Save Freedom: We must stop the destruction of the International Space Station
Tuesday, 02 July 2024 12:00
How the Applied Physics Laboratory is tackling Artemis moon exploration
Tuesday, 02 July 2024 12:00

Orbit Fab completes ground test of satellite fueling payload
Tuesday, 02 July 2024 10:15

New satellite to show how AI advances Earth observation
Tuesday, 02 July 2024 07:10
Artificial intelligence technologies have achieved remarkable successes and continue to show their value as backbones in scientific research and real-world applications.
ESA’s new Φsat-2 mission, launching in the coming weeks, will push the boundaries of AI for Earth observation – demonstrating the transformative potential of AI for space technology.
Determining the safest Mars caves for future astronauts
Monday, 01 July 2024 18:10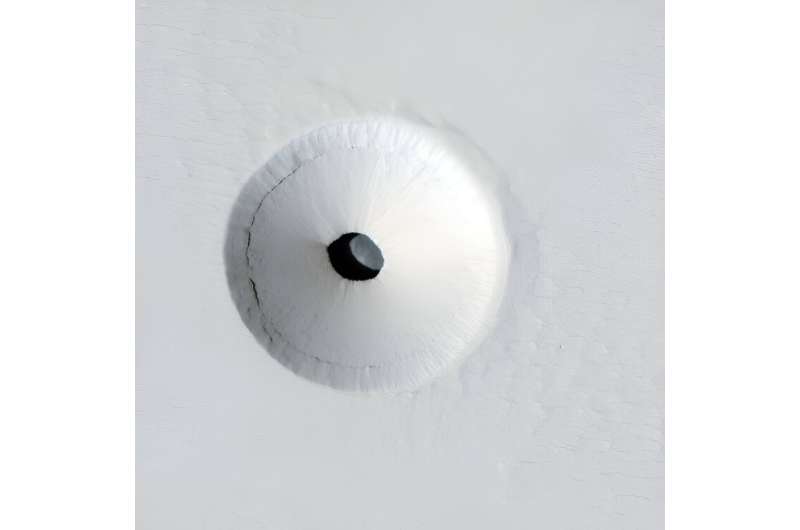
When astronauts land on Mars someday, they might have to live in lava caves or lava tubes to survive the harsh radiation that rains down on the Martian surface every second. But which caves could offer them the best chance of survival?
This is what a recent study presented at the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference hopes to address as Dr. Anatoliy P. Vidmachenko from the National University of Life and Environmental Sciences of Ukraine investigated where, how, and why lava tubes and lava caves could aid future Mars astronauts regarding their survival.
This study holds the potential to help scientists and engineers help mitigate risks for future Mars astronauts and what steps that need to be taken to make that a reality.
NASA shares two new Moon to Mars architecture white papers
Monday, 01 July 2024 17:54
NASA has released two white papers associated with the agency's Moon to Mars architecture efforts. The papers, one on lunar mobility drivers and needs, and one on lunar surface cargo, detail NASA's latest thinking on specific areas of its lunar exploration strategy.
While NASA has established a yearly cadence of releasing new documents associated with its Moon to Mars architecture, the agency occasionally releases mid-cycle findings to share essential information in areas of interest for its stakeholders.
Chinese rocket takes off during test, causing local fire
Monday, 01 July 2024 16:40 Beijing: Space Pioneer, a Chinese aerospace company, experienced an accidental rocket launch during a developmental test in Gongyi, central China.
Beijing Tianbing Technology Co, also known as Space Pioneer, reported that the first stage of its Tianlong-3 rocket detached from the launch pad during a structural failure test. Initial investigations revealed no casualties, according to the co
Beijing: Space Pioneer, a Chinese aerospace company, experienced an accidental rocket launch during a developmental test in Gongyi, central China.
Beijing Tianbing Technology Co, also known as Space Pioneer, reported that the first stage of its Tianlong-3 rocket detached from the launch pad during a structural failure test. Initial investigations revealed no casualties, according to the co Samples from Lunar Far Side thicker and stickier
Monday, 01 July 2024 16:40 China's Chang'e 6 robotic probe has successfully retrieved 1,935.3 grams of lunar samples from the moon's far side, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) announced Friday morning. These samples, now in the hands of scientists, are considered scientifically invaluable.
The weight of the samples, eagerly anticipated by the scientific community, was disclosed during a handover ceremo
China's Chang'e 6 robotic probe has successfully retrieved 1,935.3 grams of lunar samples from the moon's far side, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) announced Friday morning. These samples, now in the hands of scientists, are considered scientifically invaluable.
