
Copernical Team
LISA mission moves to final design phase
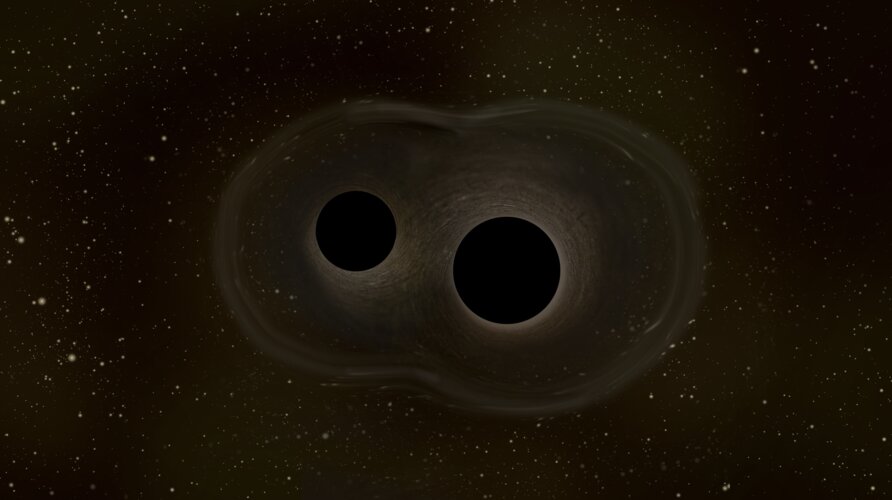

ESA’s Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) passed an important review that marks the mission as feasible for final technology development and design before adoption.
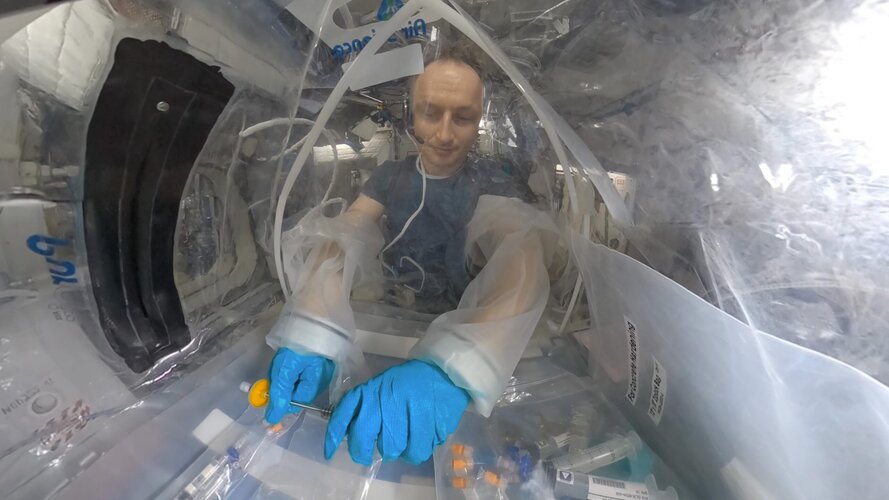
Concrete Hardening | Cosmic Kiss 360°
 Video:
00:02:47
Video:
00:02:47
Take a look inside the box and join ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer from a very special perspective as he supports the @DLR Mason/Concrete Hardening experiment.
The Concrete Hardening experiment investigates the behaviour of various concrete mixtures containing cement and sand or simulated ‘Moon dust’ combined with water and various admixtures. On Earth, higher density components tend to move downward but in weightlessness they are likely to be more evenly distributed.
Researchers will analyse the concrete mixed by Matthias in space for strength, bubble and pore distribution as well as crystal structures, comparing this to ground samples. Their findings will
NASA visualization rounds up the best-known black hole systems
 Nearby black holes and their stellar companions form an astrophysical rogues' gallery in this new NASA visualization.
Stars born with more than about 20 times the Sun's mass end their lives as black holes. As the name implies, black holes don't glow on their own because nothing can escape them, not even light. Until 2015, when astronomers first detected merging black holes through the spac
Nearby black holes and their stellar companions form an astrophysical rogues' gallery in this new NASA visualization.
Stars born with more than about 20 times the Sun's mass end their lives as black holes. As the name implies, black holes don't glow on their own because nothing can escape them, not even light. Until 2015, when astronomers first detected merging black holes through the spac SwRI-led team finds younger exoplanets better candidates when looking for other Earths
 As the scientific community searches for worlds orbiting nearby stars that could potentially harbor life, new Southwest Research Institute-led research suggests that younger rocky exoplanets are more likely to support temperate, Earth-like climates.
