Displaying items by tag: Earth observation
CGS SpA
CGS SpA is an Italian prime contractor for small satellites.
CGS SpA provides the user community with solutions for space science and space applications by:
- Exploiting the potential of small and medium satellite missions;
- Exploiting orbital and transportation systems;
- Focusing on the technologies that can be turned into products for scientific and application projects;
- Developing technologies for Earth Observation services.
NAPEOS software
NAPEOS, the NAvigation Package for Earth Observation Satellites, is a state of the art software system for GNSS data processing providing results with a very accuracy.
NAPEOS is developed and maintained by the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) of the European Space Agency (ESA). The NAPEOS developments started around 1995. In 2003 the GNSS capabilties started to be added a project that was finished in 2007. After significant testing the navigation support office at ESOC (OPS-GN) started to use the NAPEOS software in January 2008 for all its IGS activities.
A significant number of companies and individuals have been involved in the development of the NAPEOS software. Of course the major part of the GNSS work has been done at the navigation support office (OPS-GN) at ESOC with a special mentioning for the company GMV. GMV has been responsible for major parts of the actual programming of the NAPEOS source code.
At OPS-GN, in ESOC, NAPEOS supports all the activities in the International GNSS Service (IGS), the International DORIS Service (IDS), the International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS), and other international scientific communities. NAPEOS is also used for the routine precise orbit determination (POD) of several LEO missions, e.g., the ESA ENVISAT mission.
NAPEOS allows fully automated, robust, and reliable GNSS processing at very high accuracy levels with processing efficiency.
Commercial services using NAPEOS are proposed by the company PosiTim.
EOS payload family
The EOS family of payload products offers a range of imaging on-board systems for Earth observation satellites.
The EOS payload products are proposed by the company Satrec Initiative.
Aqua (EOS PM)
Aqua (EOS PM-1) is a multi-national NASA scientific research satellite in orbit around the Earth, studying the precipitation, evaporation, and cycling of water.
It is the second major component of the Earth Observing System (EOS) preceded by Terra (launched 1999) and followed by Aura (launched 2004).
MODIS instrument
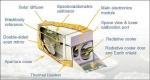
The Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a payload scientific instrument launched into Earth orbit by NASA in 1999 on board the Terra (EOS AM) Satellite, and in 2002 on board the Aqua (EOS PM) satellite.
The instruments capture data in 36 spectral bands ranging in wavelength from 0.4 µm to 14.4 µm and at varying spatial resolutions (2 bands at 250 m, 5 bands at 500 m and 29 bands at 1 km). Together the instruments image the entire Earth every 1 to 2 days. They are designed to provide measurements in large-scale global dynamics including changes in Earth's cloud cover, radiation budget and processes occurring in the oceans, on land, and in the lower atmosphere. Three on-board calibrators (a solar diffuser combined with a solar diffuser stability monitor, a spectral radiometric calibration assembly, and a black body) provide in-flight calibration. MODIS has used the Marine Optical Buoy for vicarious calibration.
GOLD mission
The mission, known as the Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk, or GOLD, involves imaging Earth's upper atmosphere from a geostationary orbit some 22,000 miles above the planet.
The mission is expected to have a direct impact on the understanding of space weather like geomagnetic storms that alter the temperature and composition of Earth's atmosphere, which can disrupt communication and navigation satellites, affecting everything from automobile GPS and cell phone coverage to television programming.
The GOLD mission is part of NASA's new Heliospheric Explorer Program designed to provide space observations to study Earth's ionosphere and thermosphere. The mission is slated for launch in 2017.
National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA)
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) is a combat support agency of the United States Department of Defense.
NGA provides timely, relevant, and accurate geospatial intelligence in support of USA national security.
Its primary mission is collecting, analyzing, and distributing geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) in support of national security. NGA was formerly known as the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA). In addition, NGA is a key component of the United States Intelligence Community.
The NGA Commercial Archive Data
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), in partnership with the Civil Applications Committee (CAC), of which NASA is a member, provides access to its immense archive of unclassified commercial high-resolution satellite data to non-DOD government agencies under terms of its NextView contract. See this website.
ISERV Pathfinder
the ISS SERVIR Environmental Research and Visualization System (ISERV) is an image acquisition installed on the ISS Destiny module to take photos of Earth from the ISS.
ISERV is a commercial camera, telescope and pointing system operated remotely from Earth by researchers at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. With ISERV NASA will be able to provide high resolution images of Earth!
DigitalGlobe
DigitalGlobe of Longmont, Colorado, USA, is a commercial vendor of space imagery and geospatial content. It is an operator of civilian remote sensing spacecraft. The company went public on the New York Stock Exchange on 14 May 2009.
Satellites:
- WorldView family of satellites.
- QuickBird
- EarlyBird
Origin:
in 1992, the company Worldview Imaging Corporation was founded.
In 1995, Worldview became EarthWatch Incorporated, after merging with a division of Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp.
In 2001, EarthWatch became DigitalGlobe.
Proba (satellite family)
PROBA (Project for On-Board Autonomy) is a family of small Earth observation satellites, part of the ESA's MicroSat program.
Proba-1 was launched by ISRO in 2001. It is a technology demonstrator turned operational Earth observation mission - ESA's smallest, less than a cubic metre in volume. Proba-1's main instrument is the Compact High Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (CHRIS), acquiring 13 square km scenes at 17 m spatial resolution in 18 user-selected visible and near-infrared wavelengths. This agile satellite can also deliver up to five different viewing angles. Nearly 20,000 environmental science images have been acquired. This small boxlike system (40×60×80 cm; 95 kg), with solar panel collectors on its surface, has remarkable image-making qualities. It hosts two Earth Observation instruments (dubbed CHRIS and HRC). It is a hyperspectral system (200 narrow bands) that image at 30 m, plus three in the visible that have 15 m resolution.
Proba-2, the second satellite in the Proba-series, has been launched on November 2, 2009, together with the SMOS mission. Proba 2 is a 0.6 × 0.6 × 0.8 meter, box-shaped structure weighing 130 kg with two deployable solar panels. It has a total of four instruments; two complementary solar observation instruments dubbed SWAP and LYRA, and two plasma measurement instruments dubbed TPMU and DSLP.
Further planned satellites in the Proba series are the formation flight Proba-3 and Proba-V (Proba Vegetation). They are on-going developments without defined launch dates.