
Copernical Team
Astronomers scan the center of the Milky Way for any sign of intelligent civilizations, find nothing but silence

Are there civilizations somewhere else in the universe? Somewhere else in the Milky Way? That's one of our overarching questions, and an answer in the affirmative would be profound.
Humanity has pursued the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) in one form or another since shortly after the advent of radio waves in the early 20th century. Efforts have waxed and waned over the decades, but the search has never been completely abandoned.
The search detected transient hints in the form of unexplained radio waves in the past, but nothing that comprises reliable evidence.
Microgravity worms help solve astronauts' muscle troubles
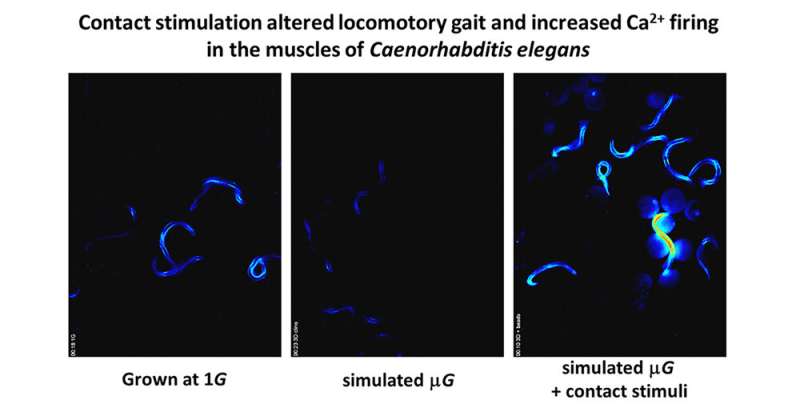
A new study on nematode worms reveals that physical contact with objects can help prevent neuromuscular decline in simulated microgravity. The research, which was published in the journal iScience, provides new insights into maintaining human health in space.
Over the past 60 years, hundreds of humans have flown into space, sometimes spending up to a year on the International Space Station. Spaceflight subjects the body to near weightlessness or microgravity, which can negatively impact health.
"Progressive neuromuscular decline in microgravity is a major health concern for humans spending time in space," explains Atsushi Higashitani, a molecular biologist at Tohoku University. "Our international team investigated the underlying reasons for these changes."
The researchers studied Caenorhabditis elegans, a nematode worm that shows similar molecular and physiological effects to humans during spaceflight, including impaired muscle performance and reduced body length.
Virgin Galactic re-opens ticket sales for $450,000

Virgin Galactic, which last year flew its flamboyant founder Richard Branson to space, will re-open ticket sales to the general public starting Wednesday, for the sum of $450,000.
Previously, only people who had paid a deposit to be on a waiting list could buy new tickets—but now sales are once more open to everyone.
"We plan to have our first 1,000 customers on board at the start of commercial service later this year, providing an incredibly strong foundation as we begin regular operations and scale our fleet," said CEO Michael Colglazier in a statement.
Established in 2004, Virgin Galactic is looking to build on the success of a high profile test mission last July, which saw Branson beat Blue Origin founder Jeff Bezos in their billionaire space race by a few days.
Deep down temperature shifts give rise to eruptions
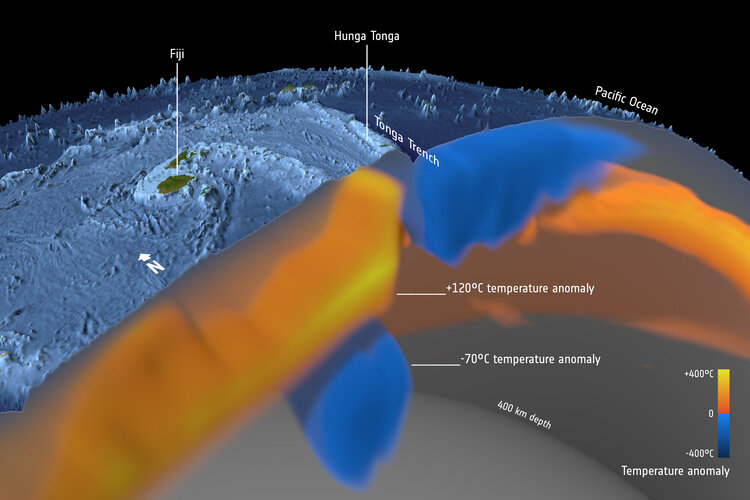
The astonishing force of the Tonga volcanic eruption shocked the world, but the fact that this underwater volcano actually erupted came as less of a surprise to geoscientists using satellite data to study changes in the temperature deep below Earth’s surface.
Watch live coverage of Space Summit

