Access the video
The DNA of stars
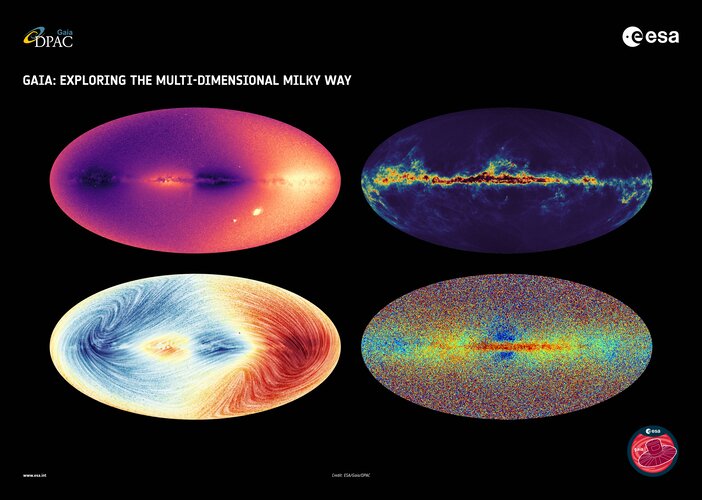
What stars are made of can tell us about their birthplace and their journey afterwards, and therefore about the history of the Milky Way. With today’s data release, Gaia is revealing the largest chemical map of the galaxy coupled to 3D motions, from our solar neigbourhood to smaller galaxies surrounding ours.
Some stars contain more ‘heavy metals’ than others. During the Big Bang, only light elements were formed (hydrogen and helium). All other heavier elements – called metals by astronomers – are built inside stars. When stars die, they release these metals into the gas and dust between the stars called the interstellar medium, out of which new stars form. Active star formation and death will lead to an environment that is richer in metals. Therefore, a star’s chemical composition is a bit like its DNA, giving us crucial information about its origin.
With Gaia, we see that some stars in our galaxy are made of primordial material, while others like our Sun are made of matter enriched by previous generations of stars. Stars that are closer to the centre and plane of our galaxy are richer in metals than stars at larger distances. Gaia also identified stars that originally came from different galaxies than our own, based on their chemical composition.