More data means more discoveries.
"At 260 megabits per second, O2O is capable of sending down 4K high-definition video from the moon," said Steve Horowitz, O2O project manager. "In addition to video and pictures, O2O will transmit and receive procedures, pictures, flight plans, and be a link between Orion and mission control on Earth."
After gathering data, O2O will send the information over laser signals to one of two ground stations in Las Cruces, New Mexico, or Table Mountain, California—both chosen for their minimal cloud coverage. The quality of images and videos sent from Orion through O2O will depend, in part, on the cloud coverage at the ground stations.
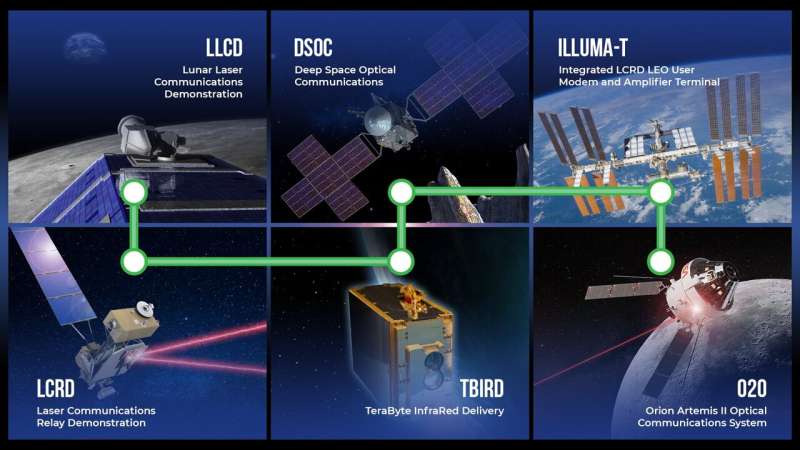
The O2O laser terminal is part of the Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) program's optical infusion effort, which is demonstrating laser communications on multiple missions. O2O was developed by a team of engineers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lincoln Laboratory (MIT-LL). This partnership has successfully led to multiple laser communications missions, such as the 2013 Lunar Laser Communications Demonstration (LLCD), the 2021 Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD), and the 2022 TeraByte InfraRed Delivery (TBIRD) payload. By demonstrating this technology in multiple space regimes, SCaN is showcasing the benefits laser communications can have for missions.
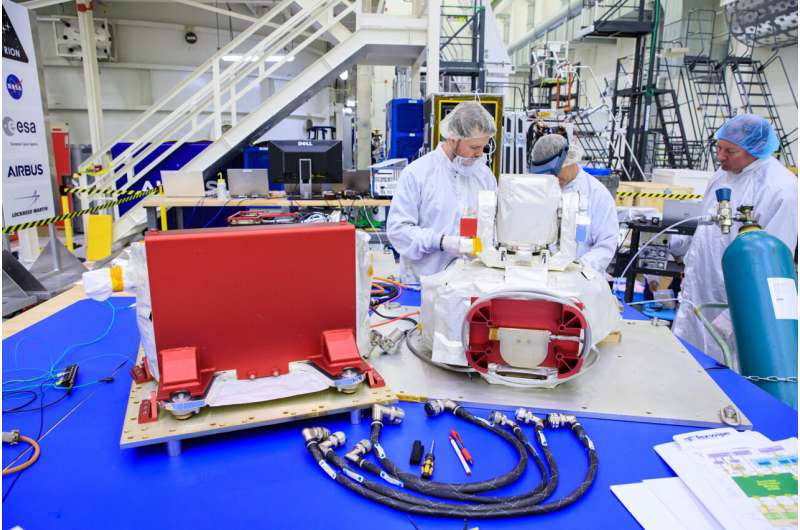
Prior to its delivery to Kennedy, the O2O laser terminal went through several levels of environmental testing to ensure that the payload can operate in the harsh environment of space.
Laser communications terminals like O2O will allow more data to reach Earth and support scientists' efforts to conduct advanced investigations. The data collected by Artemis II will inform NASA's future lunar missions and help the agency establish a long-term presence on the moon and, eventually, Mars.
Provided by NASA



