Unfortunately, we can't just recreate Earth's magnetic field on Mars. Our field is generated by a dynamo effect in Earth's core, where the convection of iron alloys generates Earth's geomagnetic field. The interior of Mars is smaller and cooler, and we can't simply "start it up" to create a magnetic dynamo. But there are a few ways we can create an artificial magnetic field, as a recent study shows.
Ideas for generating a Martian magnetic field have been proposed before, and usually involve either ground-based or orbital solenoids that create some basic level of magnetic protection. In the TV series "The Expanse," you can see a couple of scenes where you catch a glimpse of them. While this latest study acknowledges that might work, it proposes an even better solution.
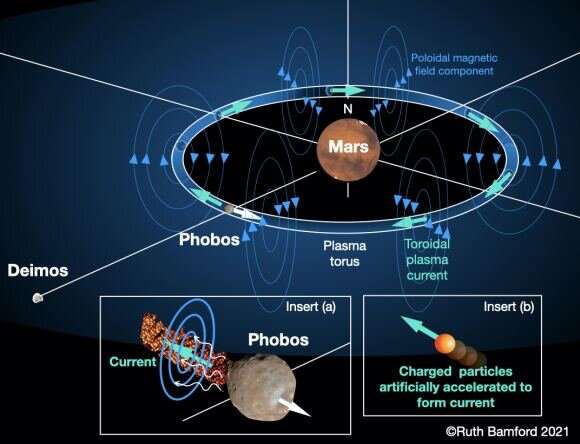
As the study points out, if you want a good planetary magnetic field, what you really need is a strong flow of charged particles, either within the planet or around the planet. Since the former isn't a great option for Mars, the team looks at the latter. It turns out you can create a ring of charged particles around Mars, thanks to its moon Phobos.
Phobos is the larger of the two Martian moons, and it orbits the planet quite closely—so closely that it makes a trip around Mars every eight hours. So the team proposes using Phobos by ionizing particles from its surface, then accelerating them so they create a plasma torus along the orbit of Phobos. This would create a magnetic field strong enough to protect a terraformed Mars.
It's a bold plan, and while it seems achievable, the engineering hurdles would be significant. But as the authors point out, this is the time for ideas. Start thinking about the problems we need to solve, and how we can solve them, so when humanity does reach Mars, we will be ready to put the best ideas to the test.