Copernical Team
Evolving time-tested technology to outmatch hypersonic weapons inside the atmosphere
 When it comes to defending against hypersonic weapons that move and maneuver at more than five times the speed of sound, you need layers of defense and multiple opportunities to take out the threat.
Seeking the first missile specifically designed to defeat hypersonic threats in their most vulnerable phase of flight, the glide phase, the MDA selected Raytheon Missiles and Defense, or RMD, a
When it comes to defending against hypersonic weapons that move and maneuver at more than five times the speed of sound, you need layers of defense and multiple opportunities to take out the threat.
Seeking the first missile specifically designed to defeat hypersonic threats in their most vulnerable phase of flight, the glide phase, the MDA selected Raytheon Missiles and Defense, or RMD, a These freeze-drying algae can awaken from cryostasis, could help spaceflights go farther
 Antarctica's McMurdo Dry Valleys contain some of Earth's coldest and driest deserts. The environment there is so extreme that the Dry Valleys have been used as Mars analogs to test prototype equipment for future Mars exploration. To survive these harsh conditions, layers of algae and bacteria in the Dry Valleys overwinter in a freeze-dried state, coming back to life in the summer when neighborin
Antarctica's McMurdo Dry Valleys contain some of Earth's coldest and driest deserts. The environment there is so extreme that the Dry Valleys have been used as Mars analogs to test prototype equipment for future Mars exploration. To survive these harsh conditions, layers of algae and bacteria in the Dry Valleys overwinter in a freeze-dried state, coming back to life in the summer when neighborin Japanese billionaire Maezawa announces crew of artists for lunar voyage
 Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa announced Thursday eight crew members who will join him for a journey around the Moon planned for 2023 on a SpaceX rocket that is still under development.
The mission, known as dearMoon, was first announced in 2018. Maezawa initially said he would invite a crew of six-to-eight artists, but later changed the entry requirements to a competition which applica
Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa announced Thursday eight crew members who will join him for a journey around the Moon planned for 2023 on a SpaceX rocket that is still under development.
The mission, known as dearMoon, was first announced in 2018. Maezawa initially said he would invite a crew of six-to-eight artists, but later changed the entry requirements to a competition which applica Artemis I landing spot abandoned over weather; mission remains on schedule
 Unsuitable weather is forcing NASA to abandon its primary landing site for the Orion spacecraft, although the mission otherwise remains on schedule, officials confirmed at a Thursday afternoon briefing.
"At present, we are on track to have a fully successful mission with some bonus objectives that we've achieved upon the way," Artemis I Mission Manager Mike Sarafin told reporters from J
Unsuitable weather is forcing NASA to abandon its primary landing site for the Orion spacecraft, although the mission otherwise remains on schedule, officials confirmed at a Thursday afternoon briefing.
"At present, we are on track to have a fully successful mission with some bonus objectives that we've achieved upon the way," Artemis I Mission Manager Mike Sarafin told reporters from J 'Phantoms' from beyond the moon could provide valuable data on cosmic radiation doses
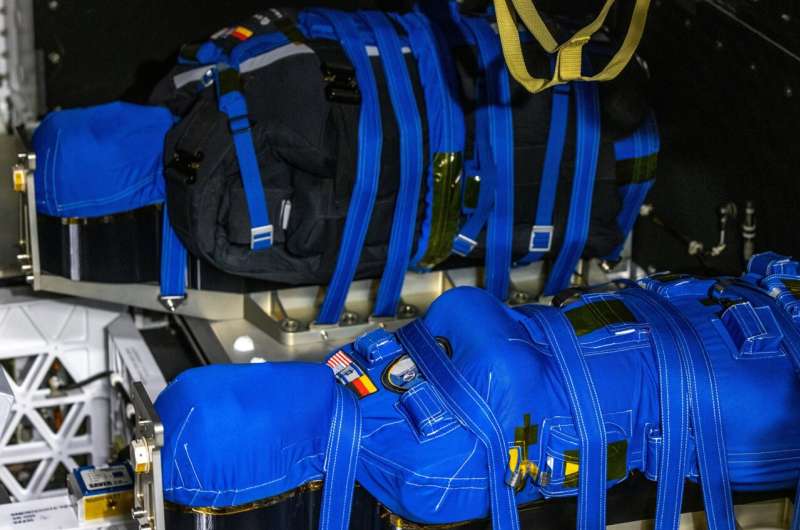

