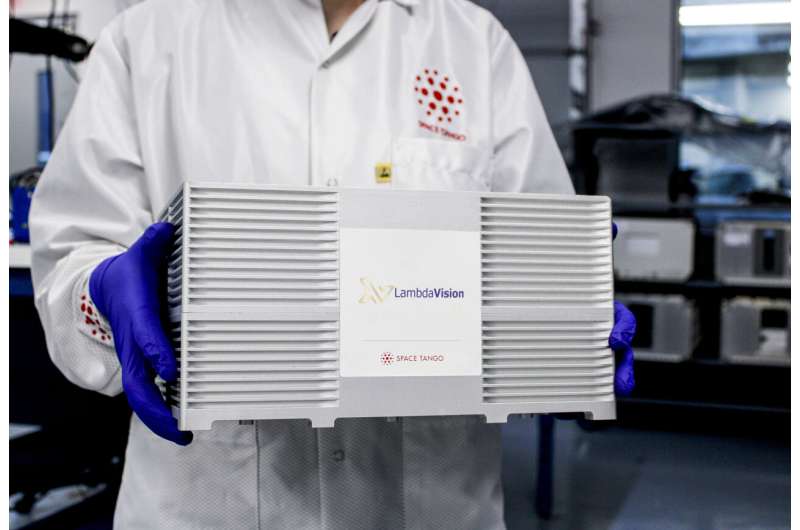
The process creates implants by applying layer after layer of a thin film. Microgravity may improve the quality and stability of the films by limiting the aggregation and sedimentation of particles that occur on Earth. The investigators from U.S.-based company LambdaVision conducted earlier experiments on the space station to determine whether the layering process worked better in microgravity. This investigation builds on that work.
The wonders of wireless
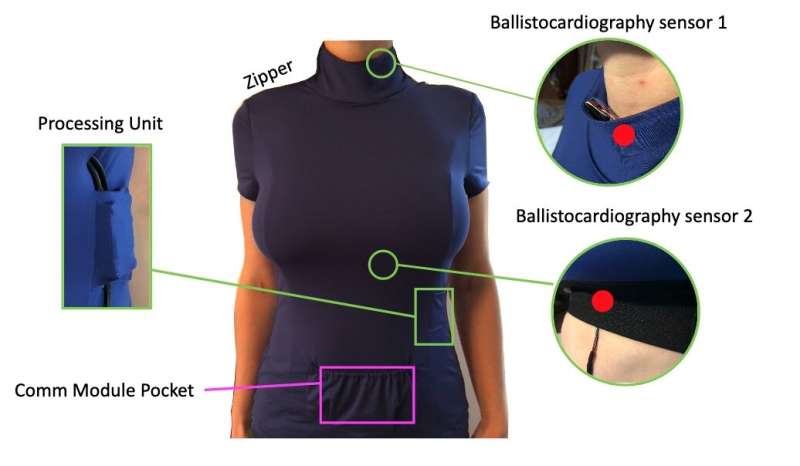
Wireless Compose-2, an investigation from ESA, demonstrates the capabilities of wireless networks to support science experiments and provide precise control and navigation of free-flying objects. One of these free-fliers is Cimon, an artificial intelligence assistant that ESA currently is testing on the space station. Wireless Compose-2 includes operation of a German Space Agency (DLR) experiment, Ballistocardiography for Extraterrestrial Applications and long-Term missions (BEAT), which uses sensors built into a garment to monitor and measure heart parameters such as blood pressure. Normally, scientists can only access these data using sonograms and computer tomography or computerized X-ray imaging. This technology could provide greater insight into performance of the cardiovascular system in space and how it changes during a long-term space mission.
Crew-4 also continues operations for experiments already under way on the space station, including:
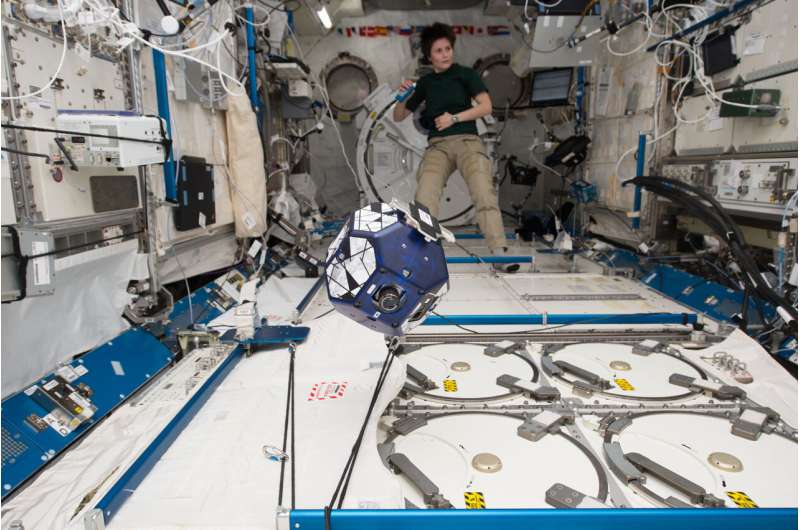

