
Copernical Team
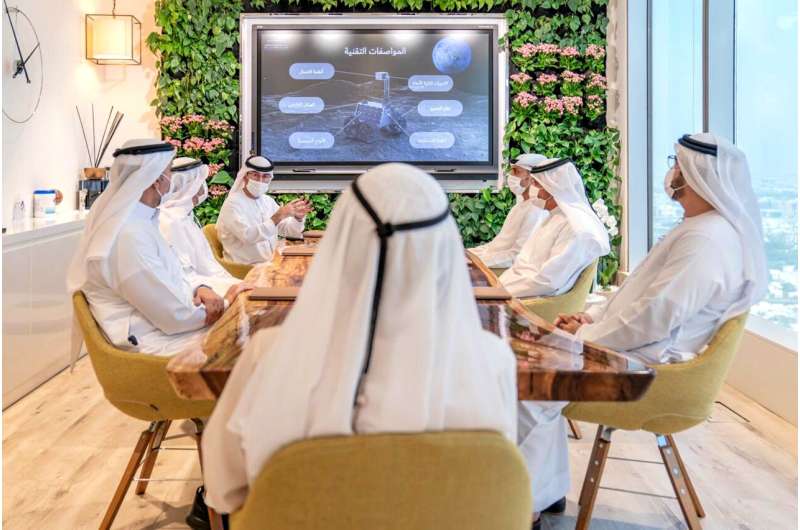
United Arab Emirates to launch first lunar rover in November

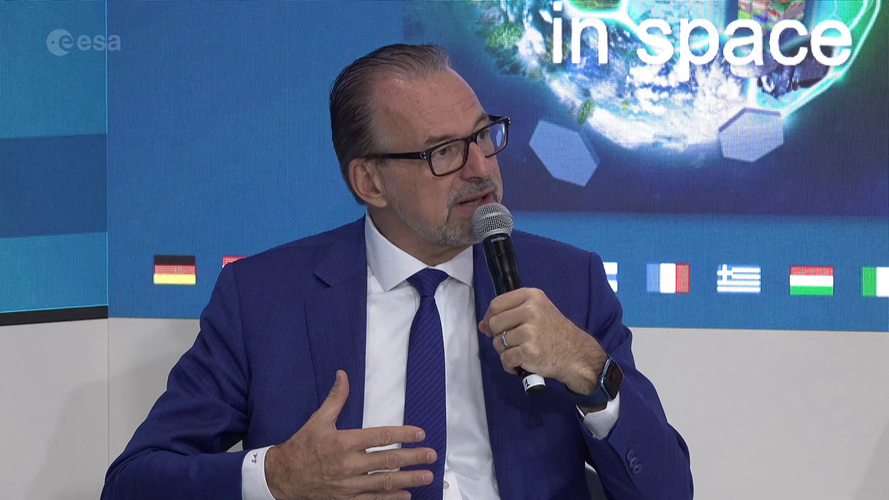
IAC 2022 - ESA DG and Directors meet the press
 Video:
00:40:00
Video:
00:40:00
The world's largest global space event takes place in Paris from 18 to 22 September 2022 and ESA, of course, will be there!
Watch the replay of the first live coming from the International Astronautical Congress with the ESA Director General and several Directors talking to the press. They will answer questions from journalists while focusing on ESA’s strategy, Agenda 2025 and the ambitious package that will be put forward at the ESA Ministerial Council in November.
Mars is mighty in first Webb observations of Red Planet
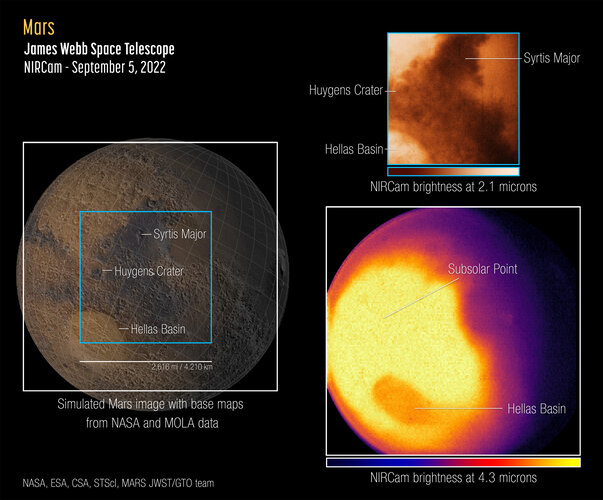
The James Webb Space Telescope captured its first images and spectra of Mars on 5 September 2022. The telescope, an international collaboration between NASA, ESA and the Canadian Space Agency, provides a unique perspective with its infrared sensitivity on our neighbouring planet, complementing data being collected by orbiters, rovers, and other telescopes.
