Copernical Team
Blue Origin's New Glenn rocket blasts off in first launch, reaches orbit
 Blue Origin, the space company founded by billionaire Jeff Bezos, launched its massive New Glenn rocket for the first time early Thursday, a livestream of the blastoff showed.
The rocket, whose inaugural mission had been delayed by several years, blasted of at 2:03 am (0703 GMT) from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Base in the US state of Florida, the webcast showed.
The mission is seen a
Blue Origin, the space company founded by billionaire Jeff Bezos, launched its massive New Glenn rocket for the first time early Thursday, a livestream of the blastoff showed.
The rocket, whose inaugural mission had been delayed by several years, blasted of at 2:03 am (0703 GMT) from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Base in the US state of Florida, the webcast showed.
The mission is seen a BlackSky wins US Space Force contracts for tactical surveillance and tracking missions
 BlackSky Technology Inc. (NYSE: BKSY) has secured several rapid procurement contracts through the U.S. Space Force's Global Data Marketplace (GDM), emphasizing its advanced analytics services in support of Tactical Surveillance, Reconnaissance, and Tracking (TacSRT) missions.
"One year in operation, this novel marketplace increases speed and accessibility to BlackSky's reliable high-cadenc
BlackSky Technology Inc. (NYSE: BKSY) has secured several rapid procurement contracts through the U.S. Space Force's Global Data Marketplace (GDM), emphasizing its advanced analytics services in support of Tactical Surveillance, Reconnaissance, and Tracking (TacSRT) missions.
"One year in operation, this novel marketplace increases speed and accessibility to BlackSky's reliable high-cadenc BlackSky secures extended contract with NRO for advanced Gen-2 imagery services
 BlackSky Technology Inc. (NYSE: BKSY) has announced a one-year extension of its Electro-Optical Commercial Layer (EOCL) contract with the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). The extension covers subscription-based high-frequency, low-latency Gen-2 imagery services and will include enhancements to BlackSky's ground architecture to improve image search functionality, operational utility, and rea
BlackSky Technology Inc. (NYSE: BKSY) has announced a one-year extension of its Electro-Optical Commercial Layer (EOCL) contract with the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). The extension covers subscription-based high-frequency, low-latency Gen-2 imagery services and will include enhancements to BlackSky's ground architecture to improve image search functionality, operational utility, and rea Engineering quantum entanglement at the nanoscale
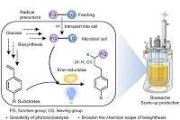
 Physicists have spent more than a century measuring and making sense of the strange ways that photons, electrons, and other subatomic particles interact at extremely small scales. Engineers have spent decades figuring out how to take advantage of these phenomena to create new technologies.
In one such phenomenon, called quantum entanglement, pairs of photons
Physicists have spent more than a century measuring and making sense of the strange ways that photons, electrons, and other subatomic particles interact at extremely small scales. Engineers have spent decades figuring out how to take advantage of these phenomena to create new technologies.
In one such phenomenon, called quantum entanglement, pairs of photons Blue Origin could launch orbital rocket Thursday or Friday
 Blue Origin, the space company founded by billionaire Jeff Bezos, could attempt its first orbital launch Thursday morning, weather permitting, a spokesperson said.
The massive New Glenn rocket is seen as critical to Blue Origin's efforts to compete with Elon Musk's SpaceX, which dominates the commercial space industry.
But its inaugural mission has been delayed by several years.
Att
Blue Origin, the space company founded by billionaire Jeff Bezos, could attempt its first orbital launch Thursday morning, weather permitting, a spokesperson said.
The massive New Glenn rocket is seen as critical to Blue Origin's efforts to compete with Elon Musk's SpaceX, which dominates the commercial space industry.
But its inaugural mission has been delayed by several years.
Att SpaceX delays latest Starship megarocket test to Thursday
This request seems a bit unusual, so we need to confirm that you're human. Please press and hold the button until it turns completely green. Thank you for your cooperation!
Press and hold the button
If you believe this is an error, please contact our support team.
185.132.36.159 : b5a41914-5a2b-4d65-8c03-50d68484
Proba-3 becomes two: Satellites successfully separate
This request seems a bit unusual, so we need to confirm that you're human. Please press and hold the button until it turns completely green. Thank you for your cooperation!
Press and hold the button
If you believe this is an error, please contact our support team.
185.132.36.159 : 1231c821-2484-4651-895d-8faa65b7
Ariane 6 central core on the move
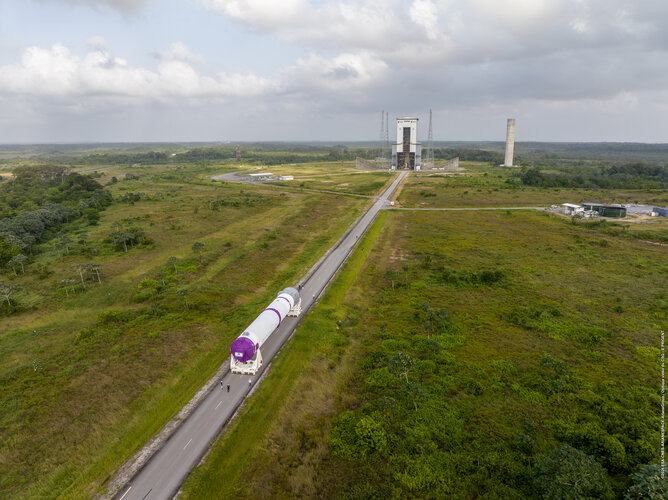 Image:
Ariane 6 Central Core being transferred from the launcher assembly building to the launch pad
Image:
Ariane 6 Central Core being transferred from the launcher assembly building to the launch pad Technological ‘to-do list’ to reach Zero Debris created

There is an increasing willingness in the space sector to tackle the problem of space debris. Yet much of the required technology to mitigate or prevent its risks is still missing.
Preventing new debris, avoiding collisions and the timely clearance of satellites from orbit at their end-of-mission are complex challenges that each require a variety of practical solutions.
Released to the public on 15 January 2025, the Zero Debris Technical Booklet is a community-driven document that identifies technologies that will contribute to the goal of Zero Debris by 2030. Essentially, the Booklet forms a technical Zero Debris 'to-do list'.
Firefly looks to punch NASA moon ticket with overnight SpaceX launch
This request seems a bit unusual, so we need to confirm that you're human. Please press and hold the button until it turns completely green. Thank you for your cooperation!
Press and hold the button
If you believe this is an error, please contact our support team.
185.132.36.159 : 802fef5c-6b62-4284-ab4e-b5e24d5a