Copernical Team
NASA's InSight Records Monster Quake on Mars
 NASA's InSight Mars lander has detected the largest quake ever observed on another planet: an estimated magnitude 5 temblor that occurred on May 4, 2022, the 1,222nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This adds to the catalog of more than 1,313 quakes InSight has detected since landing on Mars in November 2018. The largest previously recorded quake was an estimated magnitude 4.2 detected Aug.
NASA's InSight Mars lander has detected the largest quake ever observed on another planet: an estimated magnitude 5 temblor that occurred on May 4, 2022, the 1,222nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This adds to the catalog of more than 1,313 quakes InSight has detected since landing on Mars in November 2018. The largest previously recorded quake was an estimated magnitude 4.2 detected Aug. UK blogger detained in Baikonur confirms release from custody after issued fine
 UK blogger Benjamin Rich, who was recently detained near a launch pad in the Baikonur spaceport, said on Sunday that the Russian police released him after questioning and handed out a fine.
On Saturday, Roscosmos chief Dmitry Rogozin said that UK citizen Benjamin Rich and a Belarusian citizen Alina Zelupa were detained during unauthorised passage near the 112 launch pad in Baikonur and tak
UK blogger Benjamin Rich, who was recently detained near a launch pad in the Baikonur spaceport, said on Sunday that the Russian police released him after questioning and handed out a fine.
On Saturday, Roscosmos chief Dmitry Rogozin said that UK citizen Benjamin Rich and a Belarusian citizen Alina Zelupa were detained during unauthorised passage near the 112 launch pad in Baikonur and tak Phantom Space places order for more than 200 Ursa Major rocket engines
 Phantom Space Corporation, a space applications company, has announced an agreement to purchase more than 200 rocket engines from Ursa Major, America's only independent pure-play rocket propulsion company. The order includes Ursa Major's 5,000-Pound Thrust Hadley engines and the new 50,000-pound thrust Ripley engines. By using Ursa Major's Hadley engines, Phantom's Daytona rocket is slated for o
Phantom Space Corporation, a space applications company, has announced an agreement to purchase more than 200 rocket engines from Ursa Major, America's only independent pure-play rocket propulsion company. The order includes Ursa Major's 5,000-Pound Thrust Hadley engines and the new 50,000-pound thrust Ripley engines. By using Ursa Major's Hadley engines, Phantom's Daytona rocket is slated for o DLR Land Down Under
 In preparation for their ReFEx rocket launch campaign from Australia, the DLR team are visiting spaceport partner Southern Launch. As part of their visit, the DLR team will be visiting Southern Launch's spaceports; the Whalers Way Orbital Launch Complex and the Koonibba Test Range, as well as meeting with key personnel across the Australian space industry.
DLR is the Federal Republic of Ge
In preparation for their ReFEx rocket launch campaign from Australia, the DLR team are visiting spaceport partner Southern Launch. As part of their visit, the DLR team will be visiting Southern Launch's spaceports; the Whalers Way Orbital Launch Complex and the Koonibba Test Range, as well as meeting with key personnel across the Australian space industry.
DLR is the Federal Republic of Ge Roscosmos boss calls to hold Elon Musk 'accountable' for supporting Ukraine 'fascists'
 Elon Musk has responded after Dmitry Rogozin, the head of Russia's federal space agency Roscosmos, sent a message to Russian media accusing him of supporting "fascist forces" in Ukraine.
The accusation by Rogozin, shared to Twitter by Musk, comes after the chief executive of SpaceX sent user terminals for its Starlink satellite-internet system to Ukraine in February at the request of offic
Elon Musk has responded after Dmitry Rogozin, the head of Russia's federal space agency Roscosmos, sent a message to Russian media accusing him of supporting "fascist forces" in Ukraine.
The accusation by Rogozin, shared to Twitter by Musk, comes after the chief executive of SpaceX sent user terminals for its Starlink satellite-internet system to Ukraine in February at the request of offic Virgin Orbit announces next launch, dubbed 'Straight Up'
 Virgin Orbit (Nasdaq: VORB) has entered flight preparation mode for its forthcoming launch, Straight Up, that will support the United States Space Force's STP-28A mission. After departing Virgin Orbit's Long Beach rocket factory on Thursday, April 28, 2022, the rocket arrived at the Mojave Air and Space Port. It will support the Rocket Systems Launch Program (RSLP) and will carry payloads for th
Virgin Orbit (Nasdaq: VORB) has entered flight preparation mode for its forthcoming launch, Straight Up, that will support the United States Space Force's STP-28A mission. After departing Virgin Orbit's Long Beach rocket factory on Thursday, April 28, 2022, the rocket arrived at the Mojave Air and Space Port. It will support the Rocket Systems Launch Program (RSLP) and will carry payloads for th MIRI's sharper view hints at new possibilities for science
 The James Webb Space Telescope is aligned across all four of its science instruments, as seen in a previous engineering image showing the observatory's full field of view. Now, we take a closer look at that same image, focusing on Webb's coldest instrument: the Mid-Infrared Instrument, or MIRI.
The MIRI test image (at 7.7 microns) shows part of the Large Magellanic Cloud. This small satell
The James Webb Space Telescope is aligned across all four of its science instruments, as seen in a previous engineering image showing the observatory's full field of view. Now, we take a closer look at that same image, focusing on Webb's coldest instrument: the Mid-Infrared Instrument, or MIRI.
