
Copernical Team
Solar-power satellites to collect stronger sunlight
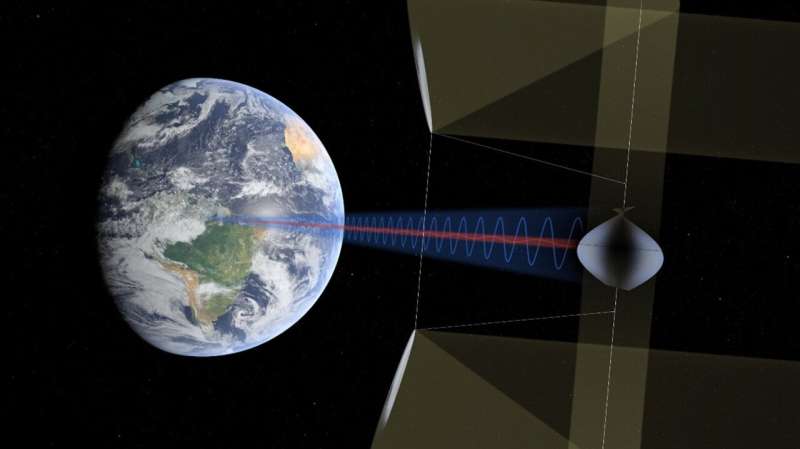
Solar energy generation keeps on becoming cheaper and more efficient, but some basic limitations will always apply: solar panels can only generate power during the daytime, and much of the sunlight is absorbed by the atmosphere as it shines downward. So ESA is working on the concept of collecting solar power up in orbit, where sunlight is up to 11 times more intense than across European territory, then beaming it down to the ground for use.
As part of that effort, a new project looks into designing solar-power satellites, which would become the largest structures ever built in space. Frazer-Nash Consultancy will study the modular construction of solar-power satellites, to efficiently disassemble them as they come to their end-of-life for reuse or recycling.
Explore further
Webb Telescope completes first multi-instrument alignment
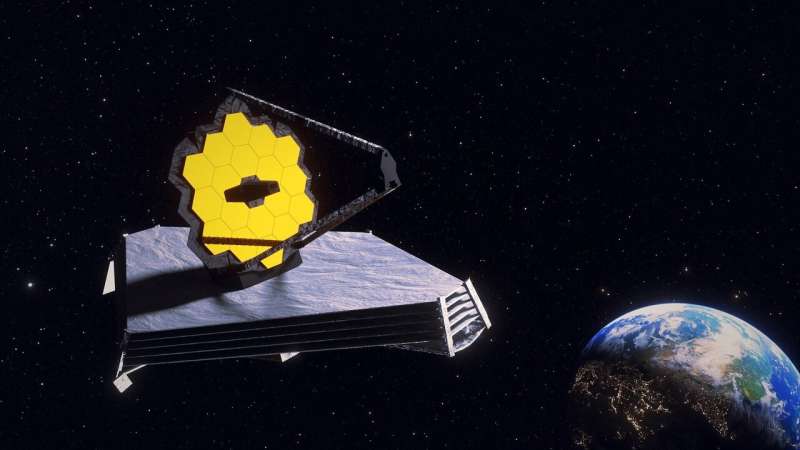

The sixth stage of aligning NASA's James Webb Space Telescope's mirrors to its scientific instruments so they will create the most accurate and focused images possible has concluded. While the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) continues its cooldown, optics teams have successfully aligned the rest of the observatory's onboard instruments to Webb's mirrors. Previous alignment efforts were so accurate that the team concluded no additional adjustments to the secondary mirror are necessary until the seventh and final stage, which will involve MIRI when it has fully cooled.
"As a general rule, the commissioning process starts with coarse corrections and then moves into fine corrections. The early secondary mirror coarse corrections, however, were so successful that the fine corrections in the first iteration of Phase Six were unnecessary," said Chanda Walker, Webb wavefront sensing and control scientist, Ball Aerospace. "This accomplishment was due to many years of planning and great teamwork among the wavefront sensing team."
Throughout the majority of the alignment process, Webb's 18 hexagonal mirrors and secondary mirror were focused into alignment to the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) instrument only.
Space debris found in rural India likely from 'China rocket'
A large metal ring and sphere that villagers in rural western India said fell from the sky over the weekend could be from a Chinese rocket launched into space last year, officials told local media.
The metal ring—reportedly two to three metres (6.5-10 feet) in diameter and weighing over 40 kilogrammes (90 pounds)—was discovered in a village field in Maharashtra state late on Saturday, district collector Ajay Gulhane told the Press Trust of India.
"We were preparing a community feast, when the sky blazed with the red disc which fell with a bang on an open plot in the village," an unnamed woman in Maharashtra's Chandrapur district told The Times of India.
"People ran to their home fearing (an) explosion and remained inside for nearly half an hour."
Another object—a large, metal ball around half a metre (1.5 feet) in diameter—fell in another village in the district, Gulhane told PTI.
"It has been collected for examination. We had sent (junior officials) to every village in the district to find if more parts of objects, if any, are lying scattered."
