
Copernical Team
NASA-built greenhouse gas detector moves closer to launch
 A state-of-the-art imaging spectrometer, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, moved closer to launch this month after being delivered to a clean room at Planet Labs PBC (Planet) in San Francisco.
Designed and built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, this science instrument will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carb
A state-of-the-art imaging spectrometer, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, moved closer to launch this month after being delivered to a clean room at Planet Labs PBC (Planet) in San Francisco.
Designed and built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, this science instrument will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carb DARPA seeks tech solutions to create autonomous capabilities for commercial drones
 Commercial drone technology is advancing rapidly, providing cost-effective and robust capabilities for a variety of civil and military missions. As small aerial vehicles play increasingly important military roles on the battlefield, adversaries are developing electromagnetic countermeasures to disrupt communication links between operator and drone, forcing the vehicle to abort mission, return to
Commercial drone technology is advancing rapidly, providing cost-effective and robust capabilities for a variety of civil and military missions. As small aerial vehicles play increasingly important military roles on the battlefield, adversaries are developing electromagnetic countermeasures to disrupt communication links between operator and drone, forcing the vehicle to abort mission, return to China launches Yaogan 39 remote sensing satellite
 China launched a Long March 2D carrier rocket on Sunday afternoon at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan province to place several remote-sensing satellites into orbit, according to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp.
The State-owned space contractor said in a news release that the rocket blasted off at 12:13 pm and transported the Yaogan 39 satellites into their preset
China launched a Long March 2D carrier rocket on Sunday afternoon at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan province to place several remote-sensing satellites into orbit, according to China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp.
The State-owned space contractor said in a news release that the rocket blasted off at 12:13 pm and transported the Yaogan 39 satellites into their preset SpaceX deploys another 22 Starlink satellites
 Elon Musk's SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket with a payload of 22 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit late Tuesday.
The rocket launched at 11:38 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
SpaceX had said prior to launch that weather was 90% favorable for liftoff.
The orbitals were deposited into space where they will join
Elon Musk's SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket with a payload of 22 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit late Tuesday.
The rocket launched at 11:38 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
SpaceX had said prior to launch that weather was 90% favorable for liftoff.
The orbitals were deposited into space where they will join Trio of Sentinel satellites map methane super-emitters
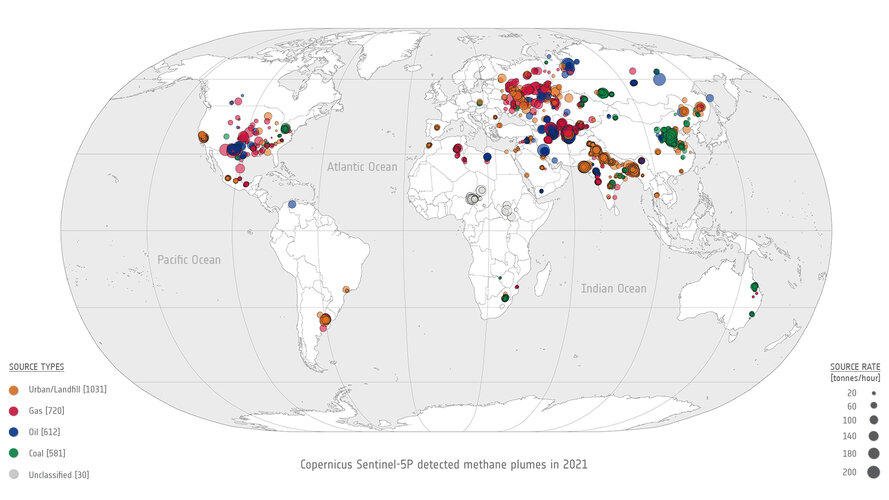
In the quest to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, detecting methane leaks – a potent contributor to global warming – has become increasingly vital. Researchers are harnessing the capabilities of cutting-edge satellite technology to monitor these leaks from space.
ESA Open Day in the framework of European Researchers’ Night

ESA will open its doors to members of the public at its Earth Observation centre in Frascati, near Rome, Italy, on 29 September, as part of its annual open day.
Spending time in space can harm the human body
 When 17 people were in orbit around the Earth all at the same time on May 30, 2023, it set a record. With NASA and other federal space agencies planning more manned missions and commercial companies bringing people to space, opportunities for human space travel are rapidly expanding.
However, traveling to space poses risks to the human body. Since NASA wants to send a manned mission to Mar
When 17 people were in orbit around the Earth all at the same time on May 30, 2023, it set a record. With NASA and other federal space agencies planning more manned missions and commercial companies bringing people to space, opportunities for human space travel are rapidly expanding.
However, traveling to space poses risks to the human body. Since NASA wants to send a manned mission to Mar Momentus to provide delivery service for Aarhus University payload
 Momentus Inc. (NASDAQ: MNTS) has signed a contract with Aarhus University for transportation and orbital delivery services in late 2024. Aarhus University will be flying its DISCO-II payload designed to provide climate monitoring. The university's DISCO-I payload was placed into Low-Earth Orbit during the Vigoride-6 mission that launched in April 2023. DISCO is the Danish Students CubeSat Progra
Momentus Inc. (NASDAQ: MNTS) has signed a contract with Aarhus University for transportation and orbital delivery services in late 2024. Aarhus University will be flying its DISCO-II payload designed to provide climate monitoring. The university's DISCO-I payload was placed into Low-Earth Orbit during the Vigoride-6 mission that launched in April 2023. DISCO is the Danish Students CubeSat Progra Iridium and McQ develop remote monitoring solution for Canadian Armed Forces in the Arctic
 Iridium Communications Inc. (NASDAQ: IRDM) is proud to announce its partner McQ Inc., in collaboration with designer and manufacturer Barnacle Systems, has introduced a remote monitoring solution for fixed assets in the Arctic supporting the Department of National Defense and Canadian Armed Forces (DND/CAF).
BRNKL Arctic Deploy is an innovative solution for the DND/CAF to monitor and secur
Iridium Communications Inc. (NASDAQ: IRDM) is proud to announce its partner McQ Inc., in collaboration with designer and manufacturer Barnacle Systems, has introduced a remote monitoring solution for fixed assets in the Arctic supporting the Department of National Defense and Canadian Armed Forces (DND/CAF).
BRNKL Arctic Deploy is an innovative solution for the DND/CAF to monitor and secur Terran Orbital announces pricing of Public Offering
 Terran Orbital Corporation (NYSE: LLAP) has announced the pricing of its previously announced public offering of 23,214,290 shares of its common stock (or common stock equivalents in lieu thereof) and warrants to purchase up to 23,214,290 shares of common stock, at a combined public offering price of $1.40 per share (or common stock equivalent in lieu thereof) and accompanying warrant.
The
Terran Orbital Corporation (NYSE: LLAP) has announced the pricing of its previously announced public offering of 23,214,290 shares of its common stock (or common stock equivalents in lieu thereof) and warrants to purchase up to 23,214,290 shares of common stock, at a combined public offering price of $1.40 per share (or common stock equivalent in lieu thereof) and accompanying warrant.
The 






