The MIRI test image (at 7.7 microns) shows part of the Large Magellanic Cloud. This small satell Webb telescope's first full color, scientific images coming in July
Get ready for a summer blockbuster.
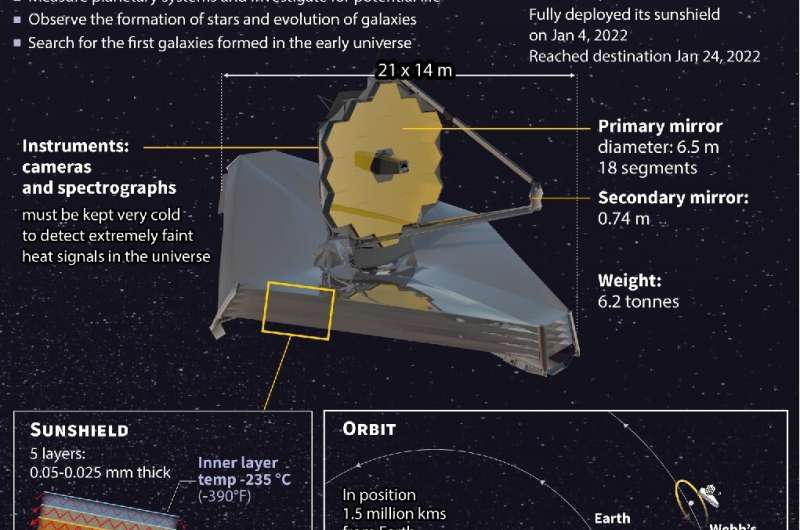
The James Webb Space Telescope will produce "spectacular color images" of the cosmos in mid-July—its first observations dedicated to its mission of scientific discovery, an astronomer overseeing the project said Monday.
The successor to Hubble has spent the last five months aligning its instruments in preparation for the big reveal, with scientists deliberately remaining coy about where the cameras will be pointed.
"We'd really like it to be a surprise," Klaus Pontoppidan, a scientist at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore told reporters, adding that the secrecy was partly due to the first targets not yet being finalized.
NASA and its partners the European Space Agency (ESA) and Canadian Space Agency (CSA) formed a committee to create a ranked list of objects, which they now intend to work through.
What does micrometeoroid damage do to gossamer structures like Webb's sunshield?
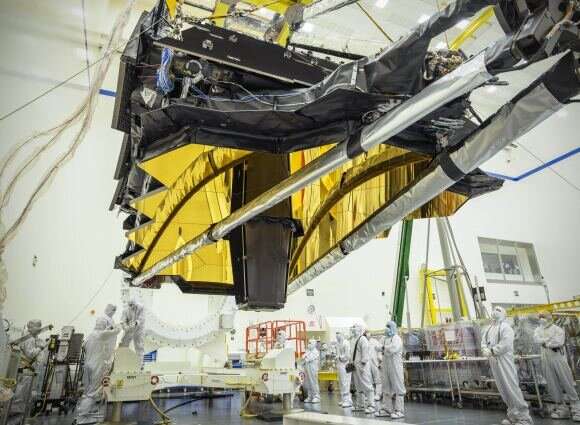

Tiny little bullets flood the solar system, each micrometeoroid a potential hazard. New research has found that the James Webb Space Telescope's thin sunshields, and future inflatable spacecraft, may be at risk.
A micrometeoroid is a tiny bit of space junk usually weighing less than a gram. Some of them are the leftover bits of the countless collisions that have occurred over the past 4.5 billion years of the history of the solar system. Most, however, come from the dust cloud that initially collapsed to form our solar system, and never got to be a part of a larger body.
MIRI and Spitzer comparison image
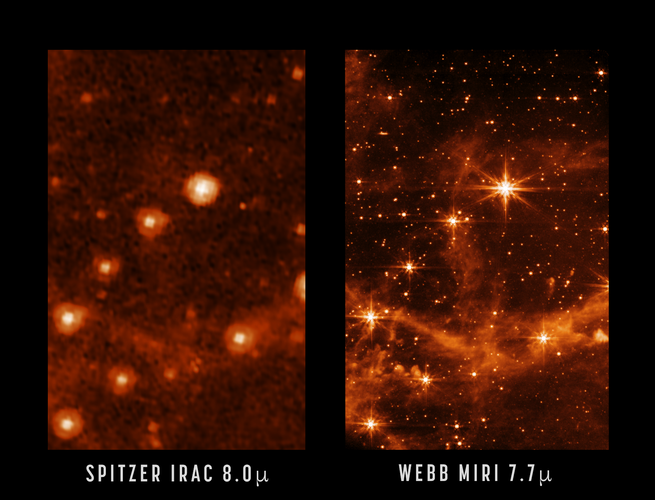 Image:
Image:
Click here to download the gif.
The James Webb Space Telescope is aligned across all four of its science instruments, as seen in a previous engineering image showing the observatory’s full field of view. Now, we take a closer look at that same image, focusing on Webb’s coldest instrument: the Mid-Infrared Instrument, or MIRI.
The MIRI test image (at 7.7 microns) shows part of the Large Magellanic Cloud. This small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way provided a dense star field to test Webb’s performance.
Here, a close-up of the MIRI image is compared to a past image