
Copernical Team
Image: The largest antenna ever tested in ESA's Hertz radio frequency test chamber
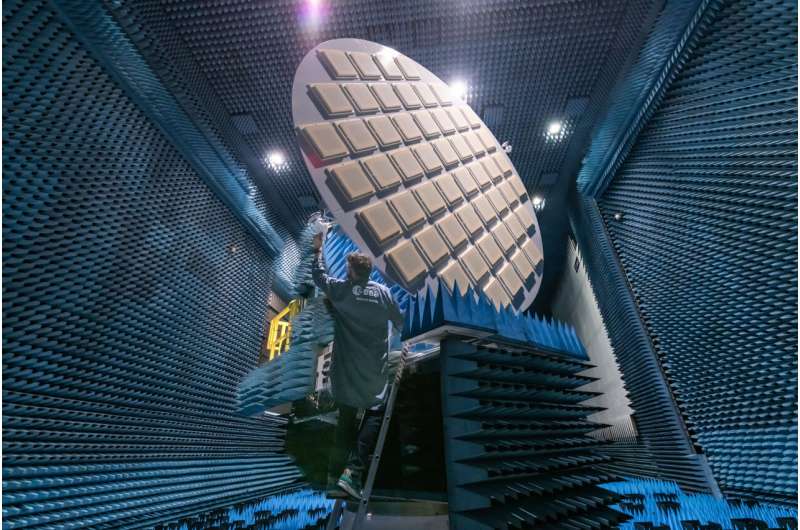

The largest antenna ever tested in ESA's Hertz radio frequency test chamber is this 5-m diameter transponder antenna, which will operate down on the ground to help calibrate the Biomass mission, which will chart all the forests on Earth.
"This is a particularly challenging test campaign both in terms of the size of the antenna and the very low P-band frequency that Biomass will be using, which allows it to pierce through forest canopies to acquire individual trees," explains ESA antenna engineer Luis Rolo, overseeing the test campaign.
"Usually when we test a large satellite here, its antenna is significantly smaller, typically between 0.5 and 2 meters across. But this entire structure is a radiating antenna in its own right, its sides coming near to the chamber walls.
"What this means is that the testing process highlight some aspects of the chamber we've never seen before, even after many years of testing. But we've come up with a measurement method involving multiple acquisitions from different spots within the chamber, combined carefully to subtract such environmental effects, yielding very accurate results.
Image: Axiom Mission 1 at Pad 39A and Artemis I at Pad 39B
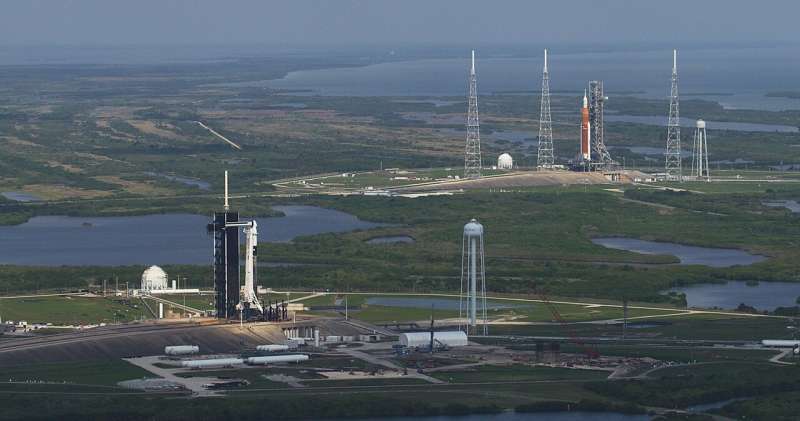

