Blow a Cosmic Kiss
Friday, 25 March 2022 09:39 Image:
Image:
We spy from way up high an ESA astronaut dangling from the International Space Station.
Matthias Maurer performed his first spacewalk during his Cosmic Kiss mission yesterday with fellow astronaut Raja Chari of NASA. Extravehicular activity or EVA 80 lasted 6 hours and 54 minutes and was not without some excitement.
An hour into the spacewalk, the camera and light assembly on Matthias’ helmet needed some readjustments, which Raja was able to fix using some wiring. The duo were then able to carry on with the tasks, which included installing hoses on a radiator beam valve module that helps regulate Space
On icy moon Enceladus, expansion cracks let inner ocean boil out
Friday, 25 March 2022 08:56 In 2006, the Cassini spacecraft recorded geyser curtains shooting forth from "tiger stripe" fissures near the south pole of Saturn's moon Enceladus - sometimes as much as 200 kilograms of water per second. A new study suggests how expanding ice during millennia-long cooling cycles could sometimes crack the moon's icy shell and let its inner ocean out, providing a possible explanation for the gey
In 2006, the Cassini spacecraft recorded geyser curtains shooting forth from "tiger stripe" fissures near the south pole of Saturn's moon Enceladus - sometimes as much as 200 kilograms of water per second. A new study suggests how expanding ice during millennia-long cooling cycles could sometimes crack the moon's icy shell and let its inner ocean out, providing a possible explanation for the gey Space X's Crew-4 Dragon capsule named 'Freedom'
Friday, 25 March 2022 08:43 Space X's fourth Dragon capsule to carry astronauts to space has been named "Freedom," bringing the name of the first capsule to fly an American into space to a new generation.
The fourth Dragon mission to carry astronauts is set to launch from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station on April 19.
The mission was originally slated to launch on Apr
Space X's fourth Dragon capsule to carry astronauts to space has been named "Freedom," bringing the name of the first capsule to fly an American into space to a new generation.
The fourth Dragon mission to carry astronauts is set to launch from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station on April 19.
The mission was originally slated to launch on Apr Earth from Space: Carrara, Italy
Friday, 25 March 2022 08:00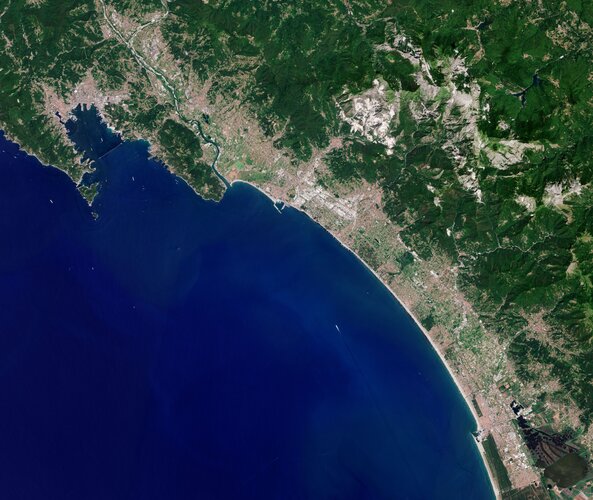
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Carrara – an Italian city known especially for its world-famous marble.
Northrop Grumman says customers are ‘lined up’ for on-orbit satellite servicing
Thursday, 24 March 2022 21:12
SpaceLogistics, a satellite-servicing firm owned by Northrop Grumman, last week successfully fired the electric propulsion system it is developing for the Mission Extension Pods it plans to launch in 2024.
The post Northrop Grumman says customers are ‘lined up’ for on-orbit satellite servicing appeared first on SpaceNews.
Panelists agree hiring remains the biggest challenge
Thursday, 24 March 2022 18:43
Hiring remains the most serious challenge space companies face.
The post Panelists agree hiring remains the biggest challenge appeared first on SpaceNews.