There were no reports of injuries or structural damage.
An Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) official told the Times that the timing of the objects' arrival was the "closest match" to the re-entry times on Saturday for debris from a Chinese rocket launched in February 2021.
Kepler telescope delivers new planetary discovery from the grave
 A new study by an international team of astrophysicists, led by the Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics has presented the amazing new discovery of a near-identical twin of Jupiter orbiting a star at a colossal distance of 17,000 light years from Earth.
The exoplanet, K2-2016-BLG-0005Lb, is almost identical to Jupiter in terms of its mass and its distance from its sun was discovered using
A new study by an international team of astrophysicists, led by the Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics has presented the amazing new discovery of a near-identical twin of Jupiter orbiting a star at a colossal distance of 17,000 light years from Earth.
The exoplanet, K2-2016-BLG-0005Lb, is almost identical to Jupiter in terms of its mass and its distance from its sun was discovered using NASA simulator helps to shed light on mysteries of Solar System
 Even in our cosmic backyard, the Solar System, many questions remain open. On Venus there are formations similar to volcanoes, but it is not known if they are active. The surface of Mars suggests that there was once a vast ocean, but how it disappeared remains unclear. On the other hand, recent detections of chemical compounds that may indicate the presence of biological activity on Mars and Ven
Even in our cosmic backyard, the Solar System, many questions remain open. On Venus there are formations similar to volcanoes, but it is not known if they are active. The surface of Mars suggests that there was once a vast ocean, but how it disappeared remains unclear. On the other hand, recent detections of chemical compounds that may indicate the presence of biological activity on Mars and Ven Making Tracks to the Delta
 Perseverance is in a drive campaign going faster than any previous rover. How fast, you may ask? Its actual speed is just under a tenth of a mile per hour, but it's faster than its predecessors. It is making comparatively rapid progress by devoting several hours per day to driving on very smooth terrain.
That has allowed Perseverance to break previous rovers' records for the distance trave
Perseverance is in a drive campaign going faster than any previous rover. How fast, you may ask? Its actual speed is just under a tenth of a mile per hour, but it's faster than its predecessors. It is making comparatively rapid progress by devoting several hours per day to driving on very smooth terrain.
That has allowed Perseverance to break previous rovers' records for the distance trave NASA's Perseverance rover listens in the thin Martian atmosphere
 Mars has a very thin atmosphere, which at the surface has a density approximately one percent that of Earth's. Until recently, it was unclear whether there is anything to hear in the barren landscape there and if it is even possible for sound to be recorded under these conditions. When NASA's Perseverance Mars rover landed on the Red Planet on 18 February 2021, it was carrying two microphones.
Mars has a very thin atmosphere, which at the surface has a density approximately one percent that of Earth's. Until recently, it was unclear whether there is anything to hear in the barren landscape there and if it is even possible for sound to be recorded under these conditions. When NASA's Perseverance Mars rover landed on the Red Planet on 18 February 2021, it was carrying two microphones. Magma makes marsquakes rock Red Planet
 Volcanic activity beneath the surface of Mars could be responsible for triggering repetitive marsquakes, which are similar to earthquakes, in a specific region of the Red Planet, researchers from The Australian National University (ANU) suggest.
New research published in Nature Communications shows scientists from ANU and the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing have discovered 47 previo
Volcanic activity beneath the surface of Mars could be responsible for triggering repetitive marsquakes, which are similar to earthquakes, in a specific region of the Red Planet, researchers from The Australian National University (ANU) suggest.
New research published in Nature Communications shows scientists from ANU and the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing have discovered 47 previo Roscosmos to Brief Russian Government on Options for Ending ISS Cooperation Soon, Rogozin Says
 The Russian space agency Roscosmos will soon inform the government of how it plans to terminate cooperation with Western partners on the International Space Station, its chief said.
"Roscosmos will present its concrete proposals on the timeline for ending ISS cooperation with US, Canadian, EU and Japanese space agencies to the leadership of our country soon," Dmitry Rogozin said on Telegra
The Russian space agency Roscosmos will soon inform the government of how it plans to terminate cooperation with Western partners on the International Space Station, its chief said.
"Roscosmos will present its concrete proposals on the timeline for ending ISS cooperation with US, Canadian, EU and Japanese space agencies to the leadership of our country soon," Dmitry Rogozin said on Telegra Aphelion Aerospace secures investment from The Mercury Group and others
 Aphelion Aerospace, based in Denver, Colorado is establishing itself as a one-stop-shop for low-cost small satellite integration and on-demand launch operations from practically anywhere around the world. Aphelion reports it has received significant investment from strategic investors including The Mercury Group, Founder Advisors, and Richtr Financial Studio. These investments are part of Apheli
Aphelion Aerospace, based in Denver, Colorado is establishing itself as a one-stop-shop for low-cost small satellite integration and on-demand launch operations from practically anywhere around the world. Aphelion reports it has received significant investment from strategic investors including The Mercury Group, Founder Advisors, and Richtr Financial Studio. These investments are part of Apheli 






