The Orion spacecraft on the Artemis I mission is carrying, as part of the MARE experiment, two human "phantoms" equipped with numerous cosmic rays detectors. The information gathered by the detectors will for the first time verify the knowledge, crucial for the presence of humans in deep space, of the effects of cosmic rays on the health of the astronauts who are to live and work in an environment devoid of the protective effects of our planet's magnetosphere.
Of the numerous dangers lurking for astronauts undertaking long-distance space travel, among the most serious and at the same time the most difficult to eliminate, is exposure to harmful doses of cosmic radiation. Data collected during the MARE experiment (MATROSHKA AstroRad Radiation Experiment) will help ensure the safety of future deep space pioneers.
Space research: Is it feasible to reuse high salinity wastewater as a plant nutrient medium for plant hydroponics?
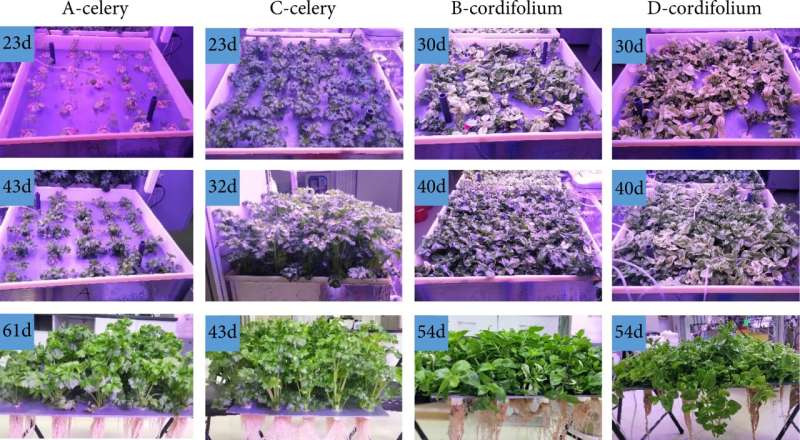

The water cycle is an important part of the controlled ecological life support system (CELSS). It involves the supply of drinking water and plant irrigation water, and the recycling of urine, sanitary waste water, and air condensate water. Using urine and sanitary wastewater for plant irrigation is an effective form of wastewater reuse, but there are three main challenges.
Firstly, some salt content in wastewater, especially sodium chloride, is high, but it is not necessary for plant growth and may inhibit plant growth.
Secondly, the wastewater contains organic components such as surfactants, which also have a negative impact on plant growth.
Thirdly, if wastewater is used as the main nutrient source, the proportion of mineral elements in wastewater might be inconsistent with the proportion the plant growth needs, which will also affect the normal growth of plants.
These freeze-drying algae can awaken from cryostasis, and could help spaceflights go farther
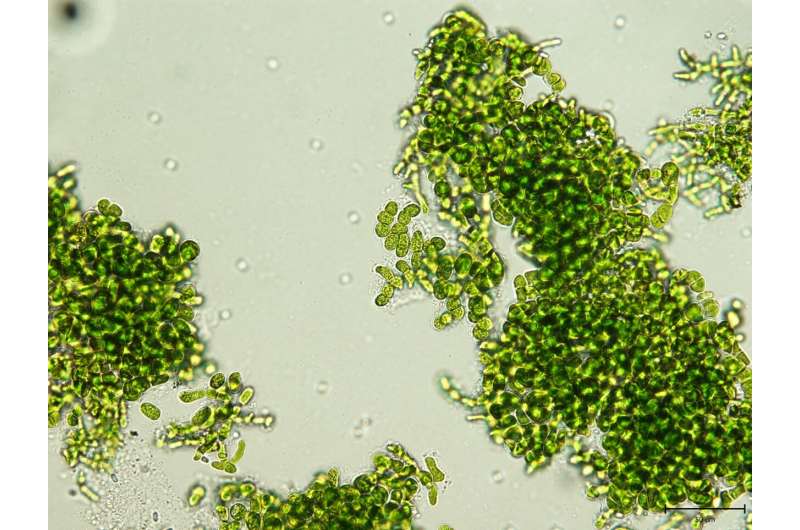
Antarctica's McMurdo Dry Valleys contain some of Earth's coldest and driest deserts. The environment there is so extreme that the Dry Valleys have been used as Mars analogs to test prototype equipment for future Mars exploration.
To survive these harsh conditions, layers of algae and bacteria in the Dry Valleys overwinter in a freeze-dried state, coming back to life in the summer when neighboring glaciers melt and water flows down the stream channels again.
NASA's Orion lunar spacecraft heads home with splashdown set for Sunday
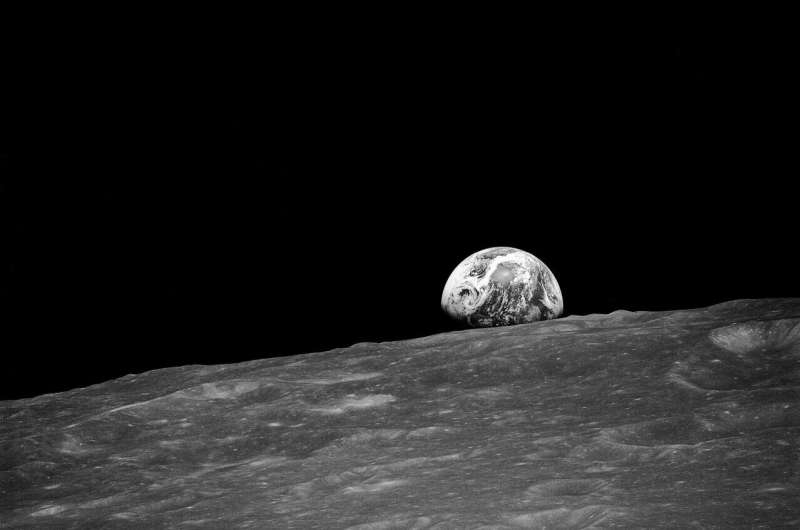

