Environmental Research Letters
Rain-fed pulses of methane from East Africa during 2018–2019 contributed to atmospheric growth rate
| Space News |
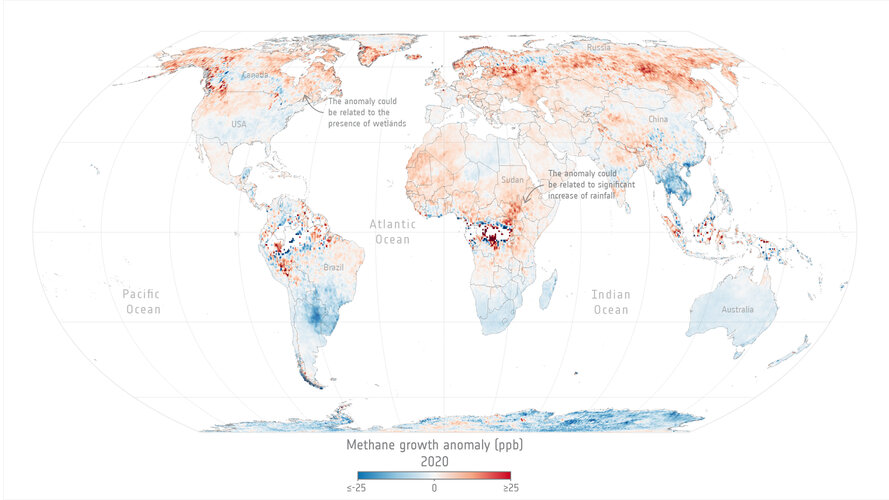
Levels of methane, the second most important greenhouse gas in our atmosphere, continued their unrelenting rise in 2020 despite the economic slowdown caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
A team of scientists, from the University of Leeds, have used data from the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite to pinpoint locations with large surges of methane emissions. These findings were presented during ESA’s Living Planet Symposium which took place last month in Bonn, Germany.
Rain-fed pulses of methane from East Africa during 2018–2019 contributed to atmospheric growth rate