NASA finalizes plans for its next cosmic mapmaker
Thursday, 24 March 2022 17:57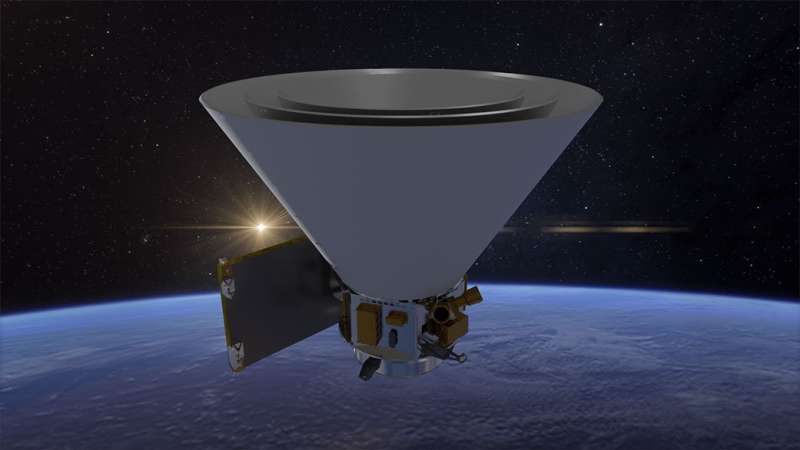
NASA's upcoming SPHEREx mission will have some similarities with the James Webb Space Telescope. But the two observatories will take dramatically different approaches to studying the sky.
The SPHEREx mission will be able to scan the entire sky every six months and create a map of the cosmos unlike any before. Scheduled to launch no later than April 2025, it will probe what happened within the first second after the Big Bang, how galaxies form and evolve, and the prevalence of molecules critical to the formation of life, like water, locked away as ice in our galaxy.
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope continues multi-instrument alignment
Thursday, 24 March 2022 17:56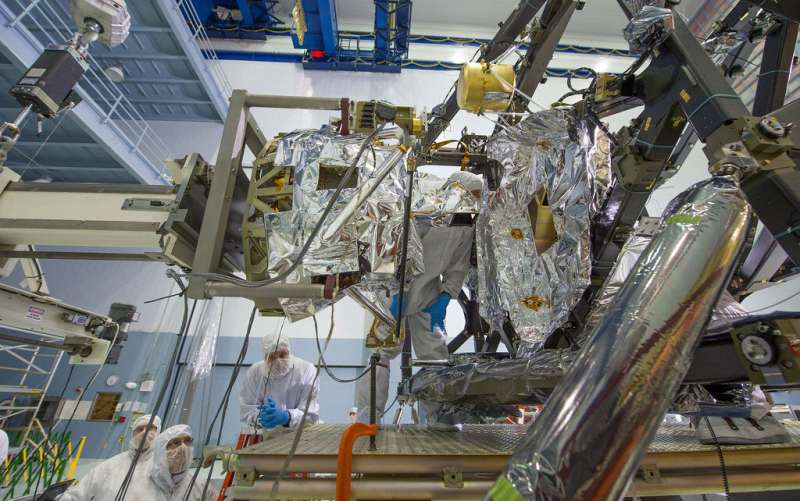
While telescope alignment continues, the James Webb Space Telescope's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) is still in cooldown mode. MIRI, which will be the coldest of Webb's four instruments, is the only instrument that will be actively cooled by a cryogenic refrigerator, or cryocooler. This cryocooler uses helium gas to carry heat from MIRI's optics and detectors out to the warm side of the sunshield. To manage the cooldown process, MIRI also has heaters onboard, to protect its sensitive components from the risk of ice forming. The Webb team has begun progressively adjusting both the cryocooler and these heaters, to ensure a slow, controlled, stable cooldown for the instrument. Soon, the team will turn off MIRI's heaters entirely, to bring the instrument down to its operating temperature of less than 7 kelvins (-447 degrees Fahrenheit, or -266 degrees Celsius).
In the meantime, after achieving alignment with the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), Webb engineers have begun aligning the telescope to the remaining near-infrared instruments, a six-week process.
Accelerating satellite production timelines improving market health
Thursday, 24 March 2022 16:43
Satellite makers are hopeful that higher frequency production rates will facilitate more innovation in the market, and fortify supply chains disrupted by the pandemic.
The post Accelerating satellite production timelines improving market health appeared first on SpaceNews.
