
Copernical Team
China scores a big win in race with US for influence on the moon

China notched a diplomatic victory in its race against the U.S. for influence in space, with Egypt agreeing to support Beijing's plan for a proposed project on the moon.
The China National Space Administration on Wednesday signed a memorandum of understanding with the Egyptian Space Agency that will see them cooperate on the International Lunar Research Station, a Chinese-backed base that's expected to begin operation around 2030.
The agreement builds on their collaboration, which saw a Chinese rocket send an Egyptian satellite into orbit from a launch center in the Gobi Desert on Monday.
That launch promotes "a shared future for mankind" and "fully demonstrates China's demeanor as a major country and the principle of extensive consultation, joint contribution, and shared benefits," said Kong Dejun, head of the international economic cooperation department at the Ministry of Commerce, according to a report by state-run broadcaster CCTV.
The new space race is adding to tensions between Beijing and Washington, as both compete to win allies in their plans to send astronauts to the moon in coming years. The agreement between China and Egypt comes just a week after the U.S.
Scholars say it's time to declare a new epoch on the moon, the 'Lunar Anthropocene'
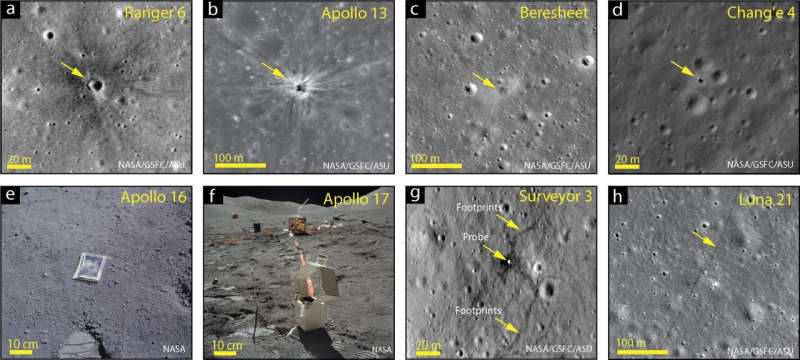
Image: Hubble captures a cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud
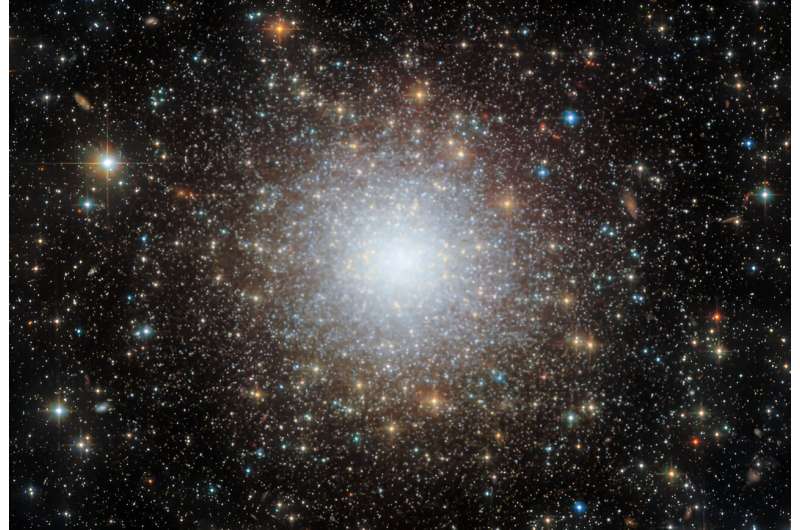

This striking Hubble Space Telescope image shows the densely packed globular cluster known as NGC 2210, which is situated in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). The LMC lies about 157,000 light-years from Earth and is a so-called satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, meaning that the two galaxies are gravitationally bound. Globular clusters are very stable, tightly bound clusters of thousands or even millions of stars. Their stability means that they can last a long time, and therefore globular clusters are often studied to investigate potentially very old stellar populations.
In fact, 2017 research using some of the data that were also used to build this image revealed that a sample of LMC globular clusters were incredibly close in age to some of the oldest stellar clusters found in the Milky Way's halo.
Week in images: 04-08 December 2023

