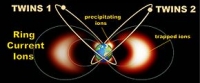
Two Wide-Angle Imaging Neutral-Atom Spectrometers (TWINS) are a pair of NASA instruments aboard two United States National Reconnaissance Office satellites in Molniya orbits.
TWINS was designed to provide stereo images of the Earth's ring current. The first instrument, TWINS-1, was launched aboard USA-184 on 28 June 2006. TWINS-2 followed aboard USA-200 on March 13, 2008. Each instrument consists of an energetic neutral atom imager and a Lyman alpha detector. The ENA imager provides indirect remote sensing of the ring current ions, and the Lyman alpha detector gives a measure of the neutral hydrogen cloud about the Earth, known as the geocorona.
The TWINS prime mission lasted two years, from 2008 to 2010, and has been followed by an extended mission which is ongoing (June 2013).