Axiom Mission 1 (Ax-1) is in the foreground on Launch Pad 39A with NASA's Artemis I in the background on Launch Pad 39B on April 6, 2022.
This is the first time two totally different types of rockets and spacecraft designed to carry humans are on the sister pads at the same time—but it won't be the last as NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida continues to grow as a multi-user spaceport to launch both government and commercial rockets.
Ax-1 liftoff is scheduled at 11:17 a.m. EDT Friday, April 8, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Explore further
Register for Living Planet Symposium 2022
Register for Living Planet Symposium 2022
Redirecting ESA programmes in response to geopolitical crisis
Press Release N° 16–2022
Following the Russian aggression against Ukraine, ESA’s Director General has initiated a comprehensive review of all activities currently undertaken in cooperation with Russia and Ukraine. The objective is to determine the possible consequences of this new geopolitical context for ESA programmes and activities and to create a more resilient and robust space infrastructure for Europe.
Webb’s coldest instrument reaches operating temperature
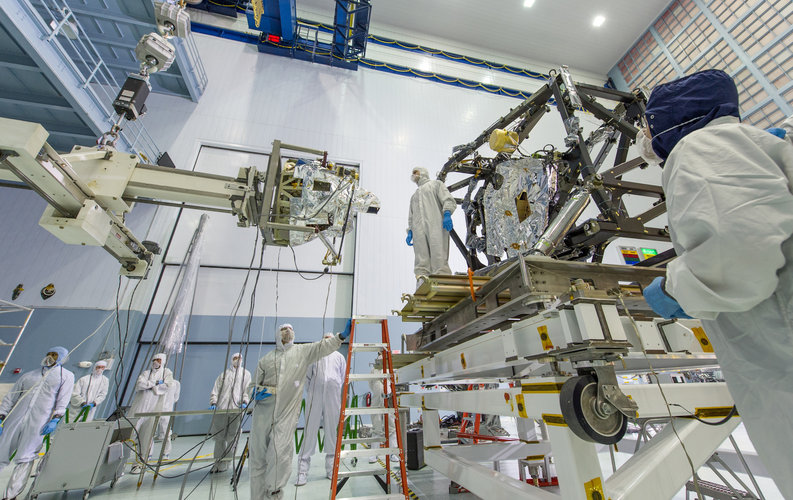

With help from a cryocooler, Webb's Mid-Infrared Instrument has dropped down to just a few degrees above the lowest temperature matter can reach and is ready for calibration.
Astronomers find freaky stars covered in helium burning ashes
 A German team of astronomers from the Universities of Tubingen and Potsdam, led by Prof. Klaus Werner, have discovered a new type of weird stars.
The spectra of the star sample, obtained by Large Binocular Telescope in Arizona, USA, and the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) based at Xinglong and operated by the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chi
A German team of astronomers from the Universities of Tubingen and Potsdam, led by Prof. Klaus Werner, have discovered a new type of weird stars.
The spectra of the star sample, obtained by Large Binocular Telescope in Arizona, USA, and the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) based at Xinglong and operated by the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chi ESO telescope captures surprising changes in Neptune's temperatures
 An international team of astronomers have used ground-based telescopes, including the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (ESO's VLT), to track Neptune's atmospheric temperatures over a 17-year period. They found a surprising drop in Neptune's global temperatures followed by a dramatic warming at its south pole.
"This change was unexpected," says Michael Roman, a postdocto
An international team of astronomers have used ground-based telescopes, including the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (ESO's VLT), to track Neptune's atmospheric temperatures over a 17-year period. They found a surprising drop in Neptune's global temperatures followed by a dramatic warming at its south pole.
"This change was unexpected," says Michael Roman, a postdocto Four billion-year-old relic from early solar system heading our way
 An enormous comet - approximately 80 miles across, more than twice the width of Rhode Island - is heading our way at 22,000 miles per hour from the edge of the solar system. Fortunately, it will never get closer than 1 billion miles from the sun, which is slightly farther from Earth than Saturn; that will be in 2031.
Comets, among the oldest objects in the solar system, are icy bodies that
An enormous comet - approximately 80 miles across, more than twice the width of Rhode Island - is heading our way at 22,000 miles per hour from the edge of the solar system. Fortunately, it will never get closer than 1 billion miles from the sun, which is slightly farther from Earth than Saturn; that will be in 2031.
Comets, among the oldest objects in the solar system, are icy bodies that Sols 3442-3443: Deoch-an-Doris
 In Scots Gaelic, "deoch-an-doris" loosely means "one for the road." Today we planned one more set of investigations on the fascinating Feorachas outcrop before we leave it behind forever.
We first visited it over a month ago as we were climbing up the Greenheugh Pediment and now we have given it a more thorough investigation on the way down thanks to some crafty driving by Curiosity's rove
In Scots Gaelic, "deoch-an-doris" loosely means "one for the road." Today we planned one more set of investigations on the fascinating Feorachas outcrop before we leave it behind forever.
We first visited it over a month ago as we were climbing up the Greenheugh Pediment and now we have given it a more thorough investigation on the way down thanks to some crafty driving by Curiosity's rove Divide and conquer: Mars rovers to be superseded by swarms of two-wheeled robots
 Skoltech scientists have proposed a concept for a modular Mars exploration rover. Leveraging the power of cooperative robotics, the new system described in an Acta Astronautica paper consists of four two-wheeled robots that can operate independently or combine in various constellations. According to the study, that approach will enable longer exploration missions that gather more information abo
Skoltech scientists have proposed a concept for a modular Mars exploration rover. Leveraging the power of cooperative robotics, the new system described in an Acta Astronautica paper consists of four two-wheeled robots that can operate independently or combine in various constellations. According to the study, that approach will enable longer exploration missions that gather more information abo 































