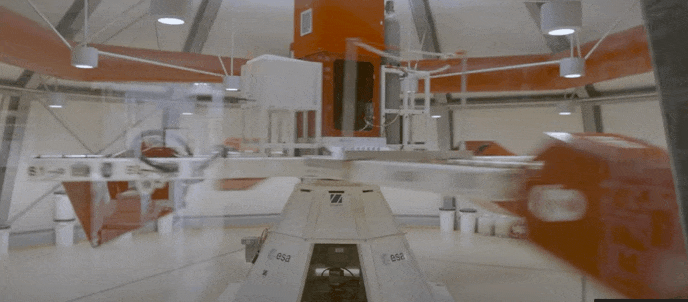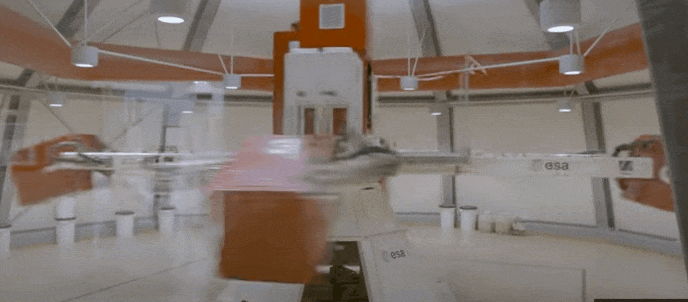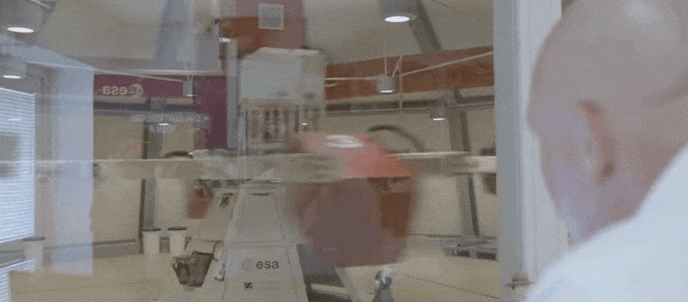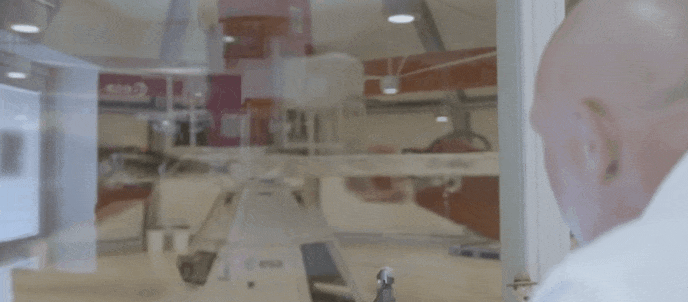
At its fastest, the centrifuge rotates at up to 67 revs per minute, with its six gondolas placed at different points along its arms weighing in at 130 kg, and each capable of accommodating 80 kg of payload.
The result is that researchers are able to increase the force of gravity at the turn of a dial. The LDC is popular with life and physical science teams, as well as for commercial experiments. Internal ESA teams use the centrifuge to see how candidate spacecraft materials and components would respond to the violent accelerations involved in launching into space.
The idea behind this new fellowship is to widen LDC access to teams from all over the world, particularly for teams from developing countries, who may otherwise lack access to such equipment. It is formally known as the ‘United Nations / European Space Agency Fellowship Programme on the Large Diameter Centrifuge Hypergravity Experiment Series’, or HyperGES for short.