The team's first thought was to eliminate other sources that could have caused the spike. First they eliminated the aurora they were searching for as part of their normal research. This area of the planet where the spike appeared on was outside the normal bounds of the auroras they studied.
Next they sought to understand whether it might have been a transient luminous event (TLE) that had popped up in their data previously. These TLEs, commonly known by the whimsical names of "elves" or "sprites," are thought to be instances of lightning in Jupiter's upper atmosphere. While they have been seen in the same general area of the event, TLEs are similar to auroras in terms of their spectral profile, and none had ever been seen that was anywhere near the size or scale of the event UVS captured this time.

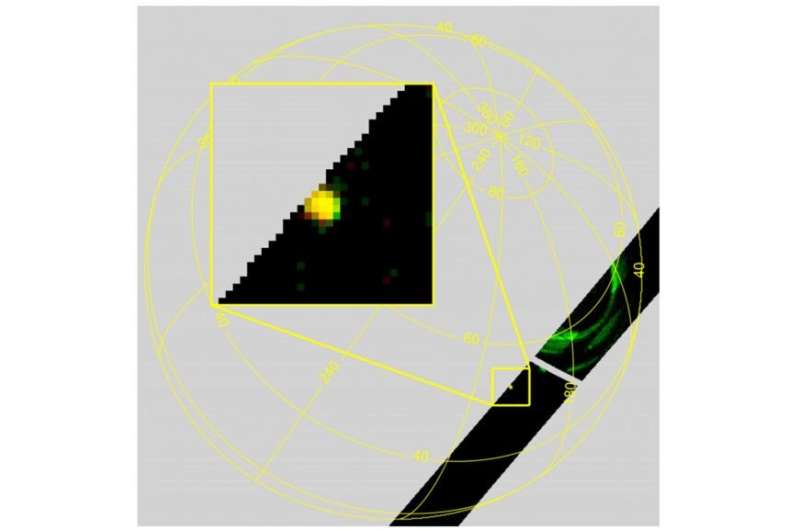
One final check required an understanding of whether the data was an artifact from the instrumentation itself. But there were many photons clustered together in one particular spatial area, making it highly unlikely that it was an artifact. If the signal was, in fact, caused by instrumentation error, it would be much more likely to be random rather than spatially concentrated the way that it was.
Through this process of elimination, and Occam's razor, it seems the team happened upon a sighting of a meteor hitting Jupiter's atmosphere. This is not the first time that astronomers have noted such an event—the most famous occurrence being comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 which impacted Jupiter in 1994. However, this is the first detection from Juno, which has been in orbit around the planet since 2016.
One advantage Juno has over previous observational efforts is that due to its proximity, it is able to detect much smaller impactors. The scientists estimate that the object they observed weighed anywhere between 250 and 5,000 kg. They also estimate that there are approximately 24,000 impacts of a similar size on Jupiter each year.

That many impacts seems like a lot considering that Juno has been in orbit for almost four and a half years, and has only found one. However, in all that time in orbit, the observational time on each individual area of the planet is less than you might think. Orbital mechanics and spacecraft stabilization techniques have huge impacts on the amount of time that UVS is able to collect data.
Juno is in an elliptical orbit around Jupiter, and only passes the planet at its closest point (known as a "perijove") once every 53 days. During each perijove, the UVS is only able to take data for approximately 10 hours. Making things even more complicated, radiation wreaks havoc with the sensor, so if the spacecraft happens to be passing through a particularly high radiation area, it is unable to collect useful data.

But that's not all—Juno itself is actually rotating, which is a way of stabilizing the spacecraft's orbit. It rotates approximately once every thirty seconds, and since the UVS is placed on one side of the spacecraft, it is only able to collect data for about 7 seconds each spacecraft rotation, if Juno is at its closest approach point.
All this rotating, orbiting and radiation navigating adds up to very little coverage over the four-year mission. With this small slice of observational time, the spacecraft still managed to capture this spectacular image of a reentry. And with a simple bit of statistics, the team has calculated that there are likely thousands more to detect each year, if Juno or another spacecraft or telescope happens to be looking the right way.
Capturing another such event would both lend credence to the theory that this event was actually a bolide (the technical name for these impactors). Additionally, it would allow the team to better calculate the total number of impacts suggested, and therefore, a rough estimate of the total amount of material added to Jupiter's mass every year.
No matter how many coincidental impacts it captures, the UVS will continue scanning for the aurora and providing great data on that spectacular light show. If it happens to catch another impact, as well, it will be another great instance of fortuitous timing playing a role in great science.



