In this region of space, it will stay in line with the Earth as it moves around the Sun, allowing Webb's sunshield to protect its sensitive equipment from heat and light.
For the giant parasol to offer effective protection, it needs the Sun, Earth and Moon to all be in the same direction, with the cold side operating at - 370 degrees Fahrenheit (-225 Celsius).
The thruster firing, known as an orbital burn, was the third such maneuver since Webb was launched on an Ariane 5 rocket on December 25.
The plan was intentional, because if Webb had gotten too much thrust from the rocket, it wouldn't be able to turn around to fly back to Earth, as that would expose its optics to the Sun, overheating and destroying them.
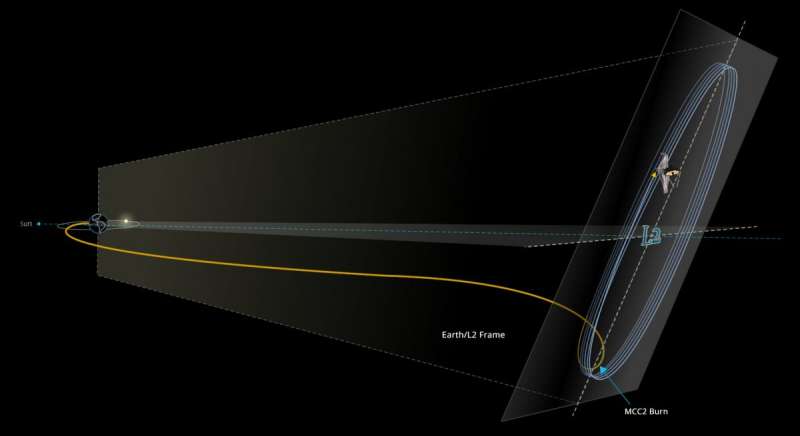
It was therefore decided to slightly underburn the rocket firing and use the telescope's own thrusters to make up the difference.
Webb, which is expected to cost NASA nearly $10 billion, is one of the most expensive scientific platforms ever built, comparable to the Large Hadron Collider at CERN, and its predecessor telescope, Hubble.
Halo orbit
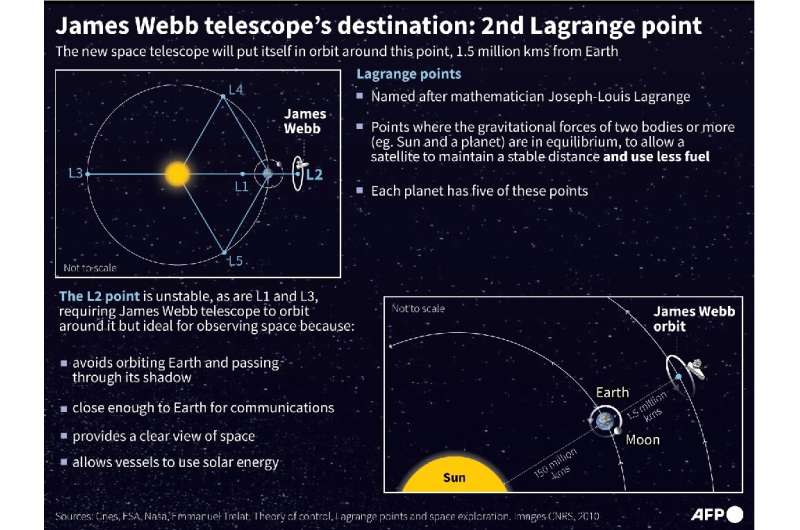
But while Hubble orbits the Earth, Webb will orbit in an area of space known as a Lagrange point, where the gravitational pull from the Sun and Earth will be balanced by the centrifugal force of the rotating system.
An object at one of these five points, first theorized by Italian French mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange, will remain stable and not fall into the gravity well of the Sun and Earth, requiring only a little fuel for adjustments.
Webb won't sit precisely at L2, but rather go around it in a "halo" at a distance similar to the Earth and Moon, completing a cycle every six months.
This will allow the telescope to remain thermally stable and to generate power from its solar panels.
Previous missions to L2 include the European Space Agency's Herschel and Planck observatories, and NASA's Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe.
Webb's position will also allow continuous communications with Earth via the Deep Space Network—three large antennas in Australia, Spain and California.
Earlier this month, NASA completed the process of unfolding Webb's massive golden mirror that will collect infrared signals from the first stars and galaxies that formed 13.5 billion years ago.
Visible and ultraviolet light emitted by the very first luminous objects has been stretched by the Universe's expansion, and arrives today in the form of infrared, which Webb is equipped to detect with unprecedented clarity.
Its mission also includes the study of distant planets, known as exoplanets, to determine their origin, evolution and habitability.
Next steps include aligning the telescope's optics, and calibrating its scientific instruments. It is expected to transmit its first images back in June or July.
Explore further
© 2022 AFP