NASA's Orion spacecraft is heading home after exiting the lunar sphere of influence.
Orion completed the return powered flyby burn that put the spacecraft on course for splashdown on Sunday. Earth's force of gravity is now the primary gravitational force acting on the spacecraft.
Flight controllers used Orion's cameras to inspect the crew module thermal protection system and European Service Module, the second of three planned external spacecraft inspections.
Teams conducted this survey early in the mission to provide detailed images of the spacecraft's external surfaces after it had flown through the portion of Earth's orbit containing the majority of space debris, and teams reported no concerns after reviewing the imagery.
This second inspection during the return phase is being used to assess the overall condition of the spacecraft several days before re-entry.
Cameras on the four solar array wings have captured a series of still images. Engineers and flight controllers at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston will review the imagery over the coming days.
A final photographic survey will be conducted Friday as Orion continues its journey home.
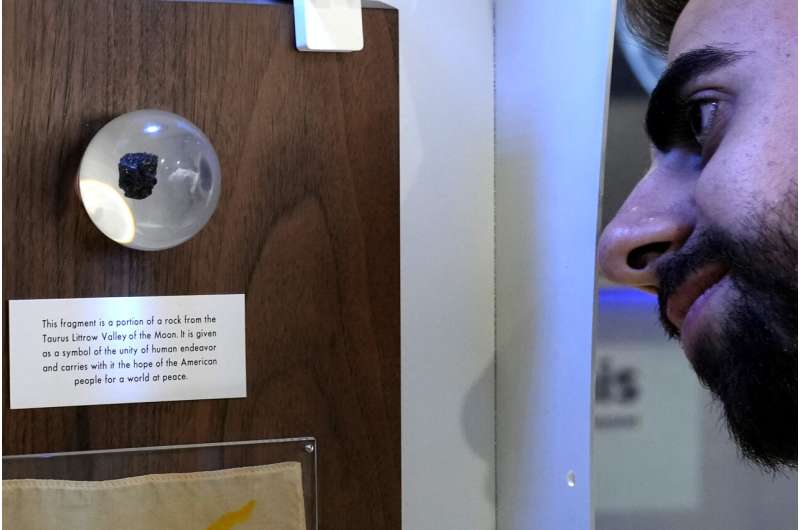
Rare Apollo mission moon rock back in Cyprus after 50 years

Sowing the seeds of future space travel
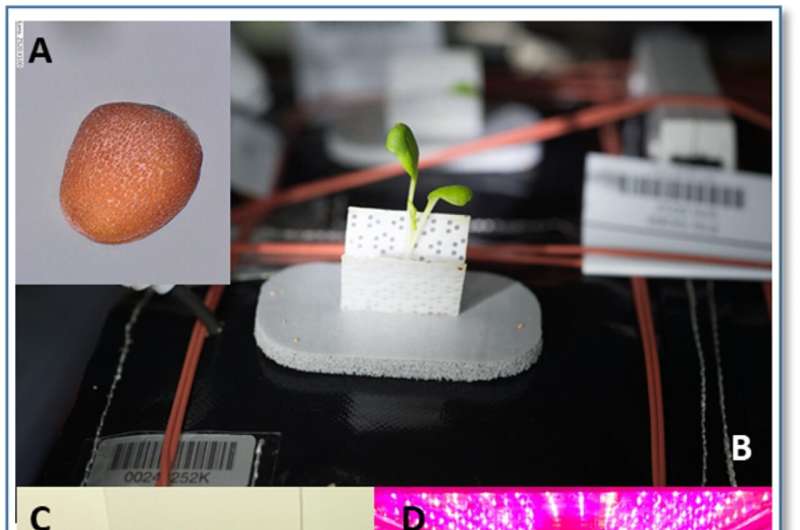

After 908 days in low Earth orbit, a small package on board the X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle-6 has come home to the delight of some biological scientists. Soon they will open an aluminum alloy container that holds samples of plant seeds that they hope can be used to sustain astronauts on long duration missions to the moon, Mars, and beyond.
Officially, it is known as a SEER experiment, short for Space Environment Exposure Research, a pathfinder mission supported by NASA's Biological and Physical Sciences Division (BPS) in collaboration with the US Air Force.
Unofficially, they're referred to as the "Thrive in Space" experiments—a way to underscore the stepping-stone research that scientists are undertaking to help advance their fundamental understanding of what it takes to grow and protect plants beyond our planet.