Lockheed Martin delivers its highest powered laser to date to US Department Of Defense
 Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT) delivered to the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering OUSD (R&E) a new benchmark: a tactically-relevant electric 300 kW-class laser, the most powerful laser that Lockheed Martin has produced to date. This 300 kW-class laser is ready to integrate with the DOD demonstration efforts including the U.S. Army's Indirect Fires Protection Capa
Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT) delivered to the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering OUSD (R&E) a new benchmark: a tactically-relevant electric 300 kW-class laser, the most powerful laser that Lockheed Martin has produced to date. This 300 kW-class laser is ready to integrate with the DOD demonstration efforts including the U.S. Army's Indirect Fires Protection Capa FCC grants Lynk first-ever license for commercial satellite-direct-to-standard-mobile-phone service
 Lynk Global, Inc. (Lynk), the world's leading satellite-direct-to-standard-phone telecoms company, has expressed its appreciation to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for granting Lynk the world's first-ever commercial license for a satellite-direct-to-standard-mobile-phone service. This FCC license enables Lynk to launch commercial services for its global constellation of satellites l
Lynk Global, Inc. (Lynk), the world's leading satellite-direct-to-standard-phone telecoms company, has expressed its appreciation to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for granting Lynk the world's first-ever commercial license for a satellite-direct-to-standard-mobile-phone service. This FCC license enables Lynk to launch commercial services for its global constellation of satellites l Satellite mission confirms cornerstone of general relativity is unshakeable
 The MICROSCOPE mission has confirmed the 'equivalence principle' with unprecedented accuracy, bolstering Einstein's general relativity.
The result, announced this week by a team led by the French space agency CNES, is a triumph for Einstein's general relativity. However, it also potentially rules out some candidate universal theories of physics.
General relativity is the best theory
The MICROSCOPE mission has confirmed the 'equivalence principle' with unprecedented accuracy, bolstering Einstein's general relativity.
The result, announced this week by a team led by the French space agency CNES, is a triumph for Einstein's general relativity. However, it also potentially rules out some candidate universal theories of physics.
General relativity is the best theory Chinese astronauts go on spacewalk from new station
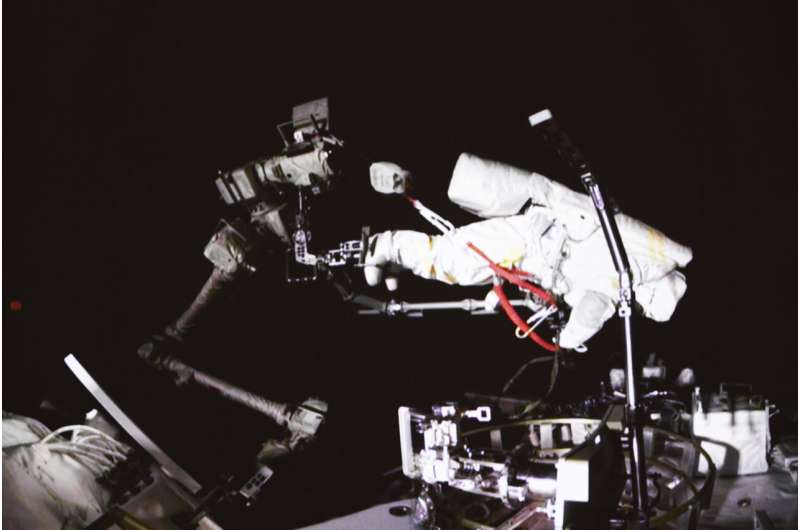

Two Chinese astronauts went on a spacewalk Saturday from a new space station that is due to be completed later this year.
Cai Xuzhe and Chen Dong installed pumps, a handle to open the hatch door from outside in an emergency, and a foot-stop to fix an astronaut's feet to a robotic arm, state media said.
Shenzhou astronauts carry out second spacewalk
 Crew members on the Shenzhou XIV mission stepped out of their spacecraft for the second spacewalk on Saturday afternoon, according to the China Manned Space Agency.
The agency said in a brief news release that Senior Colonel Cai Xuzhe opened an extravehicular activity hatch on the Tiangong space station at 1:35 pm and then floated out of the station. He was followed by mission commander Se
Crew members on the Shenzhou XIV mission stepped out of their spacecraft for the second spacewalk on Saturday afternoon, according to the China Manned Space Agency.
The agency said in a brief news release that Senior Colonel Cai Xuzhe opened an extravehicular activity hatch on the Tiangong space station at 1:35 pm and then floated out of the station. He was followed by mission commander Se How gravity gives astronomers a powerful lens on the universe
 In 1919 astronomers Arthur Eddington and Andrew Crommelin captured photographic images of a total solar eclipse. The Sun was in the constellation Taurus at the time, and a handful of its stars could be seen in the photographs. But the stars weren't quite in their expected place. The tremendous gravity of the Sun had deflected the light of these stars, making them appear slightly out of place. It
In 1919 astronomers Arthur Eddington and Andrew Crommelin captured photographic images of a total solar eclipse. The Sun was in the constellation Taurus at the time, and a handful of its stars could be seen in the photographs. But the stars weren't quite in their expected place. The tremendous gravity of the Sun had deflected the light of these stars, making them appear slightly out of place. It Jupiter to reach opposition, closest approach to Earth in 70 years
 Stargazers can expect excellent views of Jupiter the entire night of Monday, Sept. 26 when the giant planet reaches opposition. From the viewpoint of Earth's surface, opposition happens when an astronomical object rises in the east as the Sun sets in the west, placing the object and the Sun on opposite sides of Earth.
Jupiter's opposition occurs every 13 months, making the planet appear la
Stargazers can expect excellent views of Jupiter the entire night of Monday, Sept. 26 when the giant planet reaches opposition. From the viewpoint of Earth's surface, opposition happens when an astronomical object rises in the east as the Sun sets in the west, placing the object and the Sun on opposite sides of Earth.
Jupiter's opposition occurs every 13 months, making the planet appear la 