In the past, scientists have focused on planets situated within a star's habitable zone, where it is neither too hot nor too cold for liquid s
As the scientific community searches for worlds orbiting nearby stars that could potentially harbor life, new Southwest Research Institute-led research suggests that younger rocky exoplanets are more likely to support temperate, Earth-like climates.
In the past, scientists have focused on planets situated within a star's habitable zone, where it is neither too hot nor too cold for liquid s NASA Goddard scientists begin studying 50-year-old frozen Apollo 17 samples
 Scientists at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, recently received samples of the lunar surface that have been curated in a freezer at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston since Apollo 17 astronauts returned them to Earth in December 1972.
This research is part of the Apollo Next Generation Sample Analysis Program, or ANGSA, an eff
Scientists at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, recently received samples of the lunar surface that have been curated in a freezer at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston since Apollo 17 astronauts returned them to Earth in December 1972.
This research is part of the Apollo Next Generation Sample Analysis Program, or ANGSA, an eff Racks in the sand from about a hundred sols ago Sol 3463
 On sol 3415 we encountered what we unofficially dubbed 'Gator Back' terrain and decided to not fight the "creature" on the expense of our wheels but rather to turn around and go back. For those of you who like looking back into the events: the first encounter with that terrain that made us turn around was reported here on the blog on sols 3419-3420, blog 3421 showed a beautiful close up of the "
On sol 3415 we encountered what we unofficially dubbed 'Gator Back' terrain and decided to not fight the "creature" on the expense of our wheels but rather to turn around and go back. For those of you who like looking back into the events: the first encounter with that terrain that made us turn around was reported here on the blog on sols 3419-3420, blog 3421 showed a beautiful close up of the " Meteor showers to bookend overnight skywatching opportunities in May
 As the spring season continues, May could prove to be of great interest for stargazers and space enthusiasts - with a pair of potentially active meteor showers opening and closing the month.
"Meteors aren't uncommon," Bill Cooke said, who leads NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. "Earth is bombarded every day by millions of bit
As the spring season continues, May could prove to be of great interest for stargazers and space enthusiasts - with a pair of potentially active meteor showers opening and closing the month.
"Meteors aren't uncommon," Bill Cooke said, who leads NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. "Earth is bombarded every day by millions of bit UNC blood clot expert working with NASA to study blood and clots in zero gravity
 Are astronauts more likely to develop blood clots during space missions due to zero gravity? That's the question NASA is trying to answer with help from UNC School of Medicine's Stephan Moll, MD, professor in the UNC Department of Medicine. A new publication in Vascular Medicine shows the results of an occupational surveillance program spurred by the development of a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) i
Are astronauts more likely to develop blood clots during space missions due to zero gravity? That's the question NASA is trying to answer with help from UNC School of Medicine's Stephan Moll, MD, professor in the UNC Department of Medicine. A new publication in Vascular Medicine shows the results of an occupational surveillance program spurred by the development of a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) i BRICS forum on big data for sustainable development held in Beijing
 The BRICS Forum on Big Data for Sustainable Development was held both in Beijing and online on April 26, 2022. The two-day event was hosted by Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Academy of Science of South Africa, Brazilian Academy of Sciences, Russian Academy of Sciences, and Indian National Science Academy.
The forum was proposed by Chinese President Xi Jinping during his remarks at the
The BRICS Forum on Big Data for Sustainable Development was held both in Beijing and online on April 26, 2022. The two-day event was hosted by Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Academy of Science of South Africa, Brazilian Academy of Sciences, Russian Academy of Sciences, and Indian National Science Academy.
The forum was proposed by Chinese President Xi Jinping during his remarks at the GomSpace to supply mission control system for KSAT Arctic satellites
 GomSpace to deliver the Mission Control System that KSAT will use to operate the Arctic Weather Satellite
Today, GomSpace signed a contract to develop, deliver and support the Mission Control System that KSAT will use to operate the Arctic Weather Satellite mission.
The contract value is 10 MSEK and the majority of work will be done this year and next year.
The Arctic Weather S
GomSpace to deliver the Mission Control System that KSAT will use to operate the Arctic Weather Satellite
Today, GomSpace signed a contract to develop, deliver and support the Mission Control System that KSAT will use to operate the Arctic Weather Satellite mission.
The contract value is 10 MSEK and the majority of work will be done this year and next year.
The Arctic Weather S 
