ESA’s trifecta of dedicated exoplanet missions – Cheops, Plato and Ariel – will also be complemented with the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope mission.
The Characterising Exoplanet Satellite, Cheops, was launched in December 2019 and is observing bright stars known to host exoplanets, in particular Earth-to-Neptune-sized planets. It is recording the precise sizes of these relatively small planets and combined with mass measurements already calculated from other observatories, will enable the planet's density to be determined, and thus make a first-step characterisation of the nature of these worlds. Cheops will also identify candidates for additional study by future missions. For example, it will provide well-characterised targets for the international James Webb Space Telescope launching in December 2021, which will perform further detailed studies of their atmospheres.
Plato, the PLAnetary Transits and Oscillations of stars mission, is a next-generation planet hunter with an emphasis on the properties of rocky planets in orbits up to the habitable zone around Sun-like stars – the location from a star where liquid water can exist on the planet's surface. Importantly, it will also analyse the planet's host star, including its age, and thus give insight into the evolutionary state of the entire extrasolar system.
Ariel, the Atmospheric Remote-Sensing Infrared Exoplanet Large-survey mission, will perform a chemical census of a large and diverse sample of exoplanets by analysing their atmospheres in great detail, finally answering still open questions like: What are exoplanets made of, how do planets and planetary systems form, and how do planets and their atmospheres evolve?
With the complementary work of both ground- and space-based observatories, we will get closer to understanding one of humanity's biggest questions: are we alone in the Universe?



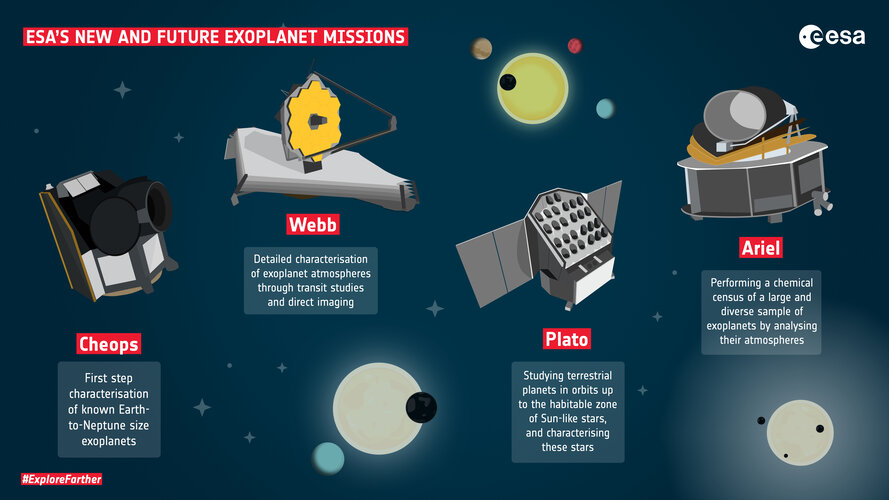 Image:
ESA’s new and future exoplanet missions
Image:
ESA’s new and future exoplanet missions