
Copernical Team
US astronaut ends record-long spaceflight in Russian capsule (Update)

A NASA astronaut caught a Russian ride back to Earth on Wednesday after a U.S. record 355 days at the International Space Station, returning with two cosmonauts to a world torn apart by war.
Mark Vande Hei landed in a Soyuz capsule in Kazakhstan alongside the Russian Space Agency's Anton Shkaplerov and Pyotr Dubrov, who also spent the past year in space.
Journey to Destination Earth begins

Today, the European Commission, ESA, the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (Eumetsat) celebrated the official launch of the Destination Earth initiative: an ambitious project that involves creating a digital replica of Earth to help us move towards a sustainable future.
A record broken: Hubble finds the most distant star ever seen
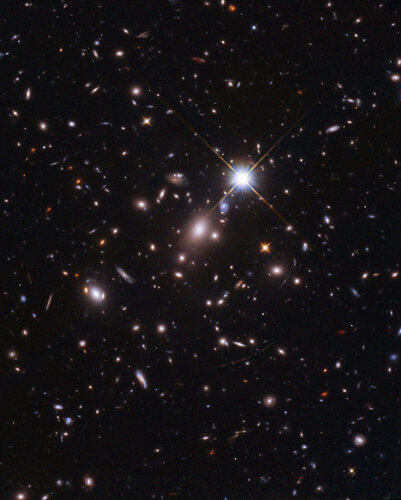 Image:
A record broken: Hubble finds the most distant star ever seen
Image:
A record broken: Hubble finds the most distant star ever seen US astronaut ends record-long spaceflight in Russian capsule

A NASA astronaut caught a Russian ride back to Earth on Wednesday after a U.S. record 355 days at the International Space Station, returning with two cosmonauts to a world torn apart by war.
Mark Vande Hei landed in a Soyuz capsule in Kazakhstan alongside the Russian Space Agency's Anton Shkaplerov and Pyotr Dubrov, who also spent the past year in space.
Martian brain freeze
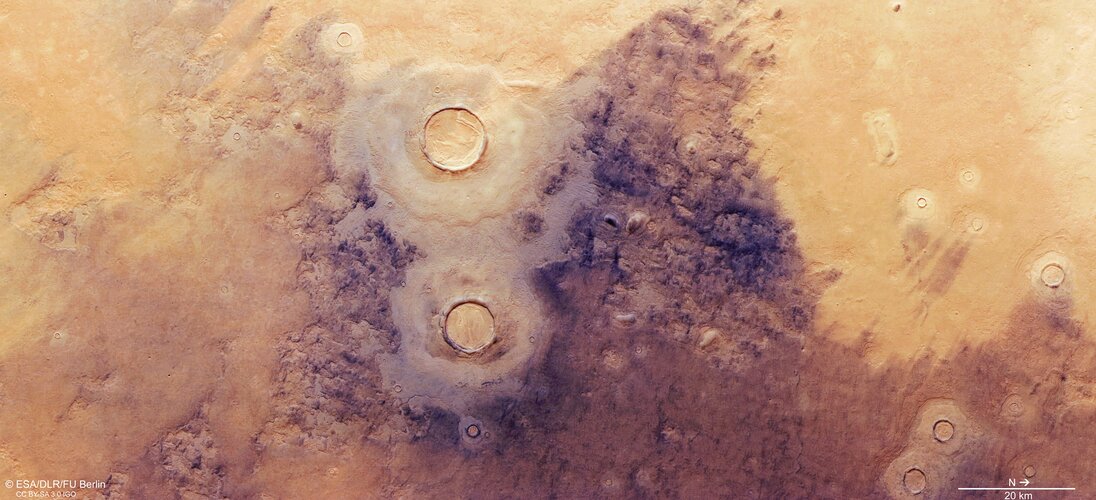
New views from ESA’s Mars Express reveal fascinating ice-related features in Mars’ Utopia region – home to the largest known impact basin not only on the Red Planet, but in the Solar System.
PickNik Robotics to work with Sierra Space on space robotics
 PickNik Robotics, a leader in robotics software and engineering services, has announced that it is collaborating with the team at Sierra Space, a leading commercial space company with 1,100 employees, more than 500 missions and over 30 years of space flight heritage. The collaboration will explore implementation of robotic autonomy and controllability for autonomous maintenance of space habitat
PickNik Robotics, a leader in robotics software and engineering services, has announced that it is collaborating with the team at Sierra Space, a leading commercial space company with 1,100 employees, more than 500 missions and over 30 years of space flight heritage. The collaboration will explore implementation of robotic autonomy and controllability for autonomous maintenance of space habitat SES to enable RPAS operations via satellite
 The latest contract awarded by the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) will see the agency continue to use SES's high-performance satellite connectivity services for Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems' (RPAS) operations, SES and EMSA announced. Under the new agreement, SES's managed connectivity service will allow end-users to receive and exchange RPAS data in near real-time and support the op
The latest contract awarded by the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) will see the agency continue to use SES's high-performance satellite connectivity services for Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems' (RPAS) operations, SES and EMSA announced. Under the new agreement, SES's managed connectivity service will allow end-users to receive and exchange RPAS data in near real-time and support the op Sidus Space announces the upcoming launch of LizzieSat
 Sidus Space, Inc. (NASDAQ:SIDU), a Space-as-a-Service satellite company focused on commercial satellite design, manufacture, launch, and data collection, is pleased to announce its forward progression towards launch of its LizzieSat (LS) satellite to the International Space Station (ISS). This mission is slated to take place later this year.
LS is a multi-mission satellite that supports cu
Sidus Space, Inc. (NASDAQ:SIDU), a Space-as-a-Service satellite company focused on commercial satellite design, manufacture, launch, and data collection, is pleased to announce its forward progression towards launch of its LizzieSat (LS) satellite to the International Space Station (ISS). This mission is slated to take place later this year.
LS is a multi-mission satellite that supports cu Quantum complexity grows linearly for an exponentially long time
 "We have found a surprisingly simple solution to an important problem in physics," says Prof. Jens Eisert, a theoretical physicist at Freie Universitat Berlin and HZB. "Our results provide a solid basis for understanding the physical properties of chaotic quantum systems, from black holes to complex many-body systems," Eisert adds.
Using only pen and paper, i.e. purely analytically, the Be
"We have found a surprisingly simple solution to an important problem in physics," says Prof. Jens Eisert, a theoretical physicist at Freie Universitat Berlin and HZB. "Our results provide a solid basis for understanding the physical properties of chaotic quantum systems, from black holes to complex many-body systems," Eisert adds.
Using only pen and paper, i.e. purely analytically, the Be At IAF anniversary celebration, a plea for continued cooperation in Space
 The International Astronautical Federation (IAF), the world's leading space advocacy. Organization founded in the French capital in 1951, held it 70th anniversary celebration here, following a brief covid- related delay. Each year, IAF organized a Grand Space meet, gathering as many as 5,000 delegates from
space agencies industries and other space-related entities with over 433 members fro
The International Astronautical Federation (IAF), the world's leading space advocacy. Organization founded in the French capital in 1951, held it 70th anniversary celebration here, following a brief covid- related delay. Each year, IAF organized a Grand Space meet, gathering as many as 5,000 delegates from
space agencies industries and other space-related entities with over 433 members fro 






























