Copernical Team
Future of space engineering is model-based
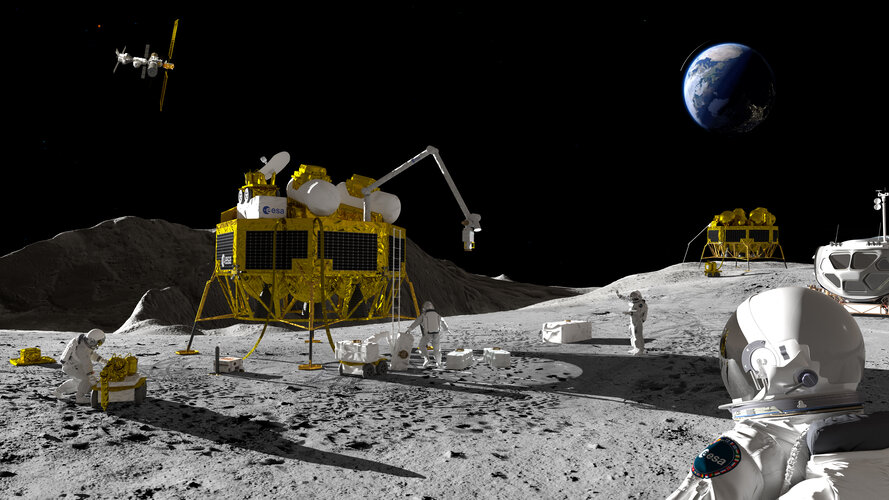
A hackathon challenged aerospace students to develop a detailed digital system model for a robotic assistant for astronauts on the Moon, able to identify key areas of interest in advance of any humans landing, guide them to their habitat and even rescue any moonwalkers in distress.
The winning team, from France’s Institut Supérieur de l'Aéronautique et de l'Espace, completed their task within just two weeks, using Model Based System Engineering to do so. This method involves creating digital models of space missions to manage their design, construction, test and operation – and has been highlighted by ESA Director General Josef
L3Harris To Acquire Aerojet Rocketdyne
 L3Harris Technologies (NYSE: LHX) and Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc. (NYSE: AJRD) together announced the signing of a definitive agreement for L3Harris to acquire Aerojet Rocketdyne for $58 per share, in an all-cash transaction valued at $4.7 billion, inclusive of net debt.
This marks L3Harris' second acquisition announcement of 2022, demonstrating its continued focus on delivering crit
L3Harris Technologies (NYSE: LHX) and Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc. (NYSE: AJRD) together announced the signing of a definitive agreement for L3Harris to acquire Aerojet Rocketdyne for $58 per share, in an all-cash transaction valued at $4.7 billion, inclusive of net debt.
This marks L3Harris' second acquisition announcement of 2022, demonstrating its continued focus on delivering crit Enjoy ESA’s Impact over the last quarter!

Enjoy ESA’s Impact over the last quarter!
Welcome to this edition of ESA Impact, an interactive publication covering stories and images from the fourth quarter of 2022.
Viasat's Ka-band in-flight connectivity system achieves STC on Gulfstream G450 aircraft
 Viasat Inc. (Nasdaq: VSAT) report that the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) approved the company's Ka-band In-flight Connectivity (IFC) solution for Gulfstream G450 aircraft, a large cabin jet often deployed on long-distance, international expeditions.
With this supplemental type certificate (STC) awarded by the FAA, Viasat's Ka-band connectivity system is now available on more than t
Viasat Inc. (Nasdaq: VSAT) report that the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) approved the company's Ka-band In-flight Connectivity (IFC) solution for Gulfstream G450 aircraft, a large cabin jet often deployed on long-distance, international expeditions.
With this supplemental type certificate (STC) awarded by the FAA, Viasat's Ka-band connectivity system is now available on more than t Voyager Space signs MoU with Canadian Space Agency
 Voyager Space, a global leader in space exploration, and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to jointly explore how the CSA and the Canadian space sector could play a role in the planning and development of Starlab, Voyager's planned commercial space station, and the George Washington Carver Science Park, Starlab's on-orbit laboratory.