Student software in space
Kibo-RPC allows students to create programs to control an Astrobee, one of the space station's free-flying robots. Sponsored by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), this program provides participants hands-on experience with science, technology, engineering, and mathematics in space, helping to inspire the next generation of explorers. During her previous flight, Cristoforetti worked on a similar student program, SPHERES-VERTIGO. For that investigation, students wrote software to use multiple free-flying satellites to construct 3D models of a target object. The ability to create such models of unknown objects in space using one or two small satellites has potential applications for a wide range of space missions. Listen to Cristoforetti talk about some of the research she conducted on her previous mission.
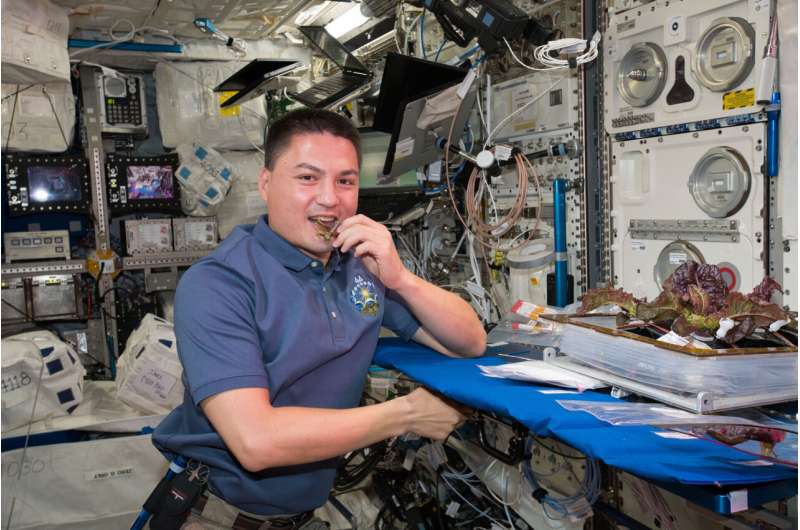

Look Ma, no soil!
XROOTS uses hydroponic (liquid-based) and aeroponic (air-based) techniques to grow plants without soil or other traditional growth media. Investigators plan to use video and still images to evaluate plant growth through the entire life cycle. Current space-based plant systems are small and use particulate media-based systems to deliver water and nutrients. These do not scale up well in space due to mass, containment, maintenance, and sanitation issues. Hydroponic and aeroponic techniques could enable production of crops on a larger scale for future space exploration. The system components developed for this investigation also could enhance cultivation of plants in terrestrial settings such as greenhouses, contributing to better food security for people on Earth. On his previous mission, Lindgren worked on Veg-01, a system that cultivated plants using pillows, small expandable units containing growth medium and seeds. That experiment produced red romaine lettuce, and Lindgren became one of the first people to taste a plant grown in space. Crew-4 members are not expected to eat the XROOTS plants, which will be sent back to Earth for analysis.
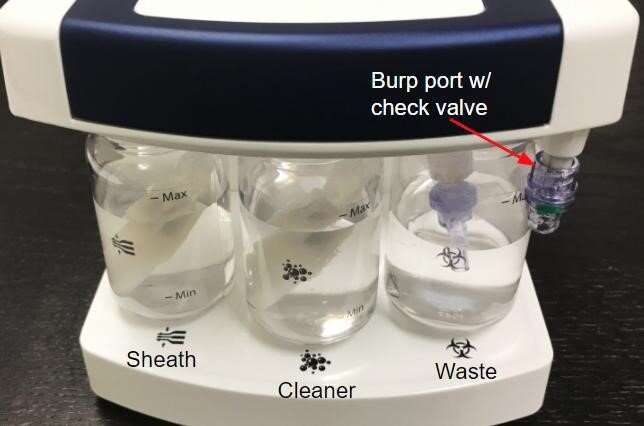

Medical monitoring
Monitoring crew health on deep-space exploration missions presents unique challenges, including limited space for medical devices and the inability to return samples to Earth for analysis. The rHEALTH demonstration tests using a modified, commercial off-the-shelf device to diagnose certain medical conditions. The device uses flow cytometry, a method using lasers to sort and identify cells, and can analyze cell count and cell characteristics; detect microorganisms, biomarkers, and proteins; and diagnose health disorders such as blood cancers. The demonstration verifies that the hardware can function in the space environment and evaluates its accuracy. This technology also could provide timely, cost-effective, reliable, and convenient diagnostic tests for patients on Earth who lack access to robust health-care infrastructure.
Explore further



