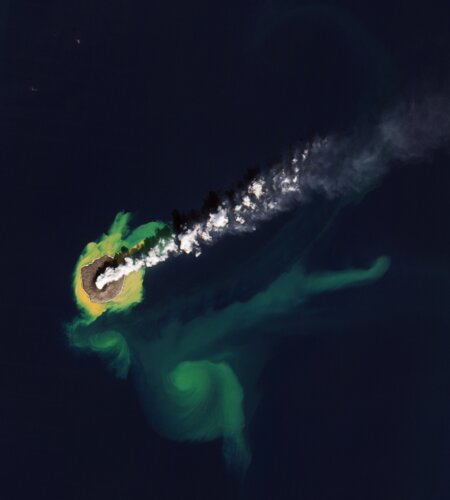
Week in images: 08-12 May 2023
Discover our week through the lens
Ariane 6 joint update report, 12 May 2023

The Ariane 6 Launcher Task Force consists of top management of ESA, launch base prime contractor CNES, launcher system prime contractor ArianeGroup and launch service provider Arianespace. This regular update will follow Task Force meetings, to report on the progress being made towards inaugural flight of the new Ariane 6 launcher.
The next update is expected on or soon after 8 June.
Researchers discover twisted fields around mysterious fast radio burst
 Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) are the brightest millisecond-duration cosmic explosions in radio bands. Their unknown origin poses challenges for astronomy as well as physics.
The Commensal Radio Astronomy FAST Survey (CRAFTS), a key program of the Five-hundred-meter Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), discovered the world's first persistently active repeating FRB, known as FRB 20190520B. Now this
Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) are the brightest millisecond-duration cosmic explosions in radio bands. Their unknown origin poses challenges for astronomy as well as physics.
The Commensal Radio Astronomy FAST Survey (CRAFTS), a key program of the Five-hundred-meter Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), discovered the world's first persistently active repeating FRB, known as FRB 20190520B. Now this 
