At the day side of the planet, facing towards its star, this iron is turned to a gas. It rises in the atmosphere and flows towards the night side.
When this gaseous iron reaches the night side of the planet, where the temperature is cooler, the iron then condenses back into a liquid and falls towards the surface. This is currently the only example we have of a planet with temperatures changes specific enough to allow it to literally rain iron at night.

2. Methane lakes on Titan
Rather than being a planet, Titan is the largest moon of Saturn. It's particularly interesting because it has a substantial atmosphere which is rare for a moon that orbits a planet.
The moon has a surface where liquid flows, like rivers on Earth. Unlike Earth, this liquid isn't water, but a mixture of different hydrocarbons. On Earth we would use these chemicals (ethane and methane) for fuel, but on Titan it's cold enough that they stay liquid and form lakes.
It's thought ice volcanoes sporadically shoot these hydrocarbons into the atmosphere as a gas to form clouds which then condense and form rain. This precipitation is not like the standard showers we might experience on Earth—it only rains about 0.1% of the time, with drops that are bigger (estimated at around 1cm) and fall five times slower, due to reduced gravity and increased drag.

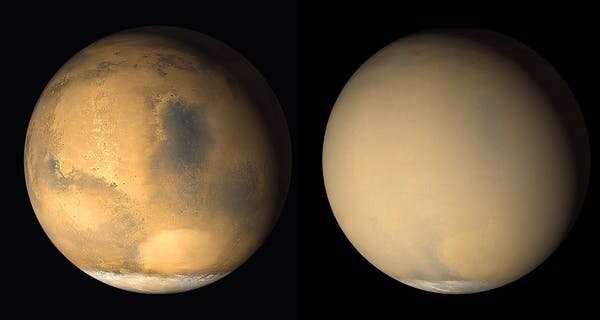
3. Winds on Mars
Mars has a completely different weather system to Earth, mainly because of how dry the planet is and how thin the atmosphere is. Without a significant magnetic field the atmosphere of Mars is open to the magnetic field of the Sun, which strips the upper atmosphere away. This has left a thin atmosphere, comprised mostly of carbon dioxide.
The recent first powered flight on Mars by the Nasa helicopter Ingenuity was amazing—not only for the exploration factor but because rotor blades provide so little lift in the thin atmosphere, which is roughly 2% of that on the Earth's surface. Its counter to this thin atmosphere is a double set of large blades rotating at around 2,500 revolutions per minute, roughly equivalent to a drone rotor speed but much faster than a passenger helicopter.
While the Martian atmosphere is thin, it certainly isn't calm. Average wind speeds of 30 km/h (20 mph) are enough to move the surface material around, and early observations from the Viking lander measured wind speeds up to 110 km/h (70 mph).
The prospect of high-speed sand and dust storms may seem a major issue for exploring the planet, but the atmosphere is thin so the pressure is tiny. For example, the scene in the film The Martian where the rocket blows over simply wouldn't happen. Mars is also famous for having large-scale dust storms which obscure the view of the surface and can last for weeks at a time.
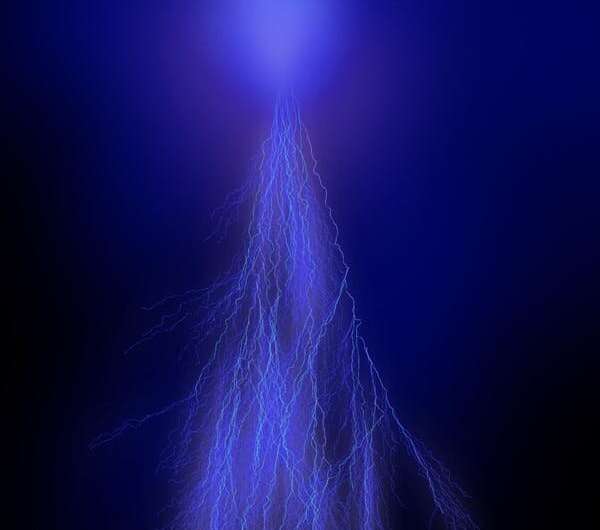
4. Lightning on Jupiter
In 1979, Voyager 1 flew past Jupiter and saw lightning strikes. Then in 2016, the Juno mission performed an in depth look at lightning storms on Jupiter.
On the Earth, most of the lightning is concentrated near the equator. But on Jupiter the stability of the atmosphere means most convection and turbulence occurs near the polar regions, which is where the lightning strikes mainly happen. Instead of the Earth-based lightning generation method of supercooled water droplets colliding with ice, on Jupiter, a charge builds up in snowballs of ammonia. This ammonia acts as an antifreeze for the water, keeping it liquid at much higher altitudes.
Jupiter even has less commonly known lightning called sprites and elves. Sprites are formed from lightning which rises from the clouds towards the upper atmosphere and creates a short-lived reddish glow, while elves are rings formed when the lightning strike reaching the charged part of our atmosphere (the ionosphere). These were predicted in 1921, but were not photographed on Earth until 1989, mainly due to storm clouds being in the way.
These so-called transient luminous events have now been observed on Jupiter as well , providing important information on the Jovian atmosphere as well as how these lightning formations are created and sustained.

While there are many different possibilities for weather on exoplanets, the biggest challenge is observing them in enough detail to identify what their atmosphere—if they have one—is comprised of.
The next discovery of an exoplanet weather system could be Earth-like, it could be similar to one of the examples above, or it could be something even more incredible.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()



