
Copernical Team
Satellite broadband firms join forces
 A French and British firm joined forces in the fast-growing satellite broadband market on Tuesday.
French operator Eutelsat said it had signed a merger with British group OneWeb to seal its plan to create a new "champion" in the market.
The pair first announced plans to merge in July when they signed a memorandum of understanding to unite and become "a leading global player in connectivi
A French and British firm joined forces in the fast-growing satellite broadband market on Tuesday.
French operator Eutelsat said it had signed a merger with British group OneWeb to seal its plan to create a new "champion" in the market.
The pair first announced plans to merge in July when they signed a memorandum of understanding to unite and become "a leading global player in connectivi 'Sail' to de-orbit would-be space junk
 As the number of rocket launches, planetary missions and satellite activities continues to grow, so does junk in space, and many have been pondering the question of how to reduce the amount of debris orbiting Earth. Now, China may have found a solution with its newly deployed "sail" technology.
Hundreds of millions of items of human-made debris are continually circling Earth, including bro
As the number of rocket launches, planetary missions and satellite activities continues to grow, so does junk in space, and many have been pondering the question of how to reduce the amount of debris orbiting Earth. Now, China may have found a solution with its newly deployed "sail" technology.
Hundreds of millions of items of human-made debris are continually circling Earth, including bro An early start to a long weekend - Sols 3660-3664
 On a usual week of Curiosity operations, Friday plans take the longest since they span the whole weekend. This rare Monday morning, however, we're planning five sols to start covering Tuesday - Monday of operations so the team can spend Thanksgiving on Earth. When we plan a large chunk of sols like this, the first couple sols are lightweight with minimal risk activities from environmental sensor
On a usual week of Curiosity operations, Friday plans take the longest since they span the whole weekend. This rare Monday morning, however, we're planning five sols to start covering Tuesday - Monday of operations so the team can spend Thanksgiving on Earth. When we plan a large chunk of sols like this, the first couple sols are lightweight with minimal risk activities from environmental sensor Marines Must Fight for Space
 Marines must contribute to the fight for space. No, this is not some far-flung future of Colonial or UN Space Command Marines fighting alien hordes. And despite its ongoing force transformation, the Marine Corps is not going to add a space-shuttle door-gunner military occupational specialty any time soon. The most recent "Force Design 2030 Update" argued that "the enduring function for [Stand-In
Marines must contribute to the fight for space. No, this is not some far-flung future of Colonial or UN Space Command Marines fighting alien hordes. And despite its ongoing force transformation, the Marine Corps is not going to add a space-shuttle door-gunner military occupational specialty any time soon. The most recent "Force Design 2030 Update" argued that "the enduring function for [Stand-In Xi: China open to space exchanges, cooperation
 President Xi Jinping reiterated on Monday China's wish to work with other nations to carry out space exploration and development. Xi wrote in a congratulatory letter to the United Nations/China 2nd Global Partnership Workshop on Space Exploration and Innovation that the country is willing to deepen its cooperation and exchanges with other nations to advance space exploration and the peaceful use
President Xi Jinping reiterated on Monday China's wish to work with other nations to carry out space exploration and development. Xi wrote in a congratulatory letter to the United Nations/China 2nd Global Partnership Workshop on Space Exploration and Innovation that the country is willing to deepen its cooperation and exchanges with other nations to advance space exploration and the peaceful use SpaceX Dragon supply ship launch scrubbed by bad weather
 The launch of a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft to resupply the International Space Station was scrubbed Tuesday afternoon because of bad weather, NASA officials said.
The CRS-26 mission had been set to launch on a new Falcon 9 rocket at 3:54 p.m. EST from Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The attempt was reset to Saturday at 2:20 p.m.
NASA engineers called a halt to the countdown at T-m
The launch of a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft to resupply the International Space Station was scrubbed Tuesday afternoon because of bad weather, NASA officials said.
The CRS-26 mission had been set to launch on a new Falcon 9 rocket at 3:54 p.m. EST from Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The attempt was reset to Saturday at 2:20 p.m.
NASA engineers called a halt to the countdown at T-m Advanced Space leads first ever commercial mission to operate at the moon
 Advanced Space LLC., a leading space tech solutions company, is the first commercial entity to own an operational satellite at the Moon. CAPSTONE, the Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment, has finalized its insertion into a Near Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO).
