NASA's James Webb Space Telescope team continues to work its way through the 17 science instrument modes. This week they checked off numbers (5) NIRCam grism time series and (4) imaging time series, both used to study exoplanets and other time-variable sources; (12) NIRISS aperture masking interferometry mode, for direct detection of a faint object that is very close to a bright one; (11) NIRISS wide-field slitless spectroscopy, for studying distant galaxies; and (9) NIRSpec bright-object time series, for studying exoplanets. That totals seven modes approved to date, with 10 still to go.
This week, we are featuring MIRI's medium-resolution spectroscopy mode and sharing our first spectroscopic engineering data. We asked two of the MIRI commissioning team members—David Law, of the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI), and Alvaro Labiano, of the Centro de Astrobiologίa (CAB)—to explain this mode to us:
"One of Webb's most complex instrument modes is with the MIRI Medium Resolution Spectrometer (MRS). The MRS is an integral-field spectrograph, which provides spectral and spatial information simultaneously for the entire field of view. The spectrograph provides three-dimensional 'data cubes' in which every pixel in an image contains a unique spectrum. Such spectrographs are extremely powerful tools to study the composition and kinematics of astronomical objects, as they combine the benefits of both traditional imaging and spectroscopy.
"The MRS is designed to have a spectral resolving power (observed wavelength divided by the smallest detectable wavelength difference) of about 3,000. That is high enough to resolve key atomic and molecular features in a variety of environments. At the highest redshifts, the MRS will be able to study hydrogen emission from the first galaxies. At lower redshifts, it will probe molecular hydrocarbon features in dusty nearby galaxies and detect the bright spectral fingerprints of elements such as oxygen, argon, and neon that can tell us about the properties of ionized gas in the interstellar medium. Closer to home, the MRS will produce maps of spectral features due to water ice and simple organic molecules in giant planets in our own solar system and in planet-forming disks around other stars.
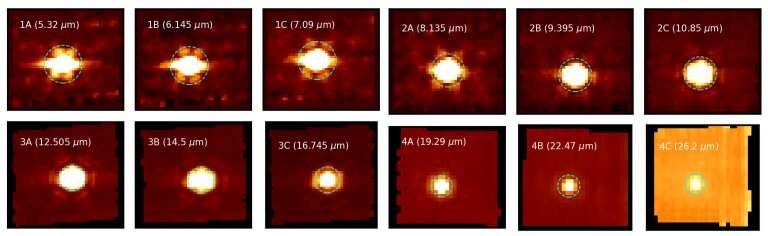
"In order to cover the wide 5 to 28 micron wavelength range as efficiently as possible, the MRS integral field units are broken up into twelve individual wavelength bands, each of which must be calibrated individually. Over the past few weeks, the MIRI team (a large international group of astronomers from the U.S. and Europe) has been focusing primarily on calibrating the imaging components of the MRS. They want to ensure that all twelve bands are spatially well aligned with each other and with the MIRI Imager, so that it can be used to place targets accurately into the smaller MRS field of view. We show some early test results from this alignment process, illustrating the image quality achieved in each of the twelve bands using observations of the bright K giant star HD 37122 (located in the southern sky near the Large Magellanic Cloud).
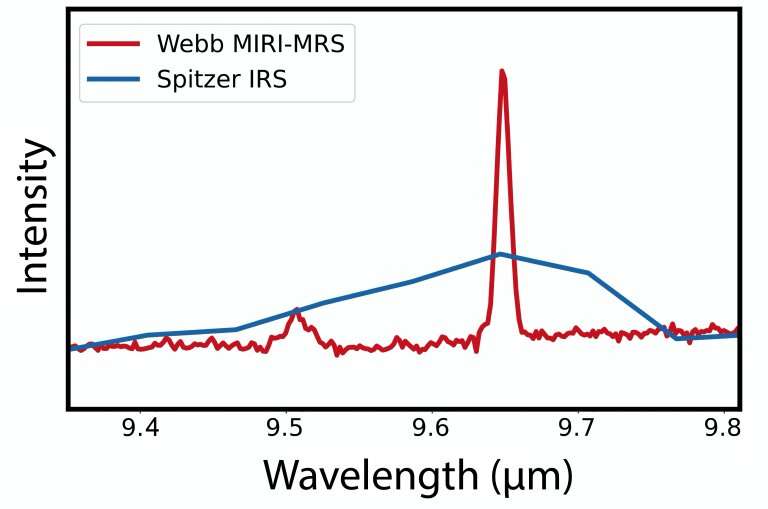
"Once the spatial alignment and image quality of the several bands are well characterized, the MIRI team will prioritize calibrating the spectroscopic response of the instrument. This step will include determining the wavelength solution and spectral resolution throughout each of the twelve fields of view using observations of compact emission-line objects and diffuse planetary nebulae ejected by dying stars. We show the exceptional spectral resolving power of the MRS with a small segment of a spectrum obtained from recent engineering observations of the active galactic nucleus at the core of Seyfert galaxy NGC 6552. Once these basic instrument characteristics are established, it will be possible to calibrate MRS so that it is ready to support the wealth of Cycle 1 science programs due to start in a few short weeks."