
Copernical Team
Chinese astronauts successfully grow rice in space
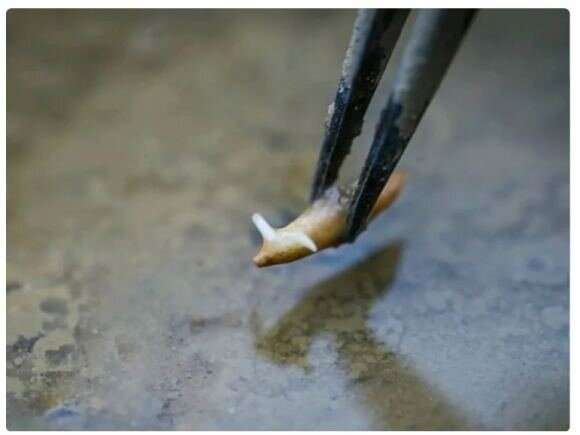

Rice is one of the world's staple crops. It is regularly eaten by more than half the world's population. And now, it's been grown in microgravity, on board the newly launched Chinese Wentian space laboratory.
Wentian launched in July and joined up with the Tianhe module of China's new space station. Its original complement of eight experiments included one that attempted to grow rice in microgravity.
Rice typically grows to 3 to 4 feet over four months, and the stalks on Wentian have not been able to complete their entire maturation cycle since the experiment started in July. However, they seem to be on track compared to their Earth-bound counterparts.
There were actually two types of rice launched as part of the experiment. A tall shoot variety reached almost 30 centimeters in the first month of growth, and a dwarf variety reached around 5 cm. Both of these growth amounts are on par for these particular rice varieties on Earth.
What's being done to protect astronauts from radiation in deep space?
In 1982, author James Michener published his sprawling novel "Space." In it, he describes a fictional Apollo 18 mission to the moon. While the astronauts are on the surface, the sun unleashes a huge storm, trapping them outside of their protective capsule.
Frank Drake has passed away but his equation for alien intelligence is more important than ever

How many intelligent civilizations should there be in our galaxy right now? In 1961, U.S. astrophysicist Frank Drake, who passed away on September 2 at the age of 92, came up with an equation to estimate this. The Drake equation, dating from a stage in his career when he was "too naive to be nervous" (as he later put it), has become famous and bears his name.
This places Drake in the company of towering physicists with equations named after them including James Clerk Maxwell and Erwin Schrödinger. Unlike those, Drake's equation does not encapsulate a law of nature. Instead it combines some poorly known probabilities into an informed estimate.
Whatever reasonable values you feed into the equation (see image above) it is hard to avoid the conclusion that we shouldn't be alone in the galaxy. Drake remained a proponent and a supporter of the search for extraterrestrial life throughout his days, but has his equation really taught us anything?
Webb captures a cosmic tarantula
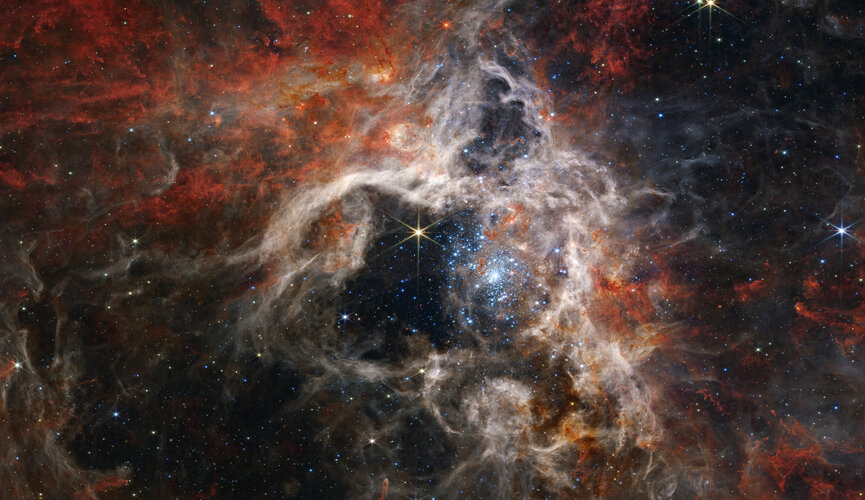