This non-b
Voyager Space, a global leader in space exploration, and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to jointly explore how the CSA and the Canadian space sector could play a role in the planning and development of Starlab, Voyager's planned commercial space station, and the George Washington Carver Science Park, Starlab's on-orbit laboratory.
This non-b Measuring gamma-ray bursts' hidden energy unearths clues to the evolution of the universe
 Gamma-ray bursts are the most luminous explosions in the universe, allowing astrologists to observe intense gamma rays in short durations. Gamma-ray bursts are classified as either short or long, with long gamma-ray bursts being the result of massive stars dying out. Hence why they provide hidden clues about the evolution of the universe.
Gamma-ray bursts emit gamma rays as well as radio w
Gamma-ray bursts are the most luminous explosions in the universe, allowing astrologists to observe intense gamma rays in short durations. Gamma-ray bursts are classified as either short or long, with long gamma-ray bursts being the result of massive stars dying out. Hence why they provide hidden clues about the evolution of the universe.
Gamma-ray bursts emit gamma rays as well as radio w Rocket Lab reschedules 1st US launch to January
 Rocket Lab USA, Inc (Nasdaq: RKLB) ("Rocket Lab"), a leading launch and space systems company, has announced the launch window for its first Electron mission from U.S. soil has been rescheduled to January 2023.
The move of the planned launch window from December 2022 to early 2023 was driven by weather and the additional time that the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) at
Rocket Lab USA, Inc (Nasdaq: RKLB) ("Rocket Lab"), a leading launch and space systems company, has announced the launch window for its first Electron mission from U.S. soil has been rescheduled to January 2023.
The move of the planned launch window from December 2022 to early 2023 was driven by weather and the additional time that the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) at North Korea conducts 'final-stage test' for spy satellite: state media
 North Korea carried out an "important final-stage test" for the development of a spy satellite, which it will complete by April next year, state media said on Monday.
The report comes a day after Seoul's military said it had detected launches by Pyongyang of two medium-range ballistic missiles, the North's latest in a year of unprecedented weapons tests.
Analysts say developing such a sa
North Korea carried out an "important final-stage test" for the development of a spy satellite, which it will complete by April next year, state media said on Monday.
The report comes a day after Seoul's military said it had detected launches by Pyongyang of two medium-range ballistic missiles, the North's latest in a year of unprecedented weapons tests.
Analysts say developing such a sa China's space sector set to rocket into future
 Chen Li, who owns a restaurant in Longlou, a coastal township in China's southernmost province of Hainan, said he is grateful to the country's space industry because it has boosted business at his eatery in recent years.
"So many people came to Longlou before the launch of the Wentian space lab. There was 'a mountain of people, a sea of people'. A lot of tourists came to my restaurant to g
Chen Li, who owns a restaurant in Longlou, a coastal township in China's southernmost province of Hainan, said he is grateful to the country's space industry because it has boosted business at his eatery in recent years.
"So many people came to Longlou before the launch of the Wentian space lab. There was 'a mountain of people, a sea of people'. A lot of tourists came to my restaurant to g NanoAvionics to supply Constellr with two satellites to help saving 60 billion tons of water globally
 Kongsberg NanoAvionics has signed a contract with thermal data provider Constellr to supply it with two of its flagship MP42 microsatellite buses. Having recently raised 10 million euros, Germany-based Constellr will use the two satellites to develop the world's first scalable water stress monitoring system.
Collaborating since the very early days of the German startup, NanoAvionics has al
Kongsberg NanoAvionics has signed a contract with thermal data provider Constellr to supply it with two of its flagship MP42 microsatellite buses. Having recently raised 10 million euros, Germany-based Constellr will use the two satellites to develop the world's first scalable water stress monitoring system.
Collaborating since the very early days of the German startup, NanoAvionics has al