Millennium Space to launch to orbit a 3D printed satellite structure
Thursday, 24 March 2022 14:56
Millennium Space Systems plans to launch to orbit a 3D printed metal flight structure the company intends to use to build its next generation of satellite buses.
The post Millennium Space to launch to orbit a 3D printed satellite structure appeared first on SpaceNews.
Tracking sunspots up close
Thursday, 24 March 2022 14:45US Space Force Cis-lunar Highway Patrol System to patrol around the moon
Thursday, 24 March 2022 14:09
As human activity extends outward into the solar system, we'll need a way to keep track of space junk, and the growing number of missions around the moon and beyond.
Recently, the newly-formed U.S. Space Force announced plans to create CHPS, the Cis-lunar Highway Patrol System. Despite an acronym harking back to a certain cheesy TV series in the 1970s, CHPS will provide a serious look at space traffic further out in orbit around the Earth-moon system. Such a network is vital, as private companies and space agencies are set to return to the moon in a big way in the coming decade.
"The CHPS program will deliver space domain awareness, in a region that is one thousand times greater than our current area of responsibility," says CHPS program manager Michael Lopez in a recent press release. "AFRL is interested in hearing from companies that may have ideas that differ from ours, and could contribute to the satellite's capabilities."
The problem was highlighted recently with the impact of a rocket booster on the moon on March 4.
Zooming into the Sun with Solar Orbiter
Thursday, 24 March 2022 13:00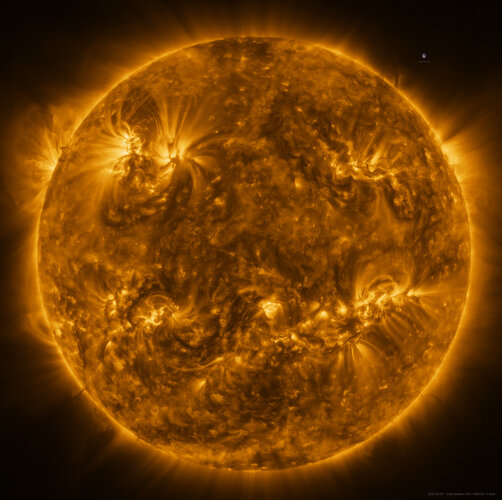
Solar Orbiter’s latest images shows the full Sun in unprecedented detail. They were taken on 7 March, when the spacecraft was crossing directly between the Earth and Sun.
Arianespace and SpaceX work to adjust launch manifests
Thursday, 24 March 2022 12:59
Arianespace says it is working to remanifest payloads that were to launch on Soyuz rockets while SpaceX says it’s finding ways to accommodate new customers on its vehicles.
The post Arianespace and SpaceX work to adjust launch manifests appeared first on SpaceNews.
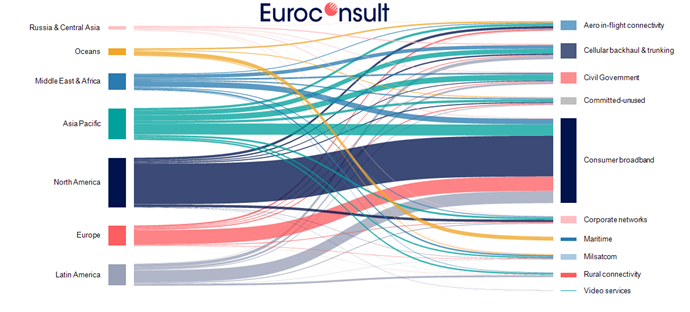
High Throughput Satellites Poised To Become Leading Commercial Growers In Space Infrastructure, With Wholesale Capacity Revenues Projected To Top $100B By 2030
Thursday, 24 March 2022 11:17PARIS, WASHINGTON, MONTREAL, YOKOHAMA, SYDNEY, TOULOUSE, 23 March, 2022 – Euroconsult has released the 6th edition of its High Throughput Satellites (HTS) report – its in-depth analysis of geostationary (GEO) and non-geostationary (NGSO) HTS markets including major drivers, strategic issues, competitive landscape and detailed forecasts of capacity supply and associated demand take-up.