Now that history has been made, the small spacecraft is ready to begin operations
Advanced Space LLC., a leading space tech solutions company, is the first commercial entity to own an operational satellite at the Moon. CAPSTONE, the Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment, has finalized its insertion into a Near Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO).
Now that history has been made, the small spacecraft is ready to begin operations An exoplanet atmosphere as never seen before
 The JWST just scored another first: a detailed molecular and chemical portrait of a distant world's skies.
The telescope's array of highly sensitive instruments was trained on the atmosphere of a "hot Saturn"-a planet about as massive as Saturn orbiting a star some 700 light-years away-known as WASP-39 b. While JWST and other space telescopes, including Hubble and Spitzer, previously have
The JWST just scored another first: a detailed molecular and chemical portrait of a distant world's skies.
The telescope's array of highly sensitive instruments was trained on the atmosphere of a "hot Saturn"-a planet about as massive as Saturn orbiting a star some 700 light-years away-known as WASP-39 b. While JWST and other space telescopes, including Hubble and Spitzer, previously have Family portrait
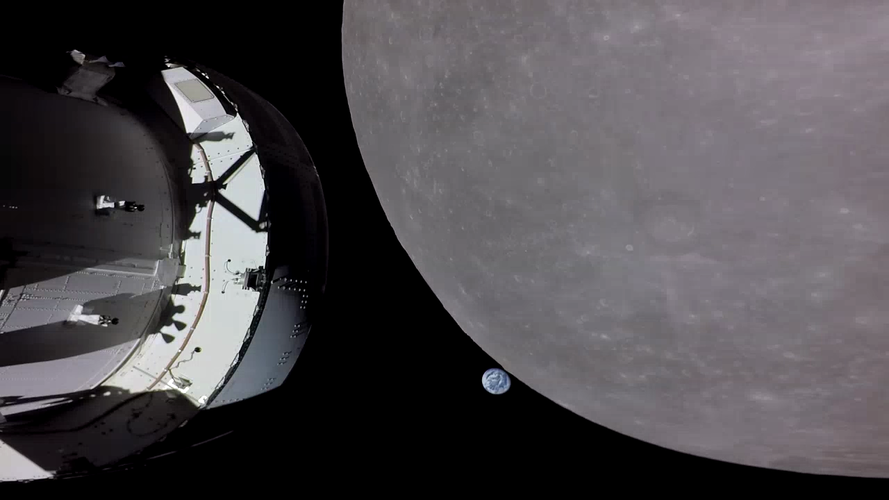 Image:
Image:
The Orion spacecraft with European Service Module (left), Earth (middle) and the Moon (right) are captured in this ‘family portrait’ by Orion’s solar array camera during the spacecraft’s closet approach to the lunar surface.
Six days into the 25-day Artemis I mission, the Orion spacecraft performed a key manoeuvre: just a little more than 130 km from the lunar surface, the main engine on the European Service Module – a repurposed Space Shuttle engine that is now on its 20th spaceflight – fired for just under 150 seconds to push the spacecraft and head towards a lunar orbit using
France, Germany, Italy agree on next-generation space rockets

France, Germany and Italy, the three biggest contributors to the European Space Agency, said Tuesday they have agreed to guarantee the future of the next-generation Ariane 6 and Vega-C rocket launcher systems.
The countries also reaffirmed a preference for European rockets, after the agency was forced to turn to US firm SpaceX to launch two future scientific missions.
The ministers in charge of space for the ESA's 22 member states are meeting in Paris on Tuesday and Wednesday to determine the agency's funding for the next three years, with a 3.2-billion-euro ($3.3-billion) plan for European space launchers high on the agenda.
"The public funding necessary to equilibrate the Ariane 6 and Vega-C institutional and commercial exploitation will be reviewed in order to take into account the evolution of market prices, institutional prices, economic conditions," said a joint ministerial statement from France's Bruno Le Maire, Germany's Robert Habeck and Italy's Adolfo Urso.
The ESA has had to scramble to find a way to get its missions into space after Russia withdrew its Soyuz rockets in response to European sanctions over Moscow's war in Ukraine earlier this year.