European leaders will reaffirm plans to launch Europe on a world-leading trajectory during a high-level space summit being held on 16 February in Toulouse, France. Join us for live coverage on ESA Web TV, starting at 12:45 CET.
Taiwan researchers join ISRO in satellite launch mission for first time
 The launch of the Earth Observation Satellite (EOS-04), scheduled for September 2021, was delayed due to the pandemic as engineers and scientists were working remotely. However, to make up for the delay, the Indian space agency has planned 19 missions, including a Moon landing, in 2022.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on Monday launched a satellite, INSPIRESat-1, jointly deve
The launch of the Earth Observation Satellite (EOS-04), scheduled for September 2021, was delayed due to the pandemic as engineers and scientists were working remotely. However, to make up for the delay, the Indian space agency has planned 19 missions, including a Moon landing, in 2022.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on Monday launched a satellite, INSPIRESat-1, jointly deve Moon should be privatised to end global poverty says 'Space Invaders' report
 The protection of the Moon is clearly stated in the 1967 Outer Space Treaty (OST) - an international document that prohibits any state to appropriate the space rock or other celestial bodies.
Researchers from the Adam Smith Institute, a British neoliberal think tank, have suggested that dividing the Moon into regions and privatising it can help end global poverty. However, there is a twist
The protection of the Moon is clearly stated in the 1967 Outer Space Treaty (OST) - an international document that prohibits any state to appropriate the space rock or other celestial bodies.
Researchers from the Adam Smith Institute, a British neoliberal think tank, have suggested that dividing the Moon into regions and privatising it can help end global poverty. However, there is a twist Innovation by the dozen: ESA funds 12 OPS-SAT experiments

ESA's OPS-SAT is a Swiss army knife in orbit. The 30-cm CubeSat packs a powerful onboard computer and an array of instruments that make it the ideal laboratory for testing innovative new technologies in space.
Thanks to the ESA Discovery programme, 12 new experiments will be doing just that, as they develop software, concepts and protocols that push the robust CubeSat to its limits and that could one day be essential parts of future spacecraft missions.
NASA's MinXSS instrument CubeSat launches to study sun's flares
The Miniature X-Ray Solar Spectrometer 3, or MinXSS-3, successfully launched on the InspireSat-1 small satellite at 7:29 p.m. EST on Feb. 13, 2022. Also known as the Dual Aperture X-ray Solar Spectrometer, or DAXSS, it is the third of three NASA-funded MinXSS CubeSats. It will spend up to a year in low-Earth orbit studying X-rays coming from flares on the sun.
The sun sometimes releases flares, which are energetic bursts of light and particles triggered by the release of magnetic energy on the sun that travel across the solar system. X-rays emitted by the sun during intense flares can interfere with GPS, radio, and other communications signals when they reach Earth. MinXSS will study the energetics of these flares in wavelengths known as soft X-rays, which are particularly impactful on Earth's ionosphere—an electrified upper layer of the atmosphere where communications signals travel.
New Tool Launches for Astronomy Software Users
 The American Astronomical Society (AAS) and partnering organizations Zenodo and the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS) has announced the launch of the Asclepias portal and broker, resources that connect software tools with scientific results to make research progress in astronomy faster, more open, and more reproducible.
Astronomers rely on scientific software to analyze data sets and
The American Astronomical Society (AAS) and partnering organizations Zenodo and the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS) has announced the launch of the Asclepias portal and broker, resources that connect software tools with scientific results to make research progress in astronomy faster, more open, and more reproducible.
Astronomers rely on scientific software to analyze data sets and 