
Copernical Team
Metal fuel for carbon-free energy on Earth… and the Moon
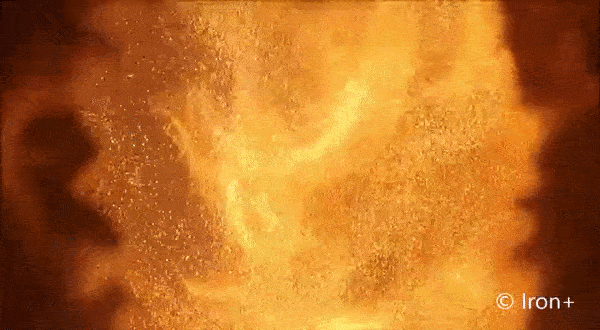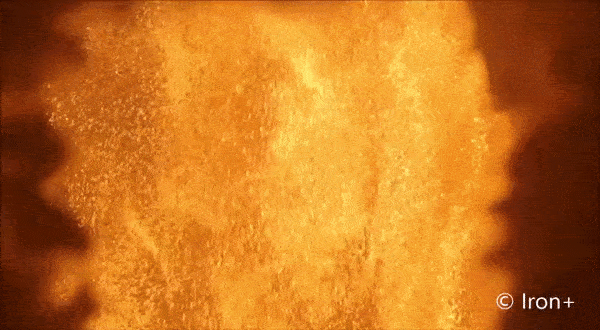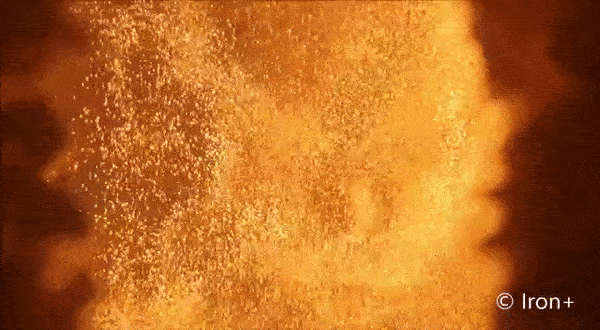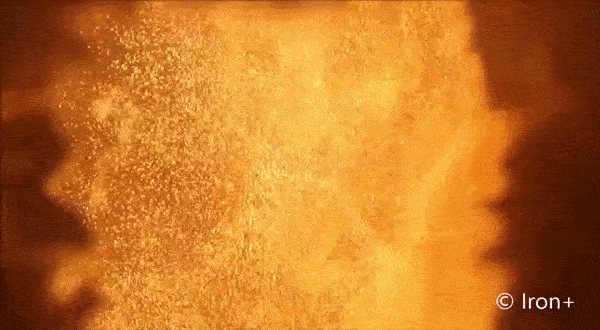
Everything burns. Given the right environment, all matter can burn by adding oxygen, but finding the right mix and generating enough heat makes some materials combust more easily than others. Researchers interested in knowing more about a type of fire called discrete burning used ESA’s microgravity experiment facilities to investigate.
Tune in for first Mars livestream

For one hour on Friday 2 June, join ESA on YouTube for a space first as live images stream down direct from Mars – this will be the closest you can get to a live view from the Red Planet.
Orion European Service Module-4 logo
 Image:
Orion European Service Module-4 logo
Image:
Orion European Service Module-4 logo China looks to expand scope of space operations with Shenzhou 16
 Traditionally, China's astronauts are selected from among fighter plane pilots with ample flying experience, as they can control the machinery and have the training to stay calm should an emergency arise in space.
Yet among the three astronauts aboard Shenzhou XVI, which is taking them to Tiangong, China's space station, is Gui Haichao, a professor from Beihang University. He is the first
Traditionally, China's astronauts are selected from among fighter plane pilots with ample flying experience, as they can control the machinery and have the training to stay calm should an emergency arise in space.
Yet among the three astronauts aboard Shenzhou XVI, which is taking them to Tiangong, China's space station, is Gui Haichao, a professor from Beihang University. He is the first Private flight with 2 Saudi astronauts returns from space station with Gulf of Mexico splashdown