The weight of the samples, eagerly anticipated by the scientific community, was disclosed during a handover ceremo Nanomedicine Promises Cure for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Monday, 01 July 2024 16:40 One of most lethal forms of cancer, Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PADC), has been classed on wrong side of chemosensitivity scale- those varieties that are very resistant to chemotherapy. The prognosis for PADC diagnosed at a late stage is poor, with a 5-year survival of less than 10%. However, nanomedicine may actually help constitute a plausible avenue for improving effectiveness of PADC t
One of most lethal forms of cancer, Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PADC), has been classed on wrong side of chemosensitivity scale- those varieties that are very resistant to chemotherapy. The prognosis for PADC diagnosed at a late stage is poor, with a 5-year survival of less than 10%. However, nanomedicine may actually help constitute a plausible avenue for improving effectiveness of PADC t A desert moss that has the potential to grow on Mars
Monday, 01 July 2024 12:52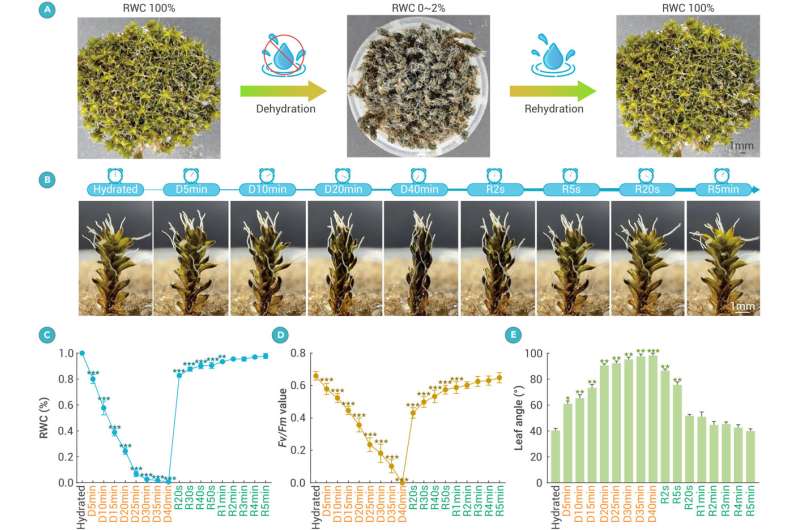
The desert moss Syntrichia caninervis is a promising candidate for Mars colonization thanks to its extreme ability to tolerate harsh conditions lethal to most life forms. The moss is well known for its ability to tolerate drought conditions, but researchers report in the journal The Innovation that it can also survive freezing temperatures as low as −196°C, high levels of gamma radiation, and simulated Martian conditions involving these three stressors combined. In all cases, prior dehydration seemed to help the plants cope.
"Our study shows that the environmental resilience of S. caninervis is superior to that of some of highly stress-tolerant microorganisms and tardigrades," write the researchers, who include ecologists Daoyuan Zhang and Yuanming Zhang and botanist Tingyun Kuang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
"S. caninervis is a promising candidate pioneer plant for colonizing extraterrestrial environments, laying the foundation for building biologically sustainable human habitats beyond Earth.
ESA astronaut class of 2022: Astro Chat with Katherine Bennell-Pegg
Monday, 01 July 2024 12:30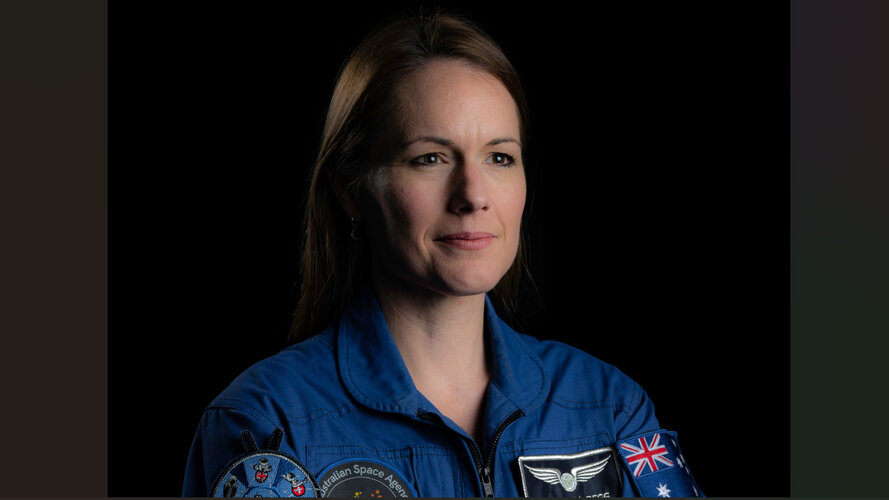 Video:
00:38:43
Video:
00:38:43
Australian Space Agency astronaut candidate Katherine Bennell-Pegg joined ESA’s astronaut candidates from the class of 2022 for basic training through a cooperation agreement with ESA. Tune in as she shares her experiences in astronaut training, her favourite lessons, and what keeps her inspired on her journey to the stars!
This is episode 7 of our ESA Explores podcast series introducing the ESA astronaut class of 2022, recorded in March 2024.
Find out more about the ESA astronaut class of 2022.
Turion wins Space Force contract for debris-capture technology
Monday, 01 July 2024 12:03





