On approach, a prospective new comet to the inner solar system stands a 40% chance of having its orbit altered by Jupiter. A prime example was long-period comet Hale-Bopp, which had its orbit shortened from 4,200 to 2,533 years during its 1997 perihelion passage. And as recently witnessed (twice!) in the past month, Jupiter also gets frequently smacked by incoming asteroids and comets.
Indeed, a close passage near Jupiter is a gateway into—as well as a ticket out of—the solar system.
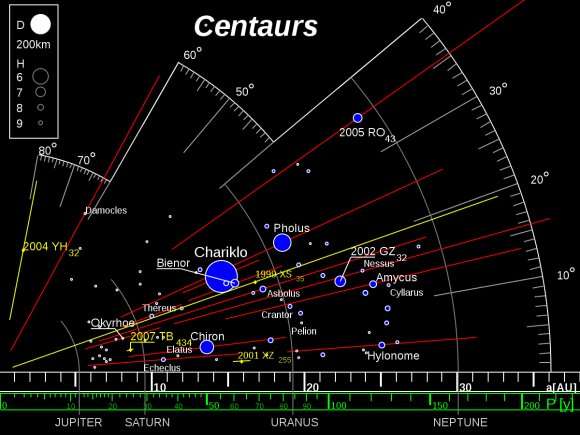
2060 Chiron was the first Centaur asteroid discovered and recognized as such in 1977, followed by 5145 Pholus in 1992. Today, 452 Centaurs are known, ranging from the orbit of Jupiter to Neptune. Clearly, these are intriguing transitional objects in their own right and worthy of study not only as pristine samples of the early primordial solar system, but also as transitional objects between inert icy asteroids and active comets. To get an idea of just how strange Centaurs are, witness the bizarre world of 10199 Chariklo, the only asteroid known to possess a ring system. With orbits crossing those of the main larger planets of the solar system, Centaurs have an average lifespan of only a few million years, which is short, as the multi-billion year history of the solar system goes. And though we haven't visited a Centaur yet per se, we may have gotten a preview of one of these strange objects during flybys of the outer moons of Saturn and the ice giant worlds of Uranus and Neptune during the Voyager 2 mission.

"Centaurs are extremely interesting for many reasons," lead researcher on the study Darryl Seligman (University of Chicago Department of Geophysical Sciences) told Universe Today. "I think the most intriguing aspects of this population is that they will show us the missing link in our understanding of the temporal evolution of the minor bodies in the Solar System. The Centaurs in between the giant planets serve as the source population for the Jupiter family comets, which presumably originate out past Neptune."
The spacecraft in the proposal would literally be a "mission of opportunity," loitering in the orbit of Jupiter until a suitable target drops by. NASA has had similar Discovery Class proposals in the past with the Centaurus and Chimera missions. The European Space Agency's (ESA's) proposed Comet Interceptor would carry out a similar mission plan, loitering at the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point and awaiting a target of opportunity.
Missions such as OSIRIS-Rex and New Horizons have demonstrated the capability to conduct distant asteroid rendezvous, and Juno and the recently launched Lucy mission to the Jupiter Trojans are demonstrating the ability to utilize solar power beyond the asteroid belt.
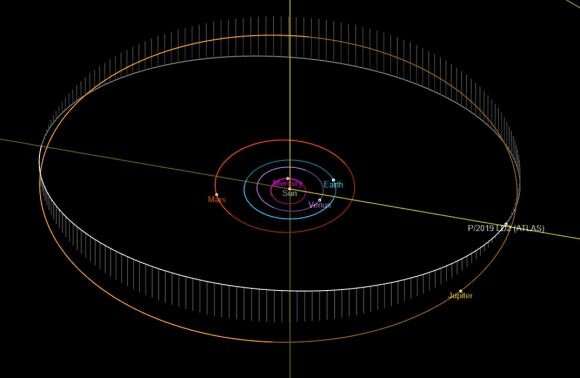
The good news is, we may not have to wait long to catch a short-period comet in the act of formation. One prospect is a recently discovered Centaur that may make the transition to an inner solar system comet over the next century. It is P/2019 LD2 ATLAS, which will make a close pass near Jupiter in 2063 at only 0.016 AU (1.5 million miles or 2.4 million kilometers) distant. Not only would this object make a suitable target, but all-sky surveys such as Vera Rubin set to see first light in 2022 will very probably uncover more potential targets.
"A Centaur mission like the one we are proposing might seem like a wild idea, but it certainly has precedent," says Seligman. "An exciting thing is that it is possible that there may be additional targets that will transition into the inner solar system sooner than LD2, maybe in the next couple of decades. If there are any additional targets that get detected, they will all be reachable for a spacecraft loitering at Jupiter's L2 point, since they all experience a period of low relative velocity with respect to Jupiter."