High winds halt Spanish rocket launch

The maiden flight of the Spanish-built Miura 1 rocket was canceled Wednesday due to high winds, startup PLD Space said, in a setback for development of the small-scale space launcher.
"We have no green light, there are gusts of wind at high altitude above our limits. That means we don't have sufficiently safe conditions to launch," a commentator said on PLD Space's livestream of the lift-off, which was to be Spain's first.
It will be several days before a new launch window opens, the commentator added.
Standing just 12 meters (40 feet) tall, the small rocket was to fly 100 kilometers (62 miles) above the Earth's surface from a military base in southern Spain.
While that distance would put it in outer space, the rocket is not powerful enough to reach orbit.
Wednesday's sub-orbital launch had been slated to bring a payload with micro-gravity experiments, as well as setting up PLD Space's plans for future rockets.
"The idea is to learn and to minimize risks for the first flights of the Miura 5", said PLD Space cofounder Raul Verdu, referring to a launcher the firm hopes will place satellites into orbit from 2025.
Wanted: European commercial cargo service for space stations around Earth
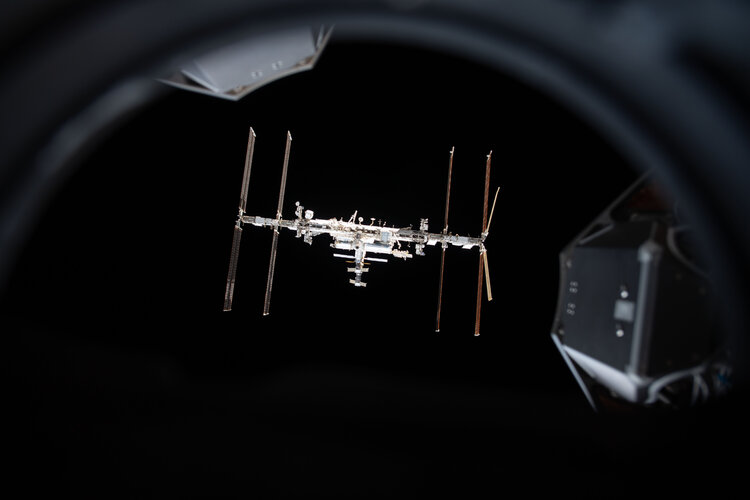

ESA invites European companies to submit proposals for commercial cargo transportation services to and from the International Space Station and future commercial low Earth orbit outposts.
GPS tracking reveals how a female baboon stopped using urban space after giving birth
Helium nuclei research advances our understanding of cosmic ray origin and propagation
 Much of our understanding of the Universe and its mysterious phenomena is based on theoretical interpretations. In order to deepen the understanding of distant objects and energetic phenomena, astronomers are looking at cosmic rays, which are high-energy charged particles composed of protons, electrons, atomic nuclei, and other subatomic particles. Such studies have revealed that cosmic rays con
Much of our understanding of the Universe and its mysterious phenomena is based on theoretical interpretations. In order to deepen the understanding of distant objects and energetic phenomena, astronomers are looking at cosmic rays, which are high-energy charged particles composed of protons, electrons, atomic nuclei, and other subatomic particles. Such studies have revealed that cosmic rays con Astronomers detected two major targets with a single telescope - a mysterious signal and its source galaxy
 Astronomers have been working to better understand the galactic environments of fast radio bursts (FRBs) - intense, momentary bursts of energy occurring in mere milliseconds and with unknown cosmic origins.
Now, a study of the slow-moving, star-forming gas in the same galaxy found to host an FRB has been published in The Astrophysical Journal. This is only the fourth-ever publication on tw
Astronomers have been working to better understand the galactic environments of fast radio bursts (FRBs) - intense, momentary bursts of energy occurring in mere milliseconds and with unknown cosmic origins.
Now, a study of the slow-moving, star-forming gas in the same galaxy found to host an FRB has been published in The Astrophysical Journal. This is only the fourth-ever publication on tw 