Week in images: 04-08 December 2023
Discover our week through the lens
Earth from Space: Hurricane Otis
 Image:
The powerful Hurricane Otis has been captured in this Copernicus Sentinel-3 image when it was approaching Mexico’s southern Pacific coast in October 2023.
Image:
The powerful Hurricane Otis has been captured in this Copernicus Sentinel-3 image when it was approaching Mexico’s southern Pacific coast in October 2023. Ice's crucial role in planet and comet formation mapped by Webb
 In a significant breakthrough, a Dutch-led international team of astronomers has harnessed the power of the James Webb Space Telescope to create the first comprehensive two-dimensional inventory of ice within a planet-forming disk surrounding a young star. The findings, published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics on December 6, open a new window into the crucial role of ice in the format
In a significant breakthrough, a Dutch-led international team of astronomers has harnessed the power of the James Webb Space Telescope to create the first comprehensive two-dimensional inventory of ice within a planet-forming disk surrounding a young star. The findings, published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics on December 6, open a new window into the crucial role of ice in the format To the moo-n: cow dung fuels Japan's space ambitions
 Japan's space industry opened potentially an udder-ly new chapter on Thursday with a start-up testing a prototype rocket engine that runs on fuel derived purely from a plentiful local source: cow dung.
The experiment saw the engine blast out a blue-and-orange flame 10-15 metres (30-50 feet) horizontally out of an open hangar door for around 10 seconds in the rural northern town of Taiki.
Japan's space industry opened potentially an udder-ly new chapter on Thursday with a start-up testing a prototype rocket engine that runs on fuel derived purely from a plentiful local source: cow dung.
The experiment saw the engine blast out a blue-and-orange flame 10-15 metres (30-50 feet) horizontally out of an open hangar door for around 10 seconds in the rural northern town of Taiki. Iran hails capsule launch as step towards human spaceflight
 Iran has launched a capsule designed to carry living beings in a step towards sending astronauts into space, state media reported Wednesday - the latest test of aerospace technology criticised by the West.
The capsule was successfully sent up to a height of 130 kilometres (80 miles), the IRNA news agency quoted Telecommunications Minister Issa Zarepour as saying.
He said the launch of t
Iran has launched a capsule designed to carry living beings in a step towards sending astronauts into space, state media reported Wednesday - the latest test of aerospace technology criticised by the West.
The capsule was successfully sent up to a height of 130 kilometres (80 miles), the IRNA news agency quoted Telecommunications Minister Issa Zarepour as saying.
He said the launch of t China's Quest for Space-Based Solar Power: A Clean Energy Revolution
 Amid global efforts to transition from fossil fuels to cleaner energy sources, Chinese scientists and engineers are pursuing an innovative solution-harnessing the abundant energy of the sun in space and beaming it back to Earth. Multiple teams in China are currently dedicated to developing the necessary technologies for constructing and operating a space-based solar power facility. This ambitiou
Amid global efforts to transition from fossil fuels to cleaner energy sources, Chinese scientists and engineers are pursuing an innovative solution-harnessing the abundant energy of the sun in space and beaming it back to Earth. Multiple teams in China are currently dedicated to developing the necessary technologies for constructing and operating a space-based solar power facility. This ambitiou Pacific Defense Secures Phase II Contract for Advanced Cislunar Space Sensor
 Pacific Defense, a leader in Modular Open Systems Approach (MOSA) technology, has announced a significant development in cislunar space situational awareness (SSA). The company has been awarded a $9.4 million Phase II contract by the Space Control Technology Branch of the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) to complete the development of a low size, weight, and power (SWaP) sensor. This sensor,
Pacific Defense, a leader in Modular Open Systems Approach (MOSA) technology, has announced a significant development in cislunar space situational awareness (SSA). The company has been awarded a $9.4 million Phase II contract by the Space Control Technology Branch of the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) to complete the development of a low size, weight, and power (SWaP) sensor. This sensor, 
