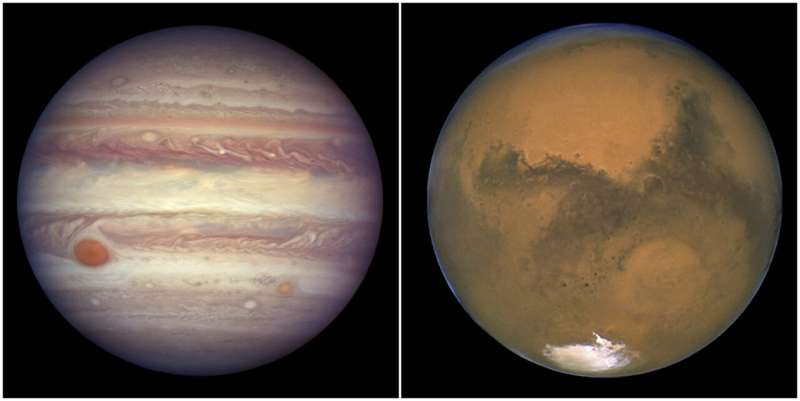
But they won't appear that much different hours or even a day earlier when the sky is dark, said Jon Giorgini of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California.
The best views will be in the eastern sky, toward constellation Taurus, before daybreak. Known as planetary conjunctions, these comic pairings happen only every three years or so.
"Such events are mostly items of curiosity and beauty for those watching the sky, wondering what the two bright objects so close together might be," he said in an email. "The science is in the ability to accurately predict the events years in advance."
Their orbits haven't brought them this close together, one behind the other, since 2018. And it won't happen again until 2033, when they'll get even chummier.
The closest in the past 1,000 years was in 1761, when Mars and Jupiter appeared to the naked eye as a single bright object, according to Giorgini. Looking ahead, the year 2348 will be almost as close.
This latest link up of Mars and Jupiter coincides with the Perseid meteor shower, one of the year's brightest showers. No binoculars or telescopes are needed.
© 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.