Thousands of never-before-seen young stars are spotted in a stellar nursery called 30 Doradus, captured by the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. Nicknamed the Tarantula Nebula for the appearance of its dusty filaments in previous telescope images, the nebula has long been a favourite for astronomers studying star formation. In addition to young stars, Webb reveals distant background galaxies, as well as the detailed structure and composition of the nebula’s gas and dust.
Zoom into the Tarantula Nebula
 Video:
00:01:00
Video:
00:01:00
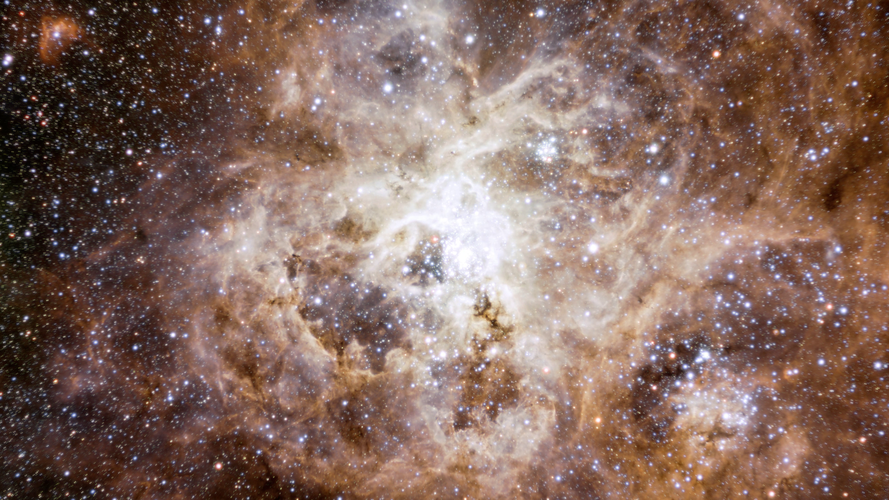
This video takes the viewer on a journey that zooms through space to reveal the Tarantula Nebula.
Thousands of never-before-seen young stars are spotted in the stellar nursery called 30 Doradus, captured by the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. It is nicknamed the Tarantula Nebula for the appearance of its dusty filaments in previous telescope images, the nebula has long been a favourite for astronomers studying star formation. In addition to young stars, Webb reveals distant background galaxies, as well as the detailed structure and composition of the nebula’s gas and dust.
AFA Air, Space, Cyber Conference set for Sept 19-21
 The Air Force Research Laboratory will highlight some of its newest technologies during the Air Force Association's Air, Space and Cyber Conference Sept. 19-21, 2022, at the Gaylord National Hotel and Convention Center in National Harbor, Maryland.
This year's theme is "America's Air and Space Forces - Yesterday, today and tomorrow (75 years in the defense of our nation)." Attendees can ex
The Air Force Research Laboratory will highlight some of its newest technologies during the Air Force Association's Air, Space and Cyber Conference Sept. 19-21, 2022, at the Gaylord National Hotel and Convention Center in National Harbor, Maryland.
This year's theme is "America's Air and Space Forces - Yesterday, today and tomorrow (75 years in the defense of our nation)." Attendees can ex A space race, a new Cold War or a bit of both
 NASA has delayed the launch of the Artemis I new moon program until at least Sept 19 after cancelling a planned launch on Saturday. The decision on Saturday was the second time in a week that the launch was scrapped.
The first time it was cancelled was on Aug 29 because one of the four engines was not "cold enough" for take-off minutes before Artemis I was set to blast off to the moon. The
NASA has delayed the launch of the Artemis I new moon program until at least Sept 19 after cancelling a planned launch on Saturday. The decision on Saturday was the second time in a week that the launch was scrapped.
The first time it was cancelled was on Aug 29 because one of the four engines was not "cold enough" for take-off minutes before Artemis I was set to blast off to the moon. The Space Compass and Skyloom sign term sheet to bring optical data relay services to EO market
 Skyloom and Space Compass (a newly formed joint venture between NTT and SKY Perfect JSAT) has announced that the companies signed a term sheet aimed to launch the first geostationary-based (GEO) data relay service over Asia that will leverage Skyloom's cutting-edge communication and networking systems for the purpose of serving the rapidly growing Earth-Observation (EO) market for real-time, hig
Skyloom and Space Compass (a newly formed joint venture between NTT and SKY Perfect JSAT) has announced that the companies signed a term sheet aimed to launch the first geostationary-based (GEO) data relay service over Asia that will leverage Skyloom's cutting-edge communication and networking systems for the purpose of serving the rapidly growing Earth-Observation (EO) market for real-time, hig Red Giant Betelgeuse was yellow some 2,000 years ago
 With progressing nuclear fusion in the center of a star, brightness, size, and color also change. Astrophysicists can derive from such properties important information on age and mass of a star. Those stars with significantly more mass than our Sun are blue-white or red - the transition from red via yellow and orange is relative rapid for astronomical time-scales.
Astrophysicists of Friedr
With progressing nuclear fusion in the center of a star, brightness, size, and color also change. Astrophysicists can derive from such properties important information on age and mass of a star. Those stars with significantly more mass than our Sun are blue-white or red - the transition from red via yellow and orange is relative rapid for astronomical time-scales.
Astrophysicists of Friedr SpaceX launches 51 Starlink satellites, orbital transfer vehicle
 SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket carrying 51 Starlink satellites to orbit as well as an orbital transfer vehicle for another company on Sunday night from Port Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, one day after NAA scrapped a mission to the moon.
The payload was sent into a low Earth orbit from Space Launch Complex 40 at 10:09 p.m. EDT.
The first stage separated and landed on th
SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket carrying 51 Starlink satellites to orbit as well as an orbital transfer vehicle for another company on Sunday night from Port Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, one day after NAA scrapped a mission to the moon.
The payload was sent into a low Earth orbit from Space Launch Complex 40 at 10:09 p.m. EDT.
The first stage separated and landed on th 






























