Displaying items by tag: rocket
Vega - rocket
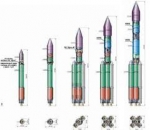
Vega (Vettore Europeo di Generazione Avanzata - European Advanced Generation Carrier) is an expendable launch system developed for Arianespace jointly by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and the European Space Agency (ESA). Italy is the leading contributor to the Vega program of ESA; other participants include France, Belgium, Spain, The Netherlands, Switzerland and Sweden. 1) 2) 3) 4)
The program began in 1998, it is managed jointly by an IPT (Integrated Project Team) composed of staff from ESA, ASI and CNES. The industrial consortium for the construction of the launcher is lead by the prime contractor ELV S.p.A. of Italy.
Instarocket App
Instarocket is a touch based program to perform early conceptual sizing on a 2 stage liquid launch vehicle.
Similar mathematics are found in ZPFCs (Zero Point Frontiers Corp) Level 0 Launch Vehicle design Process.
Instarocket is ideal for college or professional engineers needing a rough sizing solution for a 2 stage LV.
Typical results are achieved in less than 5 minutes.
App: https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/instarocket/id455325630
Aerojet Rocketdyne
Aerojet Rocketdyne is an American rocket and missile propulsion manufacturer.
Aerojet manufactures rocket motor, and is providing propulsion and energetics to the space, missile defense, strategic, tactical missile and armaments areas in support of domestic and international markets.
Headquartered in Sacramento, California, the company is owned by GenCorp. Aerojet Rocketdyne was formed in 2013 when Aerojet and Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne were merged, following the latter's acquisition by GenCorp from Pratt & Whitney.
Pegasus rocket
The Pegasus rocket is an air-launched winged space launch vehicle capable of carrying small, unmanned payloads (443 kilograms (980 lb)) into low Earth orbit.
It became operational in 1990 and remains so as of 2013. It is air-launched, as part of an expendable launch system developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation (Orbital). Three main stages burning solid propellant provide the thrust. It flies as a rocket-powered aircraft before leaving the atmosphere. The Pegasus is carried aloft below a carrier aircraft and launched at approximately 40,000 ft (12,000 m). The carrier aircraft provides flexibility to launch the rocket from anywhere rather than just a fixed pad. A high-altitude, winged flight launch also allows the rocket to avoid flight in the densest part of the atmosphere where a larger launch vehicle, carrying more fuel, would be needed to overcome air friction and gravity.
Angara rocket
The Angara rocket family is a family of space-launch vehicles being developed by the Moscow-based Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center.
(May 2013:) The rockets, which are to provide lifting capabilities between 2,000 and 40,500 kg into low earth orbit, are intended to become the mainstay of the Russian unmanned launcher fleet in the future and replace several existing systems.
Magellan Aerospace
Magellan Aerospace designs and manufactures an array of space and rocket systems.
Magellan's engineering team can develop rocket motors systems to suit custom applications or tailor an existing design to meet specific mission requirements. Their privately operated propellant plant has the ability to develop, mix, cast and cure rocket propellent.
Magellan is providing customers with solutions for space missions that include sounding rockets and payloads, space shuttle payloads, International Space Station payloads, and spacecraft buses and integration services.
Grasshopper (rocket)
Grasshopper is an experimental technology-demonstrator, suborbital reusable launch vehicle (RLV), a vertical takeoff, vertical landing (VTVL) rocket announced in 2011 for low-altitude testing that began in 2012.
Grasshopper is being developed and tested by Space Exploration Technologies (SpaceX) in order to assist development of the reusable Falcon 9 and reusable Falcon Heavy rockets, which will require vertical landings of the near-empty Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy first-stage tanks and engine assemblies.
Grasshopper is one element of the multi-element SpaceX reusable rocket launching system test program, a program that includes both low-altitude, low-speed testing of the Grasshopper vehicle at SpaceX' Texas test site, as well as high-altitude, high-speed controlled-descent tests of post-mission (spent) Falcon 9 booster stages on Falcon 9 commercial missions beginning in mid-2013.
Aerojet
[ merged in 2013 in Aerojet Rocketdyne ]
Aerojet was an American rocket and missile propulsion manufacturer based primarily in Rancho Cordova, California, with divisions in Redmond, Washington, Orange, Gainesville (both in Virginia) and Camden, Arkansas.
Aerojet was owned by GenCorp. It was one of the rare companies that provide both solid rocket motors and liquid rocket engines. Its products include a range of motors, from main engines used on a number of NASA vehicles and ballistic missiles, down to station-keeping thrusters for spacecraft. The propulsion devices include rocket motors as large as the EELV Atlas V strap-on rocket boosters.
Aerojet provided almost all of the USA Army's tactical missile rocket motors. They develop and manufacture a range of air breathing ramjet and scramjet engines. They also do research in the area of electric ion and Hall effect thrusters.
Dnepr rocket
The Dnepr rocket is a space launch vehicle named after the Dnieper River.
It is a converted ICBM used for launching artificial satellites into orbit, operated by the launch service provider ISC Kosmotras. The first launch, on April 21, 1999, successfully placed UoSAT-12, a 350 kg demonstration mini-satellite, into a 650 km circular Low Earth orbit.
The Dnepr is based on the R-36MUTTH ICBM – called the SS-18 Satan by NATO.
ARCA Space
ARCA Space is a non profit organization with main objective being the exploration and colonization of space.
In order to reach these objectives, ARCA builds and launches cost effective space vehicles. ARCA Space is using technologies already existing, in